SpringBoot自动配置原理
SpringBoot自动配置原理
在SpringBoot启动主配置类时,@SpringBootApplication 注解发挥作用进行自动配置。
@SpringBootApplication //主程序自动配置
public class SpringBoot02ConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot02ConfigApplication.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication 注解中,实际发挥作用的是 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration //实际起到自动配置的作用
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
而在@EnableAutoConfiguration 中,导入了一个自动配置选择器类 AutoConfigurationImportSelector。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) //导入自动配置选择器
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类中有一个selectImports 方法, getAutoConfigurationEntry() 获取配置信息条目。
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry
= this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata); //获取配置信息条目
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
这个方法里面的 getCandidateConfigurations() 执行的是获取候选的配置。
protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry
(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
} else {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);//获取候选的配置
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = this.getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
按住Ctrl,继续点击追查 getCandidateConfigurations() 方法,可以看到
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
//SpringFactoriesLoader 配置要在这里获取?
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories.
If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
这时候看到一个字符串,似乎越来越接近真相了。
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories.
If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."
还有一句很关键的语句。
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
SpringFactoriesLoader ? 配置要在这里获取? 看来还要继续深入。
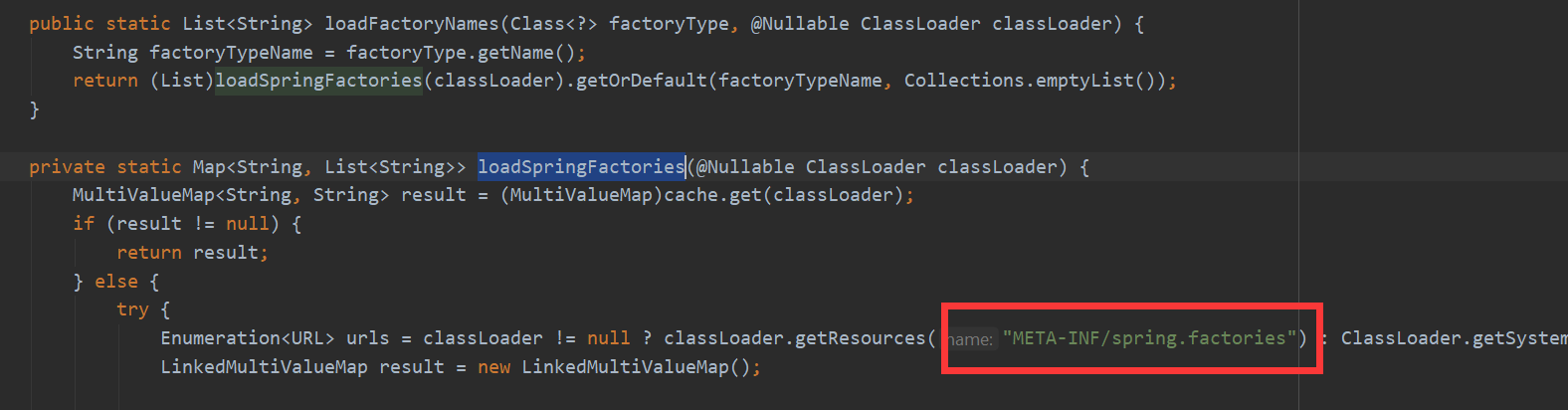
到这里可以确定是要读取在 META-INF/spring.factories 这个配置文件,这时候,我们可以去看 jar 包里的这个配置文件
名为 or.spingframework. borin-booto atonfigre.2.REEASE 的 jar 包下,有这样一个 spring.factories 配置文件。
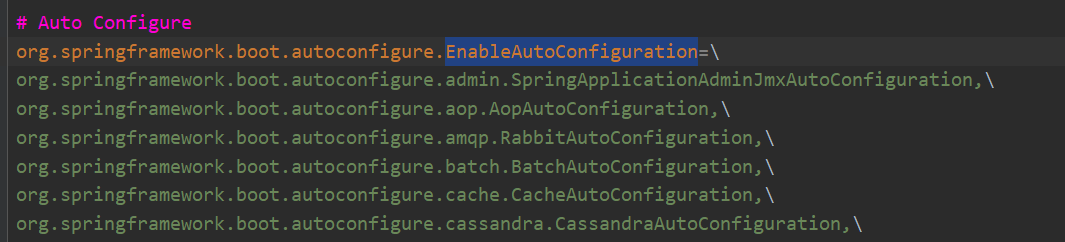
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
EnableAutoConfiguration 属性下的值所代表的配置自动都加入到容器中,不再需要我们像刚学习 Spring 时,
在 xml 配置文件中一个个去配置。极大地提高了开发效率。
下面以分析自动配置 DataSourceAutoConfiguration(数据源) 为例解释自动配置原理:
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
) //注解表明这是一个配置类,同时关闭 proxyBeanMethods ,表示这个配置类不再被代理,
//相当于用 final 修饰,不能在通过 @Bean来调用该配置类
@ConditionalOnClass({DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class})
//判断当前项目是否有数据源类,有则配置生效,查看DataSource.class源码可知是用于获取数据库连接 On表示判断是都包含
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
type = {"io.r2dbc.spi.ConnectionFactory"}
) //判断当前项目是否不包括这些Bean OnMissing表示判断是否不包含
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DataSourceProperties.class})///启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;
//将配置文件中对应的值和DataSourceProperties绑定起来;并把DataSourceProperties加入到ioc容器中
@Import({DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class, DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.class})
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
在 DataSourceProperties.class 中,我们看到了熟悉的属性。
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource"
) //从配置文件获取对应的属性值,进行绑定
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private String name;
private boolean generateUniqueName = true;
private Class<? extends DataSource> type;
private String driverClassName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
...
因此,我们可以在项目中的 application.properties 中配置相关属性。
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= # Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver.
# Auto-detected based on the URL by default. 驱动名
spring.datasource.url= # JDBC url of the database. 连接需要的url
spring.datasource.username= # Login user of the database. 用户名
spring.datasource.password= # Login password of the database. 密码口令
总结:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;给容器中添加组件
对于想要自定义配置,或者是需要自行配置的相关属性,可以再 xxx.properties 文件中配置修改。
既然自动配置需要一定条件判断才能生效,那么怎么查看 SpringBoot 已经帮助我们配置了哪些类呢?
在项目中的 application.properties 中配置
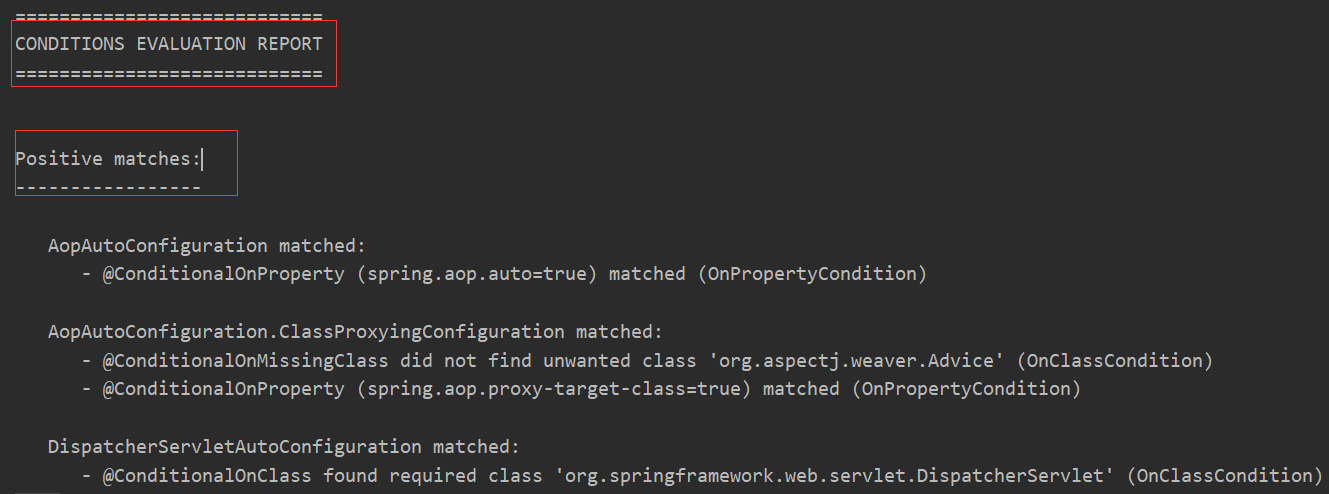
运行主程序,控制台会输出一个自动配置的报告。
2020.08.15 更新
SpringBoot 2.0 + 使用的 DataSource 数据源 为 : com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
1.0 + : 版本为 : 默认是用org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource作为数据源。
HikariDataSource 的优点:(来源网络)
-
字节码精简 :优化代码,直到编译后的字节码最少,这样,CPU缓存可以加载更多的程序代码;
-
优化代理和拦截器:减少代码,例如HikariCP的Statement proxy只有100行代码,只有BoneCP(另一数据连接池)的十分之一;
-
自定义数组类型(FastStatementList)代替ArrayList:避免每次get()调用都要进行range check,避免调用remove()时的从头到尾的扫描;
-
自定义集合类型(ConcurrentBag):提高并发读写的效率;
-
其他针对BoneCP缺陷的优化,比如对于耗时超过一个CPU时间片的方法调用的研究(但没说具体怎么优化)。
现有连接池性能比较 :hikari>druid>tomcat-jdbc>dbcp>c3p0



