BOM与DOM操作
一 BOM操作
1.1 介绍
BOM:Browser Object Model,浏览器对象模型。BOM的结构图:
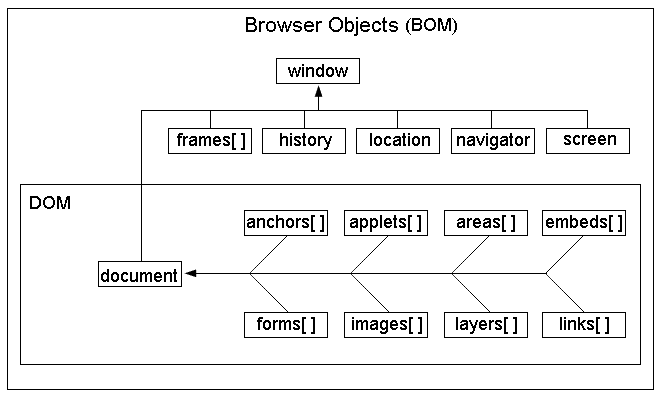
从上图可以看出来:
#1、DOM对象也是BOM的一部分
#2、window对象是BOM的顶层(核心)对象
需要注意的是
#1、在调用window对象的方法和属性时,可以省略window,例如:window.document.location可以简写为document.location
#2、全局变量也是windows对象的属性,全局的函数时window对象的方法
1.2 对象history、navigator、screen
#1、history对象包不包含浏览器的历史
history.back() //后退一页,等同于history.go(-1)
history.forward() //前进一页,等同于history.go(1)
history.go(0) //0是刷新
用的不多。因为浏览器中已经自带了这些功能的按钮:
#2、navigator对象包含了浏览器相关信息。
navigator.appName // Web浏览器全称
navigator.userAgent // 客户端绝大部分信息
navigator.platform // 浏览器运行所在的操作系统
#3、可以用screen对象得到可用的屏幕宽读和高度
screen.availWidth //可用的屏幕宽度
screen.availHeight //可用的屏幕高度

================page11.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p>第一个页</p> <a href="page22.html">点我进入下一页</a> </body> </html> ================page22.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p>第二个页</p> <a href="page33.html">点我进入下一页</a> </body> </html> ================page33.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> function back() { window.history.back() } </script> </head> <body> <p>第三个页</p> <input type="button" value="点我进入上一页" onclick="back()"> </body> </html> 练习:上一页下一页
1.3 localtion对象
location.href //获取URL
location.href="URL" // 跳转到指定页面
location.reload() //重新加载页面

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="div1">点我一下</div> <script> var oDiv = document.getElementById('div1'); oDiv.onclick = function () { window.location.href = 'https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng'; } </script> </body> </html> location.href练习1:点击盒子,跳转页面
1.4 弹出系统对话框
alert(1)是window.alert(1)的简写,因为它是window的子方法。
系统对话框有三种:
alert("egon警告你:人丑还不读书,是找不到女朋友的"); //不同浏览器中的外观是不一样的
confirm("你真的要这么做吗小伙子"); //兼容不好
prompt("输入用户名:"); //不推荐使用# 示例
var x=confirm("你真到要这么做吗")console.log(x)var username=prompt("输入用户名:")console.log(username);
1.5 打开关闭窗口
#1、open("url地址","新窗口的位置_blank或者_self","新窗口的特征")
window.open("http://www.w3school.com.cn","_blank", "width=400, height=400")
#2、close()关闭当前窗口
var x=window.open("http://www.w3school.com.cn","_blank", "width=400, height=400")
x.close()
1.6 浏览器窗口内部的高度和宽度
window.innerHeight - 浏览器窗口的内部高度
window.innerWidth - 浏览器窗口的内部宽度
1.7 定时器
#1.setTimeOut()
只在指定时间后执行一次,通常用于延迟执行某方法或功能,
//定时器 异步运行
function say(){
alert("hello");
}
//使用方法名字执行方法
var t1 = setTimeout(hello,1000);
var t2 = setTimeout("hello()",3000); //使用字符串执行方法
clearTimeout(t2); //去掉定时器
#2.setInterval()
在指定时间为周期循环执行,通常用于刷新表单,对于一些表单的假实时指定时间刷新同步,动画效果等。
//实时刷新时间单位为毫秒
var t3 = setInterval(say,3000);
var t4 = setInterval('say()',3000);
clearInterval(t3);
clearInterval(t4);
二 DOM操作
2.1 介绍
当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型(Document Object Model),DOM标准规定HTML文档中的每个成员都是一个节点(node),HTML DOM树如下图
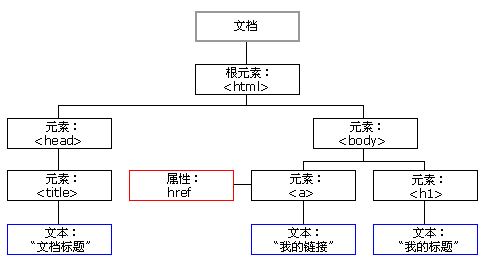
2.2 查找节点
#1、直接查找
document.getElementById #根据ID获取唯一一个标签
document.getElementsByClassName #根据class属性获取一系列标签
document.getElementsByTagName #根据标签名获取一系列标签
#2、间接查找如下表
| 语法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| childNodes | 获取所有的子节点,除了元素还有文本等 |
| children | 获取所有元素子节点,不包含文本 |
| parentNode | 获取父节点 |
| previousSibling | 获取上一个兄弟节点,包含文本 |
| previousElementSibling | 获取上一个兄弟元素节点,不包含文本 |
| nextSibling | 获取下一个兄弟节点,包含文本 |
| nextElementSibling | 获取下一个兄弟元素节点,不包含文本 |
| firstChild | 获取第一个子节点,包含文本 |
| firstElementChild | 获取第一个子节点,不包含文本 |
| lastChild | 获取最后一个子节点,包含文本 |
| lastElementChild | 获取父元素最后一个元素节点。不包含文本 |
2.3 增加节点
#1、创建新节点
var divEle = document.createElement('div');
#2、追加一个子节点(放到最后)
somenode.appendChild(新的子节点);
#3、插入一个子节点(插入到某个节点前)
somenode.insertBefore(新的子节点,某个节点);
2.4 删除、替换节点
somenode.removeChild(要删除的子节点);
somenode.replaceChild(新的子节点, 某个子节点);
2.5 修改/设置节点属性
#1、获取文本节点的值: var divEle = document.getElementById("d1") divEle.innerText divEle.innerHTML #2、设置文本节点的值: var divEle = document.getElementById("d1") divEle.innerText="1" divEle.innerHTML="<p>2</p>" #3、attribute操作 var divEle = document.getElementById("d1"); divEle.setAttribute("age","18") divEle.getAttribute("age") divEle.removeAttribute("age") #4、自带的属性还可以直接.属性名来获取和设置 imgEle.src imgEle.src="..."
2.6 获取元素的值
#适用于input、select、textarea标签
var x=document.getElementById('input')
var y=document.getElementById('select')
var z=document.getElementById('textarea')
x.value
y.value
z.value
2.7 class操作
var x=document.getElementById('div1')
x.classList.remove('col1')
x.classList.add('col1')
x.classList.contains('col1')
x.classList.toggle('col1')
2.8 css操作
obj.style.backgroundColor="red"
JS操作CSS属性的规律:
1.对于没有中横线的CSS属性一般直接使用style.属性名即可。如
obj.style.margin
obj.style.width
obj.style.left
obj.style.position
2.对含有中横线的CSS属性,将中横线后面的第一个字母换成大写即可。如:
obj.style.marginTop
obj.style.borderLeftWidth
obj.style.zIndex
obj.style.fontFamily
2.9 事件
HTML 4.0 的新特性之一是有能力使 HTML 事件触发浏览器中的动作(action),比如当用户点击某个 HTML 元素时执行一段JavaScript。下面是一个属性列表,这些属性可插入 HTML 标签来定义事件动作。
1、常用事件
onclick 当用户点击某个对象时调用的事件句柄。
ondblclick 当用户双击某个对象时调用的事件句柄。
onfocus 元素获得焦点。 // 练习:输入框
onblur 元素失去焦点。 应用场景:用于表单验证,用户离开某个输入框时,代表已经输入完了,我们可以对它进行验证.
onchange 域的内容被改变。 应用场景:通常用于表单元素,当元素内容被改变时触发.(select联动)
onkeydown 某个键盘按键被按下。 应用场景: 当用户在最后一个输入框按下回车按键时,表单提交.
onkeypress 某个键盘按键被按下并松开。
onkeyup 某个键盘按键被松开。
onload 一张页面或一幅图像完成加载。
onmousedown 鼠标按钮被按下。
onmousemove 鼠标被移动。
onmouseout 鼠标从某元素移开。
onmouseover 鼠标移到某元素之上。
onselect 在文本框中的文本被选中时发生。
onsubmit 确认按钮被点击,使用的对象是form。
2、绑定方式
#方式一: <div id="div1" onclick="changeColor(this);">我是div,我去你妹的,点我</div> <script> function changeColor(ths) { ths.style.backgroundColor="green"; } </script> 注意: this是实参,表示触发事件的当前元素。 函数定义过程中的ths为形参。 #方式二: <div id="div1">来,点亮我的绿</div> <script> var oDiv = document.getElementById('div1'); oDiv.onclick = function() { this.style.backgroundColor = 'red'; } </script>

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } html, body { height: 100%; } #bg { height: 100%; background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3); } #content { position: relative; top: 150px; width: 400px; height: 200px; line-height: 200px; text-align: center; color: red; background-color: white; margin: 0 auto; } #cancel { position: absolute; top: 0; right: 0; color: white; width: 30px; height: 30px; line-height: 30px; text-align: center; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="弹出模态框" id="btn"> <script> var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn'); var oDiv = document.createElement('div'); var oP = document.createElement('p'); var oSpan = document.createElement('span'); oDiv.id = 'bg'; oP.id = 'content'; oSpan.id = 'cancel'; oP.innerHTML = '弹出模态框'; oSpan.innerHTML = 'X'; oDiv.appendChild(oP); oP.appendChild(oSpan); oBtn.onclick = function () { this.parentNode.replaceChild(oDiv, this); }; oSpan.onclick =function () { oDiv.parentNode.replaceChild(oBtn,oDiv); } </script> </body> </html> <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } html,body { height: 100%; } #bg { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.3); display: none; } #content { position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 50%; margin-left: -150px; background-color: white; width: 300px; height: 200px; } #content p:nth-child(3) { position: absolute; top: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="弹出" id="btn"> <div id="bg"> <div id="content"> <p> <label for="inp-username">用户名: </label><input type="text" name="username" id="inp-username"> </p> <p> <label for="inp-password">密码: </label><input type="text" name="username" id="inp-password"> </p> <p> <input type="button" value="提交" > <input type="button" value="取消" id="cancel"> </p> </div> </div> <script> var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn'); var oBg = document.getElementById('bg'); var oInpUsername=document.getElementById('inp-username'); var oInpPwd=document.getElementById('inp-password'); var oInp=document.getElementById('cancel'); oBtn.onclick=function () { oBg.style.display='block'; } oInp.onclick=function () { oInpUsername.value=''; oInpPwd.value=''; oBg.style.display='none' } </script> </body> </html> 案例一:模态框

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> span { background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <form> <p> <input type="text" name="username"> <span></span> </p> <p> <input type="password" name="password"> <span></span> </p> <p> <input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"> </p> </form> <script> var isOk1=false var reg1=new RegExp('(?!^[0-9]+$)(?!^[a-zA-Z]+$)^[0-9A-Za-z]{4}$') var inp1 = document.getElementsByName("username")[0] inp1.onblur=function () { var res=reg1.test(this.value) this.style.border="1px solid red" if (!res) { this.nextElementSibling.innerText="用户名必须由4位字母和数字组成" setTimeout(function () { inp1.nextElementSibling.innerText="" inp1.value="" },3000) }else { this.style.border="1px solid green" isOk1=true } } var isOk2=false var reg2=new RegExp('(?!^[0-9]+$)(?!^[a-zA-Z]+$)^[0-9A-Za-z]{6}$') var inp2 = document.getElementsByName("password")[0] inp2.onblur=function () { var res=reg2.test(this.value) this.style.border="1px solid red" if (!res) { this.nextElementSibling.innerText="密码必须由6位字母和数字组成" setTimeout(function () { inp2.nextElementSibling.innerText="" inp2.value="" },3000) }else { this.style.border="1px solid green" isOk2=true } } var btn=document.getElementById("btn") btn.onclick=function () { if(isOk1 && isOk2) { alert("提交成功") }else { alert("请重新填写") } } </script> </body> </html> 案例十一:用户名和密码校验
每天逼着自己写点东西,终有一天会为自己的变化感动的。这是一个潜移默化的过程,每天坚持编编故事,自己不知不觉就会拥有故事人物的特质的。 Explicit is better than implicit.(清楚优于含糊)






