Servlet
前言
在微人事的项目中,我们看到了很多HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response作为参数传入到某个方法中,它通常作为HttpServlet中的service()方法传入参数;serveice()方法,它起源于Servlet接口,属于其中非常重要的一部分。
1.Servlet接口
1.1 Tomcat的工作机制(重要)
- 客户端向Servlet容器(如Tomcat)发起Http请求,此时Servlet还未初始化
- Tomcat从磁盘中加载servlet,servlet加载成功
- Tomcat将Http请求封装为request对象,转发request给对应的Servlet处理
- Servlet将request处理为response返回给Tomcat,Tomcat将request转换成Http响应
- Tomcat将Http响应给客户端
1.2 Servlet定义:
- 定义:java编写的应用成簇
- 功能:交互式地浏览和修改数据,生成动态web内容
- 狭义Servlet:实现了Servlet的接口
- 任何实现了Servlet接口的一个实现类
1.3 Servlet的结构组成:
Servlet接口、ServletRequest接口、ServletResponse接口、GenericServlet抽象类(实现了Servlet接口)、ServletContext接口、ServletConfig接口、ServletDispatcher接口、Filter接口
1.4 Servlet的工作原理:
- Servlet容器将servlet加载到内存中,并产生servlet以及它能够调用的方法;在一个应用程序中,每个Servlet类型只能有一个Servlet对象
- 用户请求致使Servlet调用Servlet的service()方法,并传入一个ServletRequest和ServletResponse对象
- ServletRequest中封装了Http请求,无需技术人员解析原始Http数据,ServletResponse表示当前用户响应,程序员直接操作该对象返回响应给客户端用户
- 对任何一个应用程序,Servlet容器还会创建一个ServletConfig对象,该对象封装了应用程序的上下文环境,每个应用程序只有一个ServletConfig,每个Servlet对象只有一个Servlet配置的ServletConfig对象
1.5 Servlet中的定义方法:
public interface Servlet{ void init(SerlvetConfig var1) throws ServletException; //返回Servlet容器传给init()方法的ServletConfig对象 Servlet getServletConfig(); void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp) throws ServletException{ } String getServletInfo(); void destroy(); }
1.6 Servlet的生命周期:
- 在上面的方法中,init()、sevice()、destroy()方法表示了Servlet对象出生到死亡的过程
- init()方法:当Servlet第一次被请求是,Servlet就会调用该方法,并传入一个ServletConfig对象初始化一个Servlet对象,在后续请求中,它不会再被调用
- service()方法:每当Servlet被请求是,Servlet就会调用该方法,init()只会被调用一次,而service像人生中的工作一样,一直工作知道去世
- destroy()方法:当要销毁Servlet时会调用该方法(卸载应用程序或关闭Serlvet容器),就会调用该方法,它也只会被调用一次
1.7 GenericServlet抽象类:
在实现Servlet的实现类中,我们都需要实现Servlet接口中的所有方法,及时不使用这些方法,而且还需要手动维护init()方法中ServletConfig对象的应用,这样显得很麻烦,GenericServlet抽象类应需而生,它实现了Servlet以及ServletConfig接口

public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable { private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings"; private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings"); private transient ServletConfig config; public GenericServlet() { } public void destroy() { } public String getInitParameter(String name) { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getInitParameter(name); } } public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getInitParameterNames(); } } public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return this.config; } public ServletContext getServletContext() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getServletContext(); } } public String getServletInfo() { return ""; } public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { this.config = config; this.init(); } public void init() throws ServletException { } public void log(String msg) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg); } public void log(String message, Throwable t) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t); } public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; public String getServletName() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getServletName(); } } }
GenericServlet中两个init()方法的作用:
public void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException{ } public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException{ this.config = config; this.init(); }
GenericServlet是一个抽象类无法产生实例,所以需要一个类继承它,就会出现覆盖的问题,如果实现该类就会覆盖该类的init()方法,那么程序员需要手动维护ServletConfig对象,这个不带参数的init()方法就是解决实现类覆盖问题的
2.javax.servlet.http
HttpServlet之所比GenericServlet强大,是因为它是GenericServlet抽象类的扩展,并且它是与Http相结合的
2.1 javax.servlet.http中的接口和类
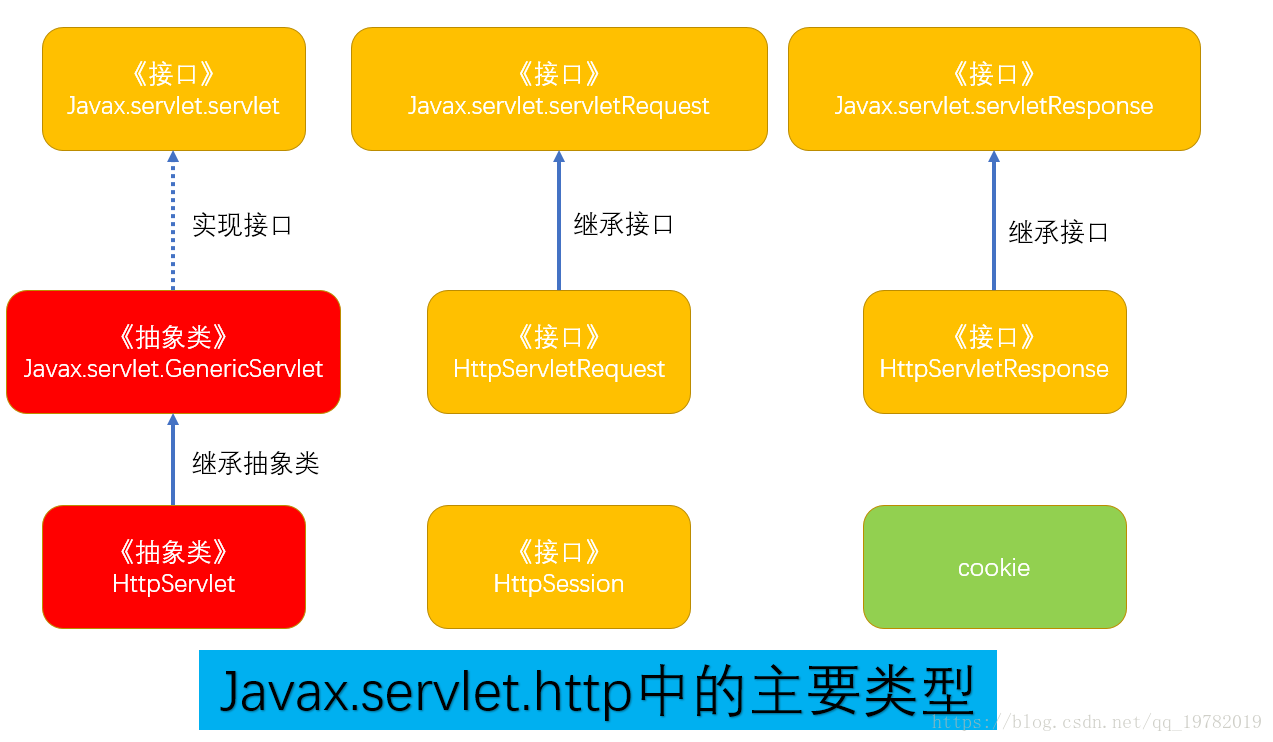
2.2 HttpServletRequest抽象类
HttpSerlvet抽象类继承于GenericServlet抽象类,覆盖了该类service()方法,并添加了自己的service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)方法
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp){ try{ HttpServlletRequest request; HttpServletResponse response;
request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
response = (HttpServletResponse)resp;
}catch(ClassCastException e){
throw new ServletException("non-Http request or response");
} this.service(reques, response);
}
上述代码中是直接将ServletRequest和ServletResponse对象转换为HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象,之所以这样转换是因为在调用Servlet的service方法时,
Servlet容器(如Tomcat)总会出传入一份HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象,预备使用Http,因此转换不会出问题。
转换之后,service()方法将来那个歌转换后的对象传入另一个service()方法,代码实现如下:

public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ String method = req.getMethod(); long lastNodified; if(method.equals("GET")){ if(lastModified = -1){ this.doGet(req, resp); }esle{ long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); if(ifModifiedSince < lastModified){ this.maybeSetLastModified(resp.lasrModified); thi.doGet(req, resp); }else{ rep.setStatus(304); } }else if(metyhod.equals("HEAD")){ lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doHead(req, resp); }else if(metyhod.equals("POST")){ this.doPost(req, resp); }else if(metyhod.equals("PUT")){ this.doPut(req, resp); }else if(metyhod.equals("DELETE")){ this.doDelete(req, resp); }else if(metyhod.equals("OPTIONS")){ this.doOptions(req, resp); }else if(metyhod.equals("TRACD")){ this.doTrace(req, resp); }else{ String errMsg = Strings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[](); errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.senError(501, errMsg); } }
1.该service方法中没有任何的服务逻辑,但是会调用doGet、doPOST、doPut、doDelete、doOptions以及doTrace方法解析HttpServletRequest方法参数。其中最常用的就是doGet、doPOST方法
2.具体的服务逻辑不需要service方法,而是重写doGet()和doPost()方法
2.3 PrintWriter和ServletOutputStream获取字符流
1.PrintWriter类的getWrite(String s )方法的write()方法将字符串设置到response缓存区。Tomcat将缓存区中的内容组装成Http响应返回给浏览器端
2.ServletOutputStream类的getOutputStream()的write(byte[] bytes)想response缓存区写入字节,再有Tomcat将字节内容组装成Http响应返回给浏览器
3.注意点:上面两类都可以发送响应消息体,但是他们之间相互排斥,不可以同时使用,否则会报异常
2.4 Response乱码问题
response乱码问题主要是两个部分,第一个response缓冲区默认编码是ISO-8859-1,不支持中文编码,修改为utf-8编码;第二个就是浏览器默认编码是GB2312也不支持中文编码,故要告诉浏览器所用utf-8编码
//1.response缓冲区编码方式为utf-8 response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //2.通知浏览器解码方式为utf-8 response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8"); //综合以上两种的response设置 response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
3.ServletContextListener
3.1 ServletContextListener
ServletContextListener是一个监听ServletContext的接口,只要实现该类就可以实现“监听ServletContext”的功能
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener{ //1.ServletContext初始化(应用启动时) void contextIninialized(ServletContextEvent var1); //2.ServletContext销毁(应用停止) void contextDestroy(ServletContextEvent var1); }
ServletContextListener工作流程:
- 应用程序启动时,ServletContext初始化,Servlet容器自动调用监听的ServletContextListener的contextInitializable(ServletContextEvent var1)方法,你并传入一个ServletContextEvent对象;
- 应用程序停止后,ServletContext销毁,Servlet容器调用该类的servletContextDestroy(ServletContextEvent var1)方法,并传入一个ServletContextEvent对象;
3.2 ServletContextListener中应用
ServletContext是一个“域对象”,存在在整个应用中,独此一份,它表示了当前应用的状态。

//ContextLoaderListener是ServletContextListener在Spring中的应用 package org.springframework.web.context; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextLis tener{ public ContextLoaderListener(){ } public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context){ super(context); } //重点 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event){ //ServletContextListener接口并没有这个方法 //所以查看该方法源码,观察它是如何实现spring实例化的 this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); } public void contextDestroyed(ServleyContextEvent event){ this.closeWebApplicationContext(envent.getServletContext()); ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext()); } }
InitWebApplicationContext()方法源码,分析是如何进行Spring容器实例化

public WebApplicationConetxt initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext){ if(servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplication.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null){ throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); }else{ Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); if(logger.isInfoEnabled()){ logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext:initialization stared"); } long startTime = System.curentTimeMills(); try{ if(this.context == null){ this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } if(this.context instanceof ConfigurableWepApplicationContext){ ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context; if(!cwac.isActive()){ if(cwac.getParent() == null){ ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); } this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } } //重点 servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.curerntThread().getContextClassLoader(); if(ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()){ curerntContext = this.context; }else if(ccl != null){ currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]"); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; }catch(RuntimeException var8){ logger.error("Context initialization failed", var8); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var8); throw var8; }catch(Error var9){ logger.error("Context initialization failed", var9); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var9); throw var9; }
代码分析:
- 首先判断Servlet中是否存在WebApplication.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE标识,如果存在抛出IllegalStateException
- 如果为空,根据createWebApplicationContext()方法,并传入ServletContext对象默认实例化一个root容器;
- 根据loadParentContext()方法为root容器设置父上下文(父一般设置为0);
- 再根据configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContex()方法传入ConfigurableWebApplicationContext对象和servletContext对象配置容器并刷新
- 通过servletContext.setAttribute()方法,并传入WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTIBUTE, this.context来注册标识,并保存在当前线程中
3.3 ServletContextListener在Spring中应用流程
- Servlet容器启动时,ServletContext对象被初始化,然后Servlet容器调用配置文件中注册的监听该类的ServletContextListener类的contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent var1)方法,在该监听器中的调用this.InitWebApplicationContext()方法实例化spring IOC容器即ApplicationContext对象;
- 当ServletContext对象创建时,就可以创建ApplicationContext对象,当前者被销毁时,后者也可以被销毁,它们共生死
4.原文链接更详细
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19782019/article/details/80292110
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19782019/article/details/80292110






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!