Elasticsearch-Mapping映射
Mapping映射
自动或手动为index中的_doc建立一种数据结构和相关配置
动态映射:dynamic mapping,自动为我们建立index,以及对应的mapping,mapping中包含了每个field对应的数据类型,以及如何分词等设置。
PUT /web_site/_doc/1
{
"post_date": "2023-01-01",
"title" : "The longer",
"content":"The longer she endured the pain",
"author_id": 1111
}
PUT /web_site/_doc/2
{
"post_date": "2023-01-02",
"title" : "The longer title",
"content":"The longer she endured the paipppn",
"author_id": 1113
}
PUT /web_site/_doc/3
{
"post_date": "2023-01-03",
"title" : "The longer title endured",
"content":"The longer she endured title the paipppn",
"author_id": 1113
}
一、基础及概念
- exact value精准匹配
GET /web_site/_search?q=post_date:2023-01-03
类似于:select * from web_site where post_date="2023-01-03"
-
full text 全文检索
es不是单纯的只是匹配完整的一个值,而是可以对值进行拆分词语后(分词)进行匹配,也可以通过缩写、大小写、时态、同义词等进行匹配 -
倒排索引
倒排索引是一种常见的索引结构,将文档的内容映射到词项上,提供了更高效的文本搜索和检索能力。
高效的文本搜索、支持复杂的查询操作 -
分词器analyzer
切分词语,提升recall召回率
给es一段句子,然后将这段句子拆分成一个一个的单个的单词,同时对每个单词进行时态转换,单复数转换
4.1 分词步骤
1). character filter:在一段文本进行分词之前,先进行预处理,eg:最常见的过滤html标签(hello -> hello), & -> and ( I & you -> I and you)
2). tokenizer:分词, eg:hello you and me -> hello, you, and, me
3). token filter:一个个小单词标准化转换 lowercase(转小写) , stop word(停用词,了 的 呢), dogs -> dog(单复数转换), liked ->like(时态转换), Tom -> tom(大小写转换), a/the/an ->干掉, mother -> mom(简写), small -> little(同义词).
4.2 内置分词器
eg: set_trans Aaa
标准分词器: set_trans, aaa
简化分词器:set, trans, aaa
空格分词器: set_trans, Aaa
特定语言分词器
-
query string根据字段分词策略
query string必须以和index建立时相同的analyzer进行分词query string对exact value和full text的区别对待
如:date:exact value精确匹配
text:fulltext全文检索 -
可以用es的dynamic mapping,让其自动建立mapping,包括自动设置数据类型;也可以提前手动创建index和mapping,自己对各个field进行设置,包括数据类型,包括索引行为,包括分词器等
二、核心数据类型及dynamic mapping
-
核心的数据类型
string :text and keyword
byte, short, integer, long,float, double
boolean
date
详见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/master/mapping-types.html -
dynamic mapping规则
true or false -> boolean
123 -> long
123.45-> double
2019-01-01-> date
"hello world"-> text/keywod -
查看mapping
GET /index/_mapping/
三. 手动管理mapping
- 创建映射
创建索引后应该立即创建映射
1.1 创建索引
PUT book
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "book"
}
1.2 创建索引对于的映射
Text文本类型:
- analyzer
通过analyzer属性指定分词器 - index
index属性指定是否索引
默认为index=true,即要进行索引,只有进行索引才可以从索引库搜索到。但是也有一些内容不需要索引,比如:商品图片地址只被用来展示图片,不进行搜索图片,此时可以将index设置为false
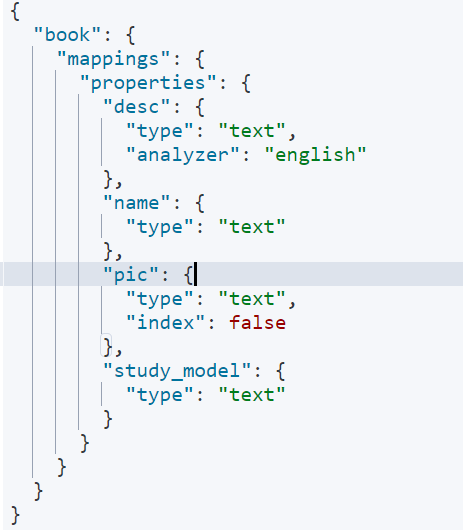
PUT book/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"name" :{
"type": "text" # 使用文本类型
},
"desc": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english", # 指定分词时使用英文分词器
"search_analyzer": "english" # 指定查询时使用英文分词器
### 指定了analyzer是指在索引和搜索都使用english,如果单独想定义搜索时使用的分词器则可以通过search_analyzer属性
},
"pic": {
"type": "text",
"index": false # 指定是否索引
},
"pic2": {
"type": "keyword"
# 取代了"index":false,通常搜索keyword是按照整体搜索
},
"study_model": {
"type": "text"
},
"created_at": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss || yyyy-MM-dd"
# 时间格式
}
}
}
{
"acknowledged": true
}
查看 book/_mapping
添加数据
PUT book/_doc/1
{
"name": "书名开发",
"desc": "简介][INFO ][o.e.c.s.Index",
"pic": "ugc/book/aa.png",
"study_model": "201002"
}
查询数据
GET /book/_search?q=开发,Info
# 在查询“开发/Info”时是可以匹配到数据的
GET /book/_search?q=desc:INFO
# 在查询desc字段为“Info”时是可以匹配到数据的
GET /book/_search?q=pic:ugc/book/aa.png
# 在查询pic字段时,因为没有添加索引 所以是查询不到数据的
keyword关键字类型
目前已经取代了"index":false,keyword字段为关键字字段,通常搜索keyword是按照整体搜索,所以创建keyword字段的索引时是不进行分词的,比如:邮政编码、手机号码、身份证等。keyword字段通常用于过虑、排序、聚合等
date日期类型
日期类型不用设置分词器,通常日期类型的字段用于排序,通过format设置日期格式。
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss || yyyy-MM-dd"
数值类型
long/integer/short/byte/double/float/half_float/scaled_float
如何选择类型:
1. 尽量选择范围小的类型,提高搜索速率
2. 对于浮点数尽量用比例因子,比如一个价格字段,单位为元,我们将比例因子设置为100这在ES中会按分存储,映射如下:
"price": {
"type": "scaled_float",
"scaling_factor": 100
}
由于比例因子为100,如果我们输入的价格是23.45则ES中会将23.45乘以100存储在ES中。如果输入的价格是23.456,ES会将23.456乘以100再取一个接近原始值的数,得出2346
使用比例因子的好处是整型比浮点型更易压缩,节省磁盘空间。
**甚至可以直接将价格设置为int类型 存“分” 查询到结果之后自己除以100
multivalue field
即数组:数组中元素必须统一类型,不能是一个string 一个int
empty field
空类型:null, [], [null]
object field
PUT /company/_doc/1
{
"address" :{
"country": "CN",
"province": "Beijing",
"city": "tongzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age" : 27,
"join_date": "2024-01-02"
}
底层存储逻辑
{
"name" : [jack],
"age" : [27],
"join_date": [2024-01-02],
"address.country" : [CN],
"address.province" : [Beijing]
"address.city" : [tongzhou],
}
1.3 修改映射
只能创建index时手动建立mapping,或者新增field mapping,但是不能update field mapping。
因为已有数据按照映射早已分词存储好。如果修改只能新增一个字段mapping
PUT book/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"new_field" : {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
修改映射报错:

1.4 删除映射
即删除索引:DELETE /book
四、定制dynamic mapping
1. 定制dynamic策略
格式:
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": true, # 默认true
"properties": {
# 字段
}
}
}
- true(默认):遇到陌生字段,就进行dynamic mapping
- false:新检测到的字段将被忽略。这些字段将不会被索引,因此将无法搜索,但仍将出现在返回点击的源字段中。这些字段不会添加到映射中,必须显式添加新字段。
- strict:遇到陌生字段,就报错
eg:
1.1 使用dynamic=false,新增一个其他参数
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": true
}
}
}
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "the title",
"content": "the title content",
"address": {
"city": "jinan"
}
}
GET /my_index/_search?q=content:title
此时在查询content字段中title时,是查询不到数据的,因为字段将不会被索引
1.2 使用dynamic=strict,新增字段
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": true
}
}
}
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "the title",
"content": "the title content",
"address": {
"city": "jinan"
}
}
此时会报错:映射设置为严格,不允许在[_doc]中动态引入[content]

2. 自定义dynamic mapping 策略
2.1 关闭日期检测
参数:date_detection
eg:
# 定义索引
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": true,
"date_detection": false,
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": true
}
}
}
}
# 插入数据
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "the title",
"content": "the title content",
"address": {
"city": "jinan"
},
"date_data": "2024-01-01"
}
# 查询mapping
GET /my_index/_mapping
查询mapping 此时看到的date_data 字段类型是text
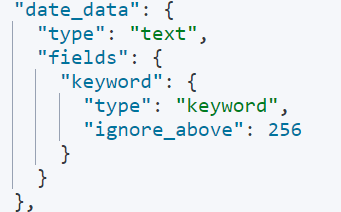
2.2 自定义日期格式
参数:dynamic_date_formats
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_date_formats": ["yyyy/MM/dd"]
}
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"date": "2024/01/02"
}
GET /my_index/_mapping
返回的mapping
{
"my_index": {
"mappings": {
"dynamic_date_formats": [
"yyyy/MM/dd"
],
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy/MM/dd"
}
}
}
}
}
2.3 数字字符串自动映射成数字类型
参数:numeric_detection
eg: "1.1"=> float(1.1),"1"=>int(1)
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"numeric_detection": true
}
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"i_f": "2024.01",
"i_i": "2024"
}
GET /my_index/_mapping
返回结果mapping
{
"my_index": {
"mappings": {
"numeric_detection": true,
"properties": {
"i_f": {
"type": "float"
},
"i_i": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
- 定制dynamic mapping模版
参数:dynamic_templates
eg:定义一个属性名以"_en"结尾的字符串类型的,将其映射为text类型并使用英文分词器
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"en": { # 模版名
"match": "*_en", # 匹配属性名为_en的
"match_mapping_type": "string", ## 匹配后缀为_en的字符串类型的
"mapping": { # 将匹配到的字段转为 text类型 分词器使用英文分词
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
]
}
}
# 插入数据
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "this is a ctitle"
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/2
{
"title_en": "this is a ctitle"
}
当查询 ctitle 时 会匹配到2个结果
但当查询 is 时 会匹配到id=1的数据,因为id=2的被英文分词了,默认去掉了停用词
模版参数
# 以aa_开头的
"match": "aa_\*"
# 不是以aa_开头的
"unmatch": "aa_\*"
# 匹配属性值是字符串的
"match_mapping_type": "string"
# 匹配路径
"path_match": "name.\*"
"path_unmatch": "name.\*"
# 匹配正则 组合使用
"match_pattern": "regex"
"match": "^aa_\d+$"
五、零停机重建索引
因index的mapping不能修改,只能新增一个index重新设置mapping,然后将数据批量查询出来,重新用bulk api写入index中,需要客户端或者服务端更改程序读取新的索引,兼容性不好
例如:
定义一个索引 自动映射成date类型,但再想新增string类型的数据就会报错
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "2024-01-01"
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/2
{
"title": "2024-01-11"
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/3
{
"title": "aaaa2024-01-01"
}
此时想要解决这个问题就只能新建一个索引,会比较麻烦,可能再使用时客户端还要更改
解决:
1). 原索引加上别名,查询时使用别名去查询
2). 新建一个索引并指定mapping
3). 通过scroll api将数据批量查询出来
4). 采用bulk api将scroll查出来的一批数据,批量写入新索引
5). 更新别名到新索引上,通过别名查询数据
# 1. 创建索引 并添加别名(prod_index)
PUT /test_my_index
PUT /test_my_index/_alias/prod_index
# 2. 添加数据
PUT /test_my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "2024-01-01"
}
PUT /test_my_index/_doc/2
{
"title": "2024-01-01"
}
# 3. 创建新索引
PUT /test_my_index2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
# 4. 通过scroll api将数据批量查询出来
GET /test_my_index/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 100
}
# 5. 采用bulk api将scroll查出来的一批数据,批量写入新索引
POST /_bulk
{"index": {"_index": "test_my_index2", "_id":1}}
{"title": "2024-01-01"}
{"index": {"_index": "test_my_index2", "_id":2}}
{"title": "2024-01-01"}
# 6. 将别名(prod_index)切换到新索引上,查询时使用别名查询
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "test_my_index",
"alias": "prod_index"
}
},
{
"add": {
"index": "test_my_index2",
"alias": "prod_index"
}
}
]
}
# 7. 添加新索引数据 使用别名查询验证是否正确
PUT /test_my_index2/_doc/3
{
"title": "this is a title for my index 2"
}
GET /prod_index/_search





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧