python学习笔记(一)---字符串与列表
字符串的一些处理
字符串的大小写
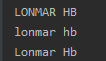
name="lonmar hb"
print(name.upper())#全大写
print(name.lower())#全小写
print(name.title())#每个单词首字母大写
输出结果将是
合并字符串
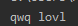
first_name="qwq"
last_name="lovl"
full_name=first_name+" "+last_name
print(full_name)
用+来拼接两个字符
上述代码结果
字符串中的空白处理
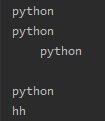
print("python")
print("python ")
print("\tpython")#\t为制表符 tab
print("\npython\nhh")# \n为换行符
运行结果
删除空白
test=" abcdefghijk "
print(test)
print(test.rstrip())#剔除右边的空白
print(test.lstrip())#剔除左边的空白
print(test.strip())#剔除两边的空白
强制转换成字符串
str()
#下面是一段错误代码
age=23
message = "Happy " + age + "rd Birthday!" print(message)
#此时会报错 TypeError: Can't convert 'int' object to str implicitly
#下面是正确的代码
age = 23 message = "Happy " + str(age) + "rd Birthday!" print(message)
#这里包含了强制类型转换,将整形转变成了字符串类型
字符串方法小结
chars.upper()
chars.lower()
chars.title()
chars1+chars2
\t tab
\n enter
chars.lstrip()删除左空白
chars.rstrip()删除右空白
chars.strip()删除两边空白
str()强制转换成字符串
列表方法
在列表中添加元素
demo1:
animals = ['dogs' , 'cats']
animals.append('sheep')
print(animals)
> ['dogs' , 'cats', 'sheep']
demo2:
animals = [] #创建一个空列表
animals.append('dog')
animals.append('cat')
print(animals)
> ['dogs', 'cats']
在列表中插入元素
使用insert放法
animals = ['dogs' , 'cats']
animals.insert(0,'sheep')
print(animals)
> ['sheep', 'dogs' , 'cats']
删除列表中的元素
del语句
animals =['sheep', 'dogs' , 'cats']
del animals[0]
print(animals)
> ['dogs' , 'cats']
pop方法来储存删除的元素
animals =['sheep', 'dogs' , 'cats']
animals_pop = animals.pop(1)
print(animals_pop)
print(animals)
>dogs
>['sheep', 'cats']
# 使用pop不仅能删除列表中指定的元素,还能定义一个变量储存该元素
remove方法
可以从列表中移除未知索引的元素
animals =['sheep', 'dogs' , 'cats']
animals.remove('dogs')
# 从列表中移除了dogs
# 但remove只移除了第一个指定的值,移除全部的值必须用循环
sort()方法对列表永久性排序
demo1:
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
cars.sort()
print(cars)
>['audi', 'bmw', 'subaru', 'toyota']
# 按照首字母的顺序对列表进行排序
demo2:
# 还可以对列表元素进行逆排序
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
cars.sort(reverse=True)
print(cars)
> ['toyota', 'subaru', 'bmw', 'audi']
sorted()方法对列表进行临时排序
cars=['toyota', 'subaru', 'bmw', 'audi']
print(cars.sorted())
print(cars)
>['audi', 'bmw', 'subaru', 'toyota']
>['toyota', 'subaru', 'bmw', 'audi']
reverse()反转列表
animals=['dogs', 'cats', 'sheeps']
animals.reverse
print(animals)
> ['sheeps', 'cats', 'dogs']
# 纯粹的将列表中元素的顺序反过来
len()确定列表的长度
len(animals)
> 3
list小结
list.append() # 像列表中最后一个位置添加元素
list.insert(num,'element') # 向列表某个位置插入元素
del(element) #删除列表中的某个元素
pop(num_index) # 删除指定索引的元素,并且还能用另一个变量储存该元素
remove(element) # 删除指定的元素,但仅仅删除列表中第一个element
sort() # 对列表中的元素进行永久排序 reverse = True 则进行逆序排序
sorted() # 对列表中的元素进行暂时排序
reverse(list) #将列表中的元素反转
len(list) # 确定列表中的元素个数
[博客内容只是本人学习过程记录的笔记,不保证质量.本人不保证技术的实用性,一切文章仅供参考,如有谬错,请留言.]

