智能玩具之图灵机器人
www.tuling123.com
图灵机器人的api文档:https://www.kancloud.cn/turing/www-tuling123-com/718218
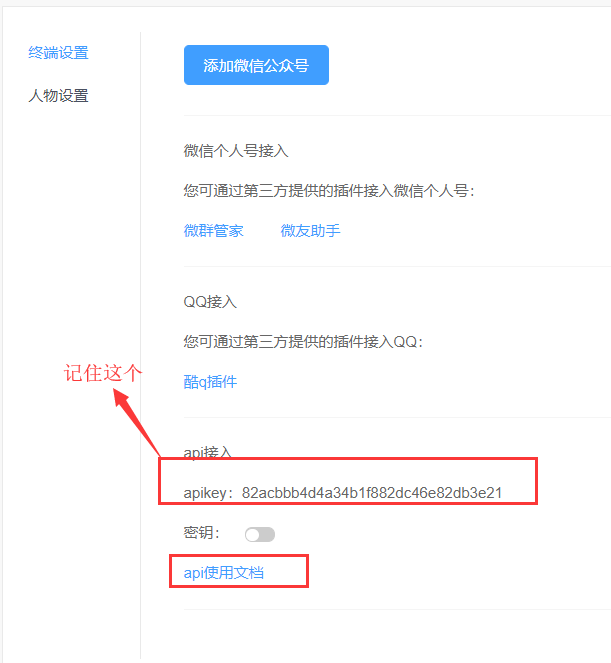
接口地址:http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2
url="http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2" import requests data={ "reqType":0, #必填项 "perception": { # 文本信息 直接输入字符串 "inputText": { "text": "你叫什么" }, # #图片信息 图片路径 # "inputImage": { # "url": "imageUrl" # }, # #地理信息 # "selfInfo": { # "location": { # "city": "北京", # "province": "北京", # "street": "信息路" # } # } }, # 必填项 "userInfo": { "apiKey": "82acbbb4d4a34b1f882dc46e82db3e21", #api文档上面的安排key值 "userId": '123123' } } #requests的post请求,序列化data res = requests.post("http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2",json=data) # print(res) #返回值为<Response [200]> # print(res.content) #返回一个字节流 # print(res.text) #返回一个文本 # print(res.json()) #返回一个字典 # print(res.json().get('intent').get('code')) #获取res的一个值 print(res.json())
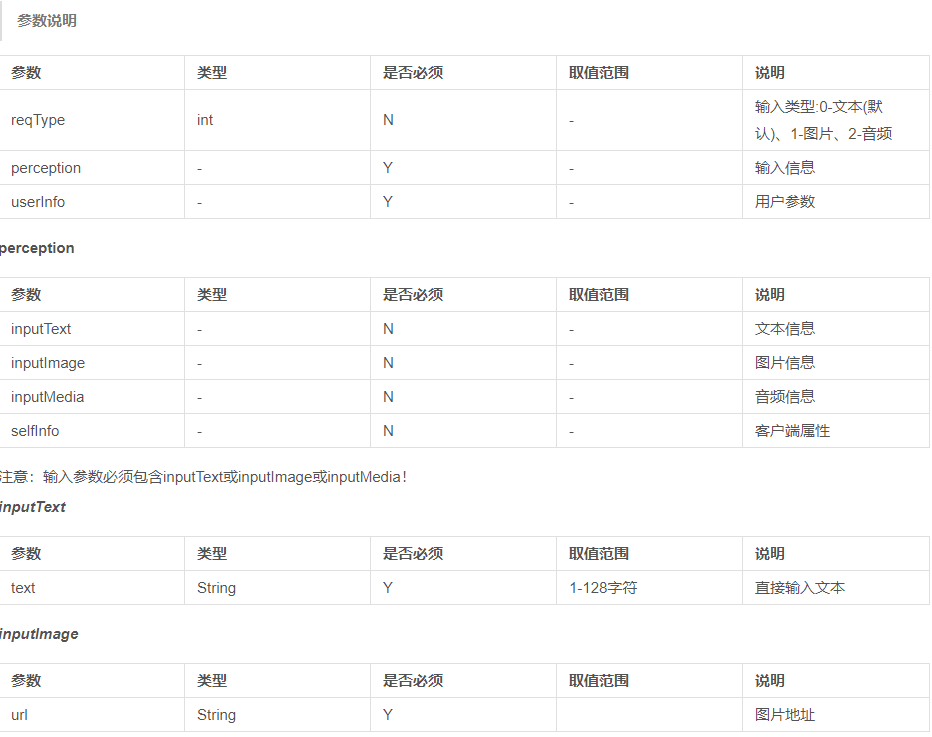
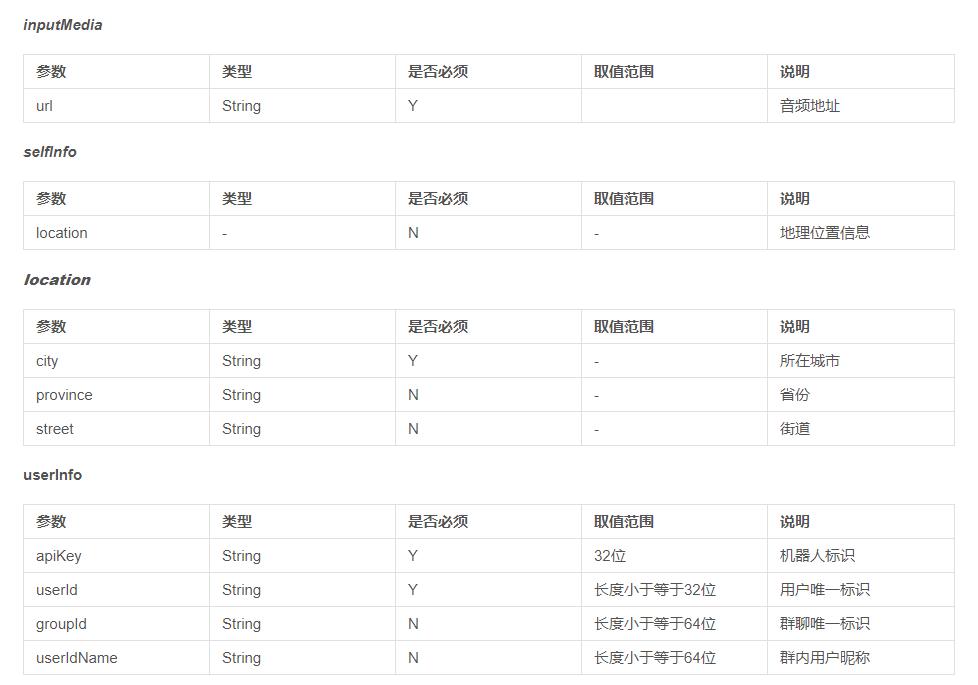
import os #语音客户端 from aip import AipSpeech, AipNlp """ 你的 APPID AK SK """ APP_ID = '16027163' API_KEY = 'wFXvuArTz8aWFou05jjs8XIG' SECRET_KEY = 'Ty6jGhtdR9GzCs8smn5HRGNNwtz0QkUQ' client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) client_nlp = AipNlp(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) #短文本接口 AipNlp #短文本校验两个文本的相似度 # res = client_nlp.simnet('你叫神马名字','你的名字是神马') # print(res)# 'score': 0.810756 #语音合成 def text2audio(text): #参数是text result = client.synthesis(text, 'zh', 1, { #将参数传进去 'vol': 5, # 音量大小 "spd": 5, # 语速 "pit": 5, # 语调 "per": 1, # 情感发音 }) # 识别正确返回语音二进制 错误则返回dict 参照下面错误码 if not isinstance(result, dict): with open('audio.mp3', 'wb') as f: f.write(result) return 'audio.mp3' # 语音识别 def audio2text(filepath): ret = client.asr(get_file_content(filepath), 'pcm', 16000, { 'dev_pid': 1536, }) return ret.get('result')[0] # 得到语音文件的文本内容 # 读取文件 (固定格式) def get_file_content(filePath): os.system(f'ffmpeg -y -i {filePath} -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 {filePath}.pcm') with open(f'{filePath}.pcm', 'rb') as fp: return fp.read() #和图灵交互的一个函数 def goto_tl(text,uid): #参数需要一个文本和userId url = "http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2" import requests data = { "reqType": 0, # 必填项 "perception": { # 文本信息 直接输入字符串 "inputText": { "text": "你叫什么" }, # #图片信息 图片路径 # "inputImage": { # "url": "imageUrl" # }, # #地理信息 # "selfInfo": { # "location": { # "city": "北京", # "province": "北京", # "street": "信息路" # } # } }, # 必填项 "userInfo": { "apiKey": "82acbbb4d4a34b1f882dc46e82db3e21", # api文档上面的安排key值 "userId": '123123' } } #获取data里面的text和userId 作为参数导入到goro_tl函数中 data['perception']['inputText']['text'] = text data['userInfo']['userId'] = uid # requests的post请求,序列化data res = requests.post(url, json=data) print(res.json()) # 返回一个文本 return res.json().get('results')[0].get('values').get('text') text=audio2text('2.m4a') #通过语音识别将语音装换成文本 #自然语言处理 if client_nlp.simnet('有音吗',text).get('score') >=0.58: #短文本相似度>=0.58 filename = text2audio('我的名字叫大王') #回复语音,通过语音合成,将文本变成语音 # os.system(f"ffplay{filename}") #使用ffplay播放器 os.system(filename) #系统自动处理需要的播放器 #goto_tl函数的实例化 answer = goto_tl(text,'123') filename = text2audio(answer) # 回复语音,通过语音合成,将文本变成语音 os.system(filename) # 系统自动处理需要的播放器



