结对项目
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/CSGrade22-34 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/CSGrade22-34/homework/13230 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 完成一个四则运算项目来了解项目开发流程 |
| 项目成员 | 李建龙 |
github地址:
https://github.com/LJL-long/LJL-long/tree/main/calculator
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| · Planning | · 计划 | 100 | 60 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| · Development | · 开发 | 480 | 420 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 300 | 360 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 60 | 45 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 45 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 360 | 420 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 30 | 30 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 150 |
| · Reporting | · 报告 | 60 | 60 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 60 | 45 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 60 |
| · 合计 | 1810 | 1835 |
设计实现过程
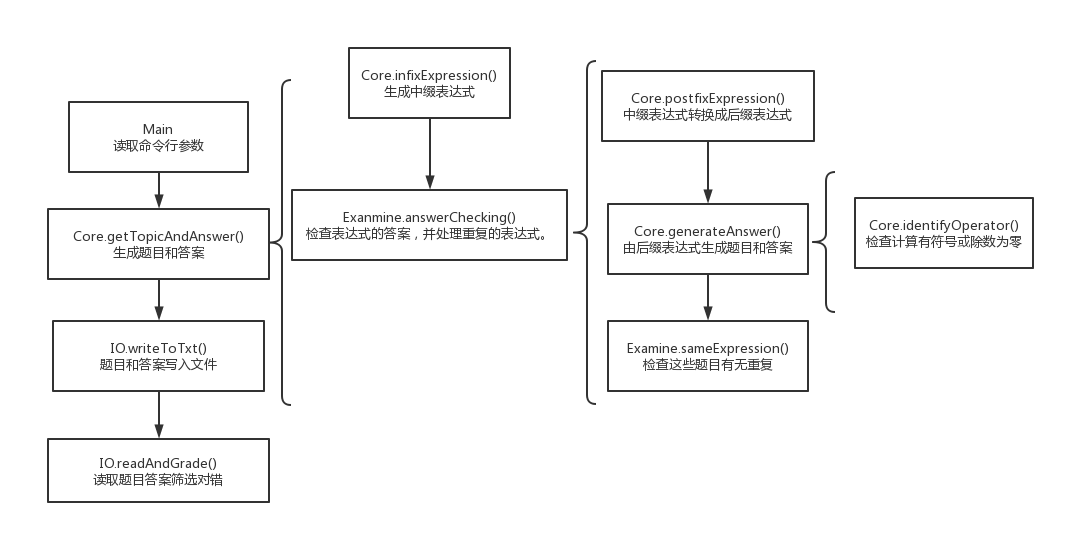
共有8个类:
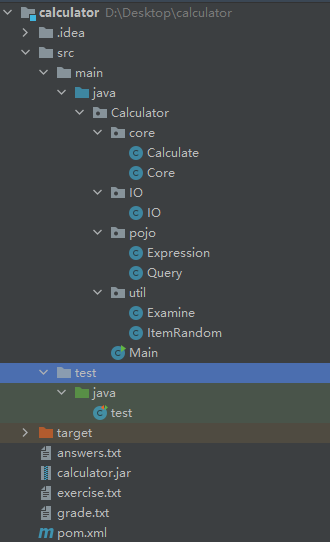
代码说明
- 生成随机的运算符数组,包括加法、减法、乘法和除法。
点击查看代码
public class ItemRandom {
/**
* 生成随机的运算符数组,包括加法、减法、乘法和除法。
*
* @return 包含随机运算符的字符数组
*/
public static char[] RanOpe() {
Random rand = new Random();
int[] ope_int = new int[3];
// 循环直到生成至少一个运算符
while (true) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// 随机生成能代表无、加、减、乘、除的数0、1、2、3、4
ope_int[i] = rand.nextInt(4 - 0) + 0;
}
if (ope_int[0] == 0 && ope_int[1] == 0 && ope_int[2] == 0) continue;
break;
}
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ope_int.length; i++) {
// 计算随机生成多少个符号
if (ope_int[i] != 0) j++;
}
char[] ope = new char[j];
for (int i = 0, k = 0; i < 3; i++) {
switch (ope_int[i]) {
case 1:
ope[k] = '+';
k++;
break;
case 2:
ope[k] = '-';
k++;
break;
case 3:
ope[k] = '×';
k++;
break;
case 4:
ope[k] = '÷';
k++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return ope;
}
/**
* 生成随机的数字数组,其中 max 参数用于指定生成的随机数字的范围。如果 max 大于1,将生成整数,否则将生成分数。
*
* @param max 生成随机数字的范围
* @return 包含随机数字的字符串数组
*/
public static String[] RanNum(int max) {
String[] num = new String[4];
Random rand = new Random();
if (max > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
int tag = rand.nextInt(3 - 0) + 0;
if (tag == 0 || tag == 1)
num[i] = String.valueOf((int) (Math.random() * max));
else
num[i] = RanFra(max);
}
} else if (max == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++)
num[i] = RanFra(max);
}
return num;
}
/**
* 生成随机的分数字符串,其中 max 参数用于指定生成的随机分数的分母的范围。
*
* @param max 生成随机分数的分母的范围
* @return 随机分数的字符串表示
*/
public static String RanFra(int max) {
int fra, zi;
Random rand = new Random();
// 分子分母不为零
do {
fra = rand.nextInt(20 - 1) + 1;
zi = rand.nextInt(20 - 1) + 1;
} while (fra == 0 || zi == 0);
Calculate cal = new Calculate();
return cal.reduction(zi, fra);
}
}
点击查看代码
package Calculator.core;
public class Calculate {
/**
* 计算表达式的值。
*
* @param number1 第一个数字(字符串形式)
* @param number2 第二个数字(字符串形式)
* @param signal 运算信号:1表示加法,2表示减法,3表示乘法,4表示除法
* @return 计算结果(字符串形式)
*/
public static String calculate(String number1, String number2, int signal) {
Calculate cal = new Calculate();
// 将字符串转换为int型分子分母
int[] array1 = cal.conversion(number1);
int[] array2 = cal.conversion(number2);
int mol1 = array1[0], den1 = array1[1], mol2 = array2[0], den2 = array2[1];
int mol, den;
switch (signal) {
case 1: // 加法
if (den1 == den2 && den1 == 1)
return String.valueOf(mol1 + mol2);
else {
den = cal.lcm(den1, den2);
mol = mol1 * den / den1 + mol2 * den / den2;
return cal.reduction(mol, den);
}
case 2: // 减法
if (den1 == den2 && den1 == 1)
return String.valueOf(mol1 - mol2);
else {
int symbol = 0; // 符号位,1表示有负号
den = cal.lcm(den1, den2);
mol = mol1 * den / den1 - mol2 * den / den2;
if (mol < 0) {
mol = -mol;
symbol = 1;
} else if (mol == 0) {
return "0";
}
if (symbol == 1)
return "-" + cal.reduction(mol, den);
else
return cal.reduction(mol, den);
}
case 3: // 乘法
if (den1 == den2 && den1 == 1)
return String.valueOf(mol1 * mol2);
else {
mol = mol1 * mol2;
den = den1 * den2;
return cal.reduction(mol, den);
}
case 4: // 除法
if (den1 == den2 && den1 == 1)
return cal.reduction(mol1, mol2);
else {
mol = mol1 * den2;
den = den1 * mol2;
return cal.reduction(mol, den);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 将字符串(无论自然数还是分数)转换为int型分子分母。
*
* @param number 输入的字符串
* @return 包含分子和分母的整数数组
*/
public int[] conversion(String number) {
int num, mol, den;
if (number.matches(".*/.*")) { // 如果是分数
String string;
if ((string = number.split("/")[0]).matches(".*'.*")) { // 如果是带分数
num = Integer.parseInt(string.split("'")[0]);
mol = Integer.parseInt(string.split("'")[1]);
} else {
num = 0;
mol = Integer.parseInt(number.split("/")[0]);
}
den = Integer.parseInt(number.split("/")[1]);
mol = mol + den * num;
} else { // 如果是自然数
mol = Integer.parseInt(number);
den = 1;
}
return new int[]{mol, den};
}
/**
* 计算最大公因数。
*
* @param a 第一个整数
* @param b 第二个整数
* @return 最大公因数
*/
int gcd(int a, int b) {
int n = Math.min(a, b);
int i;
for (i = n; i > 0; --i) {
if (a % i == 0 && b % i == 0)
break;
}
return i;
}
/**
* 计算最小公倍数。
*
* @param a 第一个整数
* @param b 第二个整数
* @return 最小公倍数
*/
int lcm(int a, int b) {
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
/**
* 分子分母化简。
*
* @param mol 分子
* @param den 分母
* @return 化简后的字符串表示
*/
public String reduction(int mol, int den) {
Calculate cal = new Calculate();
int k = cal.gcd(mol, den);
if (k == 0) {
return "0";
} else if (k != 1) {
mol = mol / k;
den = den / k;
}
if (den == 1)
return String.valueOf(mol);
if (den > mol)
return mol + "/" + den;
else
return mol / den + "'" + mol % den + "/" + den;
}
}
点击查看代码
package Calculator.core;
import Calculator.pojo.Expression;
import Calculator.pojo.Query;
import Calculator.util.Examine;
import Calculator.util.ItemRandom;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Core {
/**
* 生成题目和答案,通过调用ItemRandom类生成随机运算符和数字组合,然后检查并添加到题目列表和查询列表中。
*
* @param number 题目数量
* @param maxNum 生成的随机数字的范围
* @param expressionList 题目列表
* @param queryList 查询列表
*/
public void getTopicAndAnswer(int number, int maxNum, List<Expression> expressionList, List<Query> queryList) {
Examine check = new Examine();
while (expressionList.size() < number) {
String infix = infixExpression(ItemRandom.RanOpe(), ItemRandom.RanNum(maxNum));
check.answerChecking(infix, expressionList, queryList);
}
}
/**
* 生成中缀表达式,根据随机生成的运算符和数字数组生成中缀表达式字符串。
*
* @param ope 随机生成的运算符数组
* @param num 随机生成的数字数组
* @return 中缀表达式字符串
*/
public String infixExpression(char[] ope, String[] num) {
int i = 0;
ArrayList<String> inf = new ArrayList<>();
for (; i < ope.length; i++) {
inf.add(num[i]);
inf.add(String.valueOf(ope[i]));
}
inf.add(num[i]);
switch (ope.length) {
case 3 -> {
if ((ope[0] == '+' || ope[0] == '-') && (ope[1] == '+' || ope[1] == '-') && (ope[2] == '×' || ope[2] == '÷')) {
inf.add(0, "(");
inf.add(6, ")");
}
if ((ope[0] == '+' || ope[0] == '-') && (ope[1] == '×' || ope[1] == '÷')) {
inf.add(0, "(");
inf.add(4, ")");
}
}
case 2 -> {
if ((ope[0] == '+' || ope[0] == '-') && (ope[1] == '×' || ope[1] == '÷')) {
inf.add(0, "(");
inf.add(4, ")");
}
}
default -> {
}
}
for (i = 0; i < inf.size(); i++) {
if (inf.get(i).equals("+") || inf.get(i).equals("-") || inf.get(i).equals("×") || inf.get(i).equals("÷"))
inf.set(i, " " + inf.get(i) + " ");
}
StringBuilder infix = new StringBuilder(inf.get(0));
for (i = 1; i < inf.size(); i++) {
infix.append(inf.get(i));
}
return infix.toString();
}
/**
* 中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式。
*
* @param string 中缀表达式字符串
* @return 后缀表达式的字符串数组
*/
public String[] postfixExpression(String string) {
// 符号栈
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// 后缀表达式
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
// 将中缀表达式按空格分开
String[] splitString = string.split(" ");
for (String str : splitString) {
// 如果是左括号就入栈
if (str.matches("\\(.*")) {
list.add(str.split("\\(")[1]);
stack.push("(");
}
// 如果是右括号就把栈顶元素依次加入到列表,直到读取到左括号,将其出栈。
else if (str.matches(".*\\)")) {
list.add(str.split("\\)")[0]);
while (!stack.peek().equals("(")) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.pop();
} else if (str.matches("[+\\-×÷]")) {
// 栈为空将运算符入栈
if (stack.isEmpty()) stack.push(str);
// 如果运算符是加减,优先级最低,将栈顶元素加入到列表,如果读取到左括号或栈为空将运算符入栈
else if (str.matches("[+\\-]")) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !stack.peek().equals("(")) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(str);
}
// 如果运算符是乘除
else {
// 如果栈不为空且栈顶元素是乘除,将其出栈加入到列表。
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().matches("[×÷]")) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
// 栈顶元素是加减或为空,将运算符入栈。
stack.push(str);
}
}
// 其余符号都是表示数字,将其入栈。
else {
list.add(str);
}
}
// 最后把栈内元素全部加入到列表
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
String[] postfixString = new String[list.size()];
// 将列表元素转变为字符串数组
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
postfixString[i] = list.remove(i);
}
return postfixString;
}
/**
* 由后缀表达式生成题目答案。
*
* @param strings 后缀表达式的字符串数组
* @return 表达式计算结果的字符串
*/
public String generateAnswer(String[] strings) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String string : strings) {
// 返回true表示计算过程有负号或除数为0
if (identifyOperator(stack, string))
return "-1";
}
return stack.pop();
}
/**
* 识别运算符,返回true表示计算过程有负号。
*
* @param stack 运算符栈
* @param string 当前运算符或数字
* @return 如果计算过程中出现负号,返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean identifyOperator(Stack<String> stack, String string) {
String num, num1, num2;
switch (string) {
case "+" -> {
num2 = stack.pop();
num1 = stack.pop();
num = Calculate.calculate(num1, num2, 1);
stack.push(num);
}
case "-" -> {
num2 = stack.pop();
num1 = stack.pop();
num = Calculate.calculate(num1, num2, 2);
stack.push(num);
// 如果计算过程中出现负号,返回true
if (num != null && num.matches("-.*")) return true;
}
case "×" -> {
num2 = stack.pop();
num1 = stack.pop();
num = Calculate.calculate(num1, num2, 3);
stack.push(num);
}
case "÷" -> {
num2 = stack.pop();
num1 = stack.pop();
// 如果除数为0
if (num2.equals("0")) return true;
num = Calculate.calculate(num1, num2, 4);
stack.push(num);
}
default -> stack.push(string);
}
return false;
}
}
点击查看代码
package Calculator.IO;
import Calculator.core.Core;
import Calculator.pojo.Expression;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class IO {
/**
* 将表达式列表写入文本文件。
*
* @param exp 表达式列表
* @param exercise 文件路径,用于保存练习题
* @param answers 文件路径,用于保存答案
*/
public static void writeToTxt(List<Expression> exp, String exercise, String answers) {
try {
File exerciseFile = new File(exercise);
File answersFile = new File(answers);
// 检查文件是否存在,如果不存在则创建文件
if (!exerciseFile.exists()) {
exerciseFile.createNewFile();
}
if (!answersFile.exists()) {
answersFile.createNewFile();
}
try (
OutputStreamWriter exerciseWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(exerciseFile), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
OutputStreamWriter answersWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(answersFile), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
) {
for (int i = 0; i < exp.size(); i++) {
exerciseWriter.write(i + 1 + "-->" + exp.get(i).getString() + " = " + "\r\n");
answersWriter.write(i + 1 + "-->" + exp.get(i).getValues() + "\r\n");
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 从文件中读取练习题和答案,然后进行评分,将评分结果写入文本文件。
*
* @param exerciseFile 练习题文件路径
* @param answersFile 答案文件路径
* @param grade 评分文件路径
*/
public static void readAndGrade(String exerciseFile, String answersFile, String grade) {
try {
FileReader exerciseReader = new FileReader(exerciseFile);
FileReader answersReader = new FileReader(answersFile);
BufferedReader exerciseBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(exerciseReader);
BufferedReader answersBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(answersReader);
Core t = new Core();
ArrayList<Integer> correct = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> wrong = new ArrayList<>();
String line1;
String line2;
int i = 1;
while ((line2 = answersBufferedReader.readLine()) != null && (line1 = exerciseBufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String a1 = line2.split(">")[1];
String l1 = line1.split(">")[1];
String l2 = l1.split(" = ")[0];
String[] s = t.postfixExpression(l2);
String strAns = t.generateAnswer(s);
if (strAns.equals(a1)) correct.add(i++);
else wrong.add(i++);
}
File gradeFile = new File(grade);
if (!gradeFile.exists()) gradeFile.createNewFile();
try (OutputStreamWriter gradeWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(gradeFile), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
if (!correct.isEmpty()) {
gradeWriter.write("Correct: " + correct.size() + "(" + correct.get(0));
for (int j = 1; j < correct.size(); j++) {
gradeWriter.write("," + correct.get(j));
}
gradeWriter.write(")" + "\r\n");
} else gradeWriter.write("Correct: 0" + "\r\n");
if (!wrong.isEmpty()) {
gradeWriter.write("Wrong: " + wrong.size() + "(" + wrong.get(0));
for (int j = 1; j < wrong.size(); j++) {
gradeWriter.write("," + wrong.get(j));
}
gradeWriter.write(")" + "\r\n");
} else gradeWriter.write("Wrong: 0" + "\r\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
点击查看代码
public class test {
//测试四则运算,设置不同输入,如果和理论的输出一致则通过。
@Test
public void calculate() {
//加法
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1","2",1),equalTo("3"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1","1/2",1),equalTo("1'1/2"));
//减法
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1","2",2),equalTo("-1"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1/2","1",2),equalTo("-1/2"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("3/4","4/3",2),equalTo("-7/12"));
//乘法
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1/2","4",3),equalTo("2"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("4","2",3),equalTo("8"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("3/4","5/6",3),equalTo("5/8"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1'1/2","1'1/2",3),equalTo("2'1/4"));
//除法
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1/2","4",4),equalTo("1/8"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("4","2",4),equalTo("2"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1'1/2","6",4),equalTo("1/4"));
assertThat(Calculate.calculate("1'1/2","1'1/2",4),equalTo("1"));
}
//测试分数转换成int型分子分母,分别测试带分数真分数自然数
@Test
public void conversion() {
Calculate cal = new Calculate();
assertThat(cal.conversion("1'1/2"),equalTo(new int[]{3,2}));
assertThat(cal.conversion("3"),equalTo(new int[]{3,1}));
assertThat(cal.conversion("3/4"),equalTo(new int[]{3,4}));
}
//测试分子分母化简
@Test
public void reduction() {
Calculate cal = new Calculate();
assertThat(cal.reduction(8,7),equalTo("1'1/7"));
assertThat(cal.reduction(3,7),equalTo("3/7"));
assertThat(cal.reduction(8,6),equalTo("1'1/3"));
assertThat(cal.reduction(4,2),equalTo("2"));
}
//测试两个表达式是否相同
@Test
public void sameExpression() {
String a1="8 ÷ 4";
String b1="4 - 8";
Examine examine = new Examine();
assertFalse(examine.sameExpression(a1, b1));
String a2="8 + 4";
String b2="4 + 8";
assertTrue(examine.sameExpression(a2, b2));
String a3="(8 ÷ 2) × 3";
String b3="(2 ÷ 8) × 3";
assertFalse(examine.sameExpression(a3, b3));
}
//测试生成中缀表达式。
@Test
public void infixExpression(){
char[] ope={'+','-','×'};
String[] num={"32","5","9","3/4"};
Core core = new Core();
assertThat(core.infixExpression(ope,num),equalTo("(32 + 5 - 9) × 3/4"));
char[] ope1={'+','×'};
String[] num1={"3","6","21","3/7"};
assertThat(core.infixExpression(ope1,num1),equalTo("(3 + 6) × 21"));
char[] ope2={'×'};
String[] num2={"32","5","9","3/4"};
assertThat(core.infixExpression(ope2,num2),equalTo("32 × 5"));
}
//测试将中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式
@Test
public void postfixExpression(){
String string="9 + (3 - 1) × 3 + 10 ÷ 2";
Core core = new Core();
String[] strings= core.postfixExpression(string);
assertThat(strings[0],equalTo("9"));
assertThat(strings[1],equalTo("3"));
assertThat(strings[2],equalTo("1"));
assertThat(strings[3],equalTo("-"));
assertThat(strings[4],equalTo("3"));
assertThat(strings[5],equalTo("×"));
assertThat(strings[6],equalTo("+"));
assertThat(strings[7],equalTo("10"));
assertThat(strings[8],equalTo("2"));
assertThat(strings[9],equalTo("÷"));
assertThat(strings[10],equalTo("+"));
String string1="a + b × c + (d × e + f) × g";
String[] strings1= core.postfixExpression(string1);
assertThat(strings1[0],equalTo("a"));
assertThat(strings1[1],equalTo("b"));
assertThat(strings1[2],equalTo("c"));
assertThat(strings1[3],equalTo("×"));
assertThat(strings1[4],equalTo("+"));
assertThat(strings1[5],equalTo("d"));
assertThat(strings1[6],equalTo("e"));
assertThat(strings1[7],equalTo("×"));
assertThat(strings1[8],equalTo("f"));
assertThat(strings1[9],equalTo("+"));
assertThat(strings1[10],equalTo("g"));
assertThat(strings1[11],equalTo("×"));
assertThat(strings1[12],equalTo("+"));
}
//测试计算后缀表达式
@Test
public void generateAnswer() {
String[] strings={"9","3","1","-","3","×","+","10","2","÷","+"};
Core core = new Core();
assertThat(core.generateAnswer(strings),equalTo("20"));
}
//测试利用栈计算
@Test
public void identifyOperator() {
Stack<String> stack=new Stack<>();
Core core = new Core();
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
core.identifyOperator(stack,"+");
assertThat(stack.pop(),equalTo("3"));
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
core.identifyOperator(stack,"-");
assertThat(stack.pop(),equalTo("-1"));
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
core.identifyOperator(stack,"×");
assertThat(stack.pop(),equalTo("2"));
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
core.identifyOperator(stack,"÷");
assertThat(stack.pop(),equalTo("1/2"));
core.identifyOperator(stack,"1'1/2");
assertThat(stack.pop(),equalTo("1'1/2"));
}
//测试主方法
@Test
public void main() {
String[] strings={"-n","300","-r","120"};
Main.main(strings);
String[] strings1={"-e","exercise.txt","-a","answers.txt"};
Main.main(strings1);
}
}
项目小结
通过这次实践,学会了代码测试的方法,也努力完成了题目中代码测试的要求,这对我来说都是很大的进步。


