迭代器模式
理论
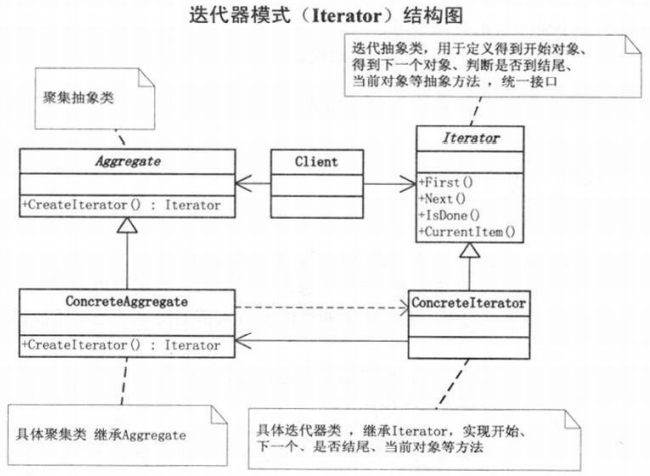
迭代器模式(Iterator),提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示。
迭代器模式的应用场景:
1. 当需要访问一个聚类对象,而且不管这些对象是什么都需要遍历的时候
2. 需要对聚类有多种方式遍历的时候
迭代器模式的优点:
迭代器模式分离了集合对象的遍历行为,抽象出一个迭代器类来负责,这样既可以做到不不暴露集合的内部结构,又可让外部代码透明地访问集合内部地数据。
实例
模拟公交车上收取车费的情况,按次序遍历收取车费
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 | #include <iostream>#include <vector>#include<string>using namespace std;//迭代器抽象类class Iterator {public: virtual string First() = 0; virtual string Next() = 0; virtual bool IsDone() = 0; virtual string CurrentItem() = 0;};//聚集抽象类class Aggregate {public: virtual Iterator* CreateIterator() = 0;};class ConcreteAggregate;//具体迭代器类class ConcreteIterator :public Iterator {public: ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate* aggregate); string First(); string Next(); bool IsDone(); string CurrentItem();private: ConcreteAggregate* aggregate; int current;};//具体聚集类class ConcreteAggregate :public Aggregate {public: ConcreteAggregate() { items = new vector<string>(); } virtual Iterator* CreateIterator() { return new ConcreteIterator(this); } int Count() { return items->size(); } string GetElement(int index) { return items->at(index); } void SetElement(int index, string object) { items->push_back(object); //items->at(index) = object; }private: vector<string>* items;};ConcreteIterator::ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate* aggregate) { this->aggregate = aggregate; this->current = 0;}string ConcreteIterator::First() { return aggregate->GetElement(0);}string ConcreteIterator::Next() { current++; if (current < aggregate->Count()) { return aggregate->GetElement(current); }}bool ConcreteIterator::IsDone() { return current >= aggregate->Count() ? true : false;}string ConcreteIterator::CurrentItem() { return aggregate->GetElement(current);}//反向迭代器class ConcreteIteratorDesc :public Iterator {public: ConcreteIteratorDesc(ConcreteAggregate* aggregate) { this->aggregate = aggregate; this->current = aggregate->Count() - 1; } string First() { return aggregate->GetElement(aggregate->Count() - 1); } string Next() { current--; if (current > 0) { return aggregate->GetElement(current); } } bool IsDone() { return current < 0 ? true : false; } string CurrentItem() { return aggregate->GetElement(current); }private: ConcreteAggregate* aggregate; int current;};int main(){ ConcreteAggregate* a = new ConcreteAggregate(); a->SetElement(0, "peopleA"); a->SetElement(1, "peopleB"); a->SetElement(2, "peopleC"); a->SetElement(3, "peopleD"); Iterator* it = a->CreateIterator(); string item1 = it->First(); while (!it->IsDone()) { cout << it->CurrentItem() << " 请买车票" << endl; it->Next(); } cout << "--------------------" << endl; Iterator* i = new ConcreteIteratorDesc(a); string item2 = i->First(); while (!i->IsDone()) { cout << i->CurrentItem() << " 请买车票" << endl; i->Next(); } system("pause"); return 0;} |




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 【杂谈】分布式事务——高大上的无用知识?