策略模式
理论
策略模式:它定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化,不会影响到使用算法的客户。
策略模式是一种定义一系列算法的方法,从概念上来看,所有这些算法都是完成相同的工作,只是实现不同,它可以以相同的方式调用所有的算法,减少了各种算法类与使用算法类之间的耦合。
策略模式简化了单元测试,因为每个算法都有自己的类,可以通过自己的接口单独测试。
实例
做一个商场收银软件,营业员根据客户所购买的单价和数量,向客户收费
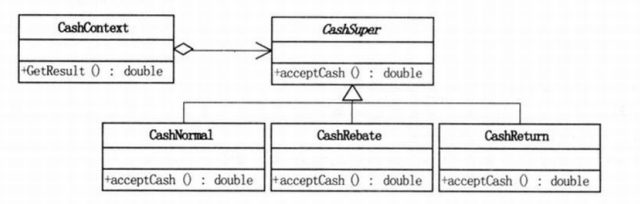
UML类图
实现代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//收费的抽象类
class CashSuper {
public:
virtual double acceptCash(double price) = 0;
};
//算法1 正常收费类
class CashNormal :public CashSuper
{
public:
double acceptCash(double price)
{
return price;
}
};
//算法2 打折收费类
class CashRebate :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashRebate(double ratio)
{
priceRatio = ratio;
}
double acceptCash(double price)
{
return price * priceRatio;
}
private:
double priceRatio = 1.0;
};
//算法3 返利收费类
class CashReturn :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashReturn(double Condition, double Return)
{
priceCondition = Condition;
priceReturn = Return;
}
double acceptCash(double price)
{
int num = (int)(price / priceCondition);
return price - num * priceReturn;
}
private:
double priceCondition = 0.0;
double priceReturn = 0.0;
};
class CashContext {
public:
CashSuper* strategy = NULL;
CashContext(CashSuper* cashSuper)
{
strategy = cashSuper;
}
double GetResult(double price)
{
return strategy->acceptCash(price);
}
~CashContext()
{
if (strategy != NULL)
{
delete strategy;
strategy = NULL;
}
}
};
//客户端
void test()
{
//商品单价
double UnitPrice;
//数量
double Quantity;
//活动选择
int choice;
cout << "商品的单价: " << endl;
cin >> UnitPrice;
cout << "商品的数量: " << endl;
cin >> Quantity;
cout << "商品的收费标准: " << endl;
cout << "1. 正常收费 " << endl << "2. 打八折" << endl << "3. 满300减100" << endl;
cin >> choice;
CashContext* Context = NULL;
switch (choice)
{
case(1):
Context = new CashContext(new CashNormal);
break;
case(2):
Context = new CashContext(new CashRebate(0.8));
break;
case(3):
Context = new CashContext(new CashReturn(300, 100));
break;
}
double result = 0.0;
result = Context->GetResult(UnitPrice * Quantity);
cout << "商品的总价格:" << result << endl;
delete Context;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
缺点:判断过程放在了客户端,暴露了太多的细节
改进:策略模式结合简单工厂模式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//收费的抽象类
class CashSuper {
public:
virtual double acceptCash(double price) = 0;
};
//算法1 正常收费类
class CashNormal :public CashSuper
{
public:
double acceptCash(double price)
{
return price;
}
};
//算法2 打折收费类
class CashRebate :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashRebate(double ratio)
{
priceRatio = ratio;
}
double acceptCash(double price)
{
return price * priceRatio;
}
private:
double priceRatio = 1.0;
};
//算法3 返利收费类
class CashReturn :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashReturn(double Condition, double Return)
{
priceCondition = Condition;
priceReturn = Return;
}
double acceptCash(double price)
{
int num = (int)(price / priceCondition);
return price - num * priceReturn;
}
private:
double priceCondition = 0.0;
double priceReturn = 0.0;
};
class CashContext {
public:
CashSuper* strategy = NULL;
CashContext(int choice)
{
switch (choice)
{
case(1):
//正常收费
strategy = new CashNormal;
break;
case(2):
//打八折
strategy = new CashRebate(0.8);
break;
case(3):
//满300减100
strategy = new CashReturn(300, 100);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
double GetResult(double price)
{
return strategy->acceptCash(price);
}
~CashContext()
{
if (strategy != NULL)
{
delete strategy;
strategy = NULL;
}
}
};
//客户端
void test()
{
//商品单价
double UnitPrice;
//数量
double Quantity;
//活动选择
int choice;
cout << "商品的单价: " << endl;
cin >> UnitPrice;
cout << "商品的数量: " << endl;
cin >> Quantity;
cout << "商品的收费标准: " << endl;
cout << "1. 正常收费 " << endl << "2. 打八折" << endl << "3. 满300减100" << endl;
cin >> choice;
double result;
CashContext context(choice);
result = context.GetResult(UnitPrice * Quantity);
cout << "商品的总价格:" << result << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
简单工厂+策略模式,客户端只需要知道 CashContext 类

