造轮子-Java泛型堆排
个人博客地址:http://kyle.org.cn/2018/03/13/heapsort/
Java实现泛型堆排算法,用于N个对象中选择最大或者最小的前M个,其中M<=N
类似于Mysql中order by + limit的功能,如果有类似场景的需求,可以直接拷贝到项目中使用
Github源码地址:https://github.com/Kyle-Wilson1/Algorithm_Java/tree/master/heapsort
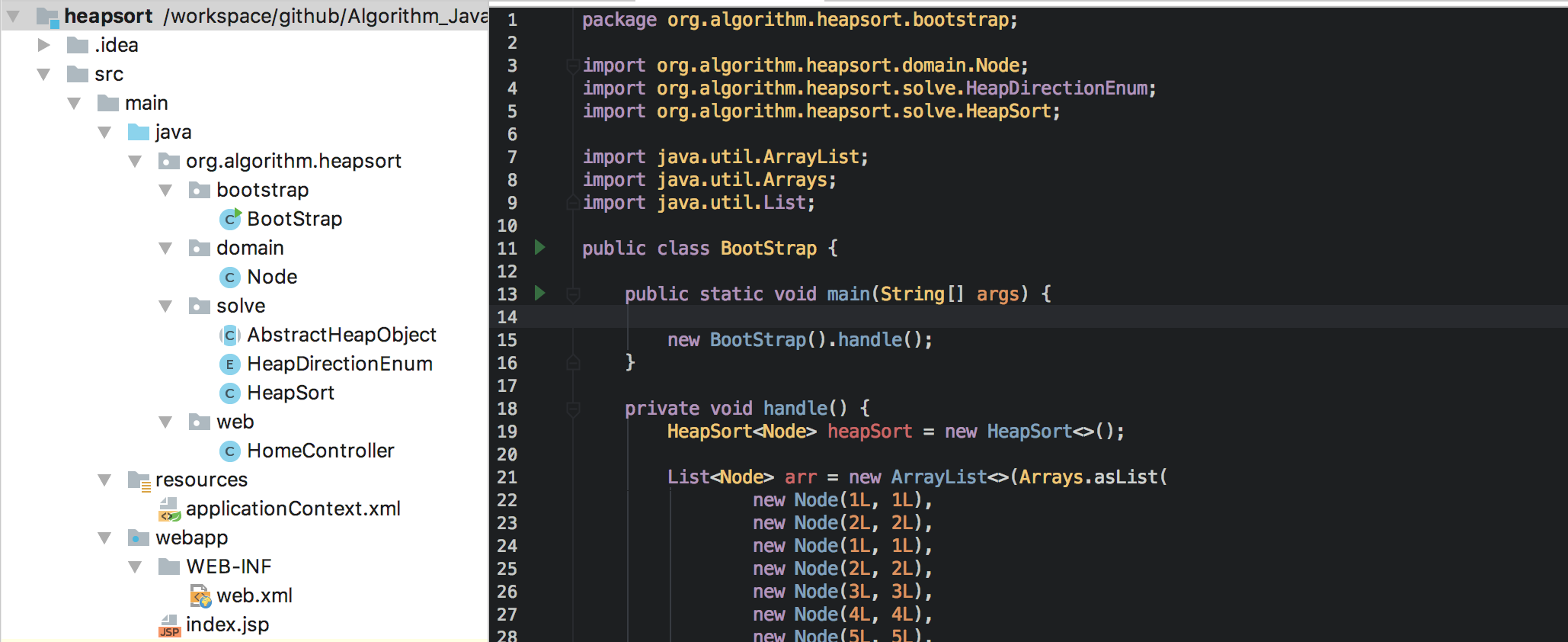
工程目录结构
- BootStrap:启动类,测试入口
- Node:排序的对象
- AbstractHeapObject:对象需要实现的接口
- HeapDirectionEnum:堆方向枚举
- HeapSort:堆排算法实现类
- HomeController:web api测试
启动类
- 作为程序的入口,写了一些测试数据
public class BootStrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BootStrap().handle();
}
private void handle() {
HeapSort<Node> heapSort = new HeapSort<>();
List<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(
new Node(1L, 1L),
new Node(2L, 2L),
new Node(1L, 1L),
new Node(2L, 2L),
new Node(3L, 3L),
new Node(4L, 4L)));
heapSort.setDirection(HeapDirectionEnum.MAX_ROOT);
heapSort.setHeapCapability(5);
heapSort.buildHeap(arr);
heapSort.getHeap().forEach(System.out::println);
List<Node> arr1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(
new Node(1L, 1L),
new Node(2L, 2L),
new Node(3L, 3L),
new Node(4L, 4L),
new Node(5L, 5L)));
heapSort.buildHeap(arr1);
System.out.println("insert arr1:");
heapSort.getHeap().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("pop: " + heapSort.heapPop());
}
}
测试结果如下:
Node{key=3, value=3}
Node{key=2, value=2}
Node{key=1, value=1}
Node{key=1, value=1}
Node{key=2, value=2}
insert arr1:
Node{key=2, value=2}
Node{key=2, value=2}
Node{key=1, value=1}
Node{key=1, value=1}
Node{key=1, value=1}
pop: Node
定义对象接口
- 对于要排序的对象,必须先实现该接口
- getKey()返回某一个对象要用于排序的字段
public abstract class AbstractHeapObject {
public abstract Long getKey();
}
排序对象
- 待排序的类实现,需要实现AbstractHeapObject接口
public class Node extends AbstractHeapObject {
private Long key;
private Long value;
public Node(Long key, Long value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public Long getKey() {
return key;
}
public Long getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"key=" + key +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
定义堆排方向枚举
- 大根堆,适用于N个数中求最小的前M个数
- 小根堆,适用于N个数中求最大的前M个数
public enum HeapDirectionEnum {
//大根堆,适用于N个数中求最小的前M个数
MAX_ROOT(0, "MAX_ROOT", "大根堆"),
//小根堆,适用于N个数中求最大的前M个数
MIN_ROOT(1, "MIN_ROOT", "小根堆");
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String remark;
HeapDirectionEnum(Integer id, String name, String remark) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.remark = remark;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
}
堆排核心算法
- 堆的向上调整,向下调整,弹出堆等实现
public class HeapSort<T extends AbstractHeapObject> {
private List<T> sourceData;
private HeapDirectionEnum direction;
private List<T> heap;
private int heapCapability;
public void setDirection(HeapDirectionEnum direction) {
this.direction = direction;
}
public void setHeapCapability(int heapCapability) {
this.heapCapability = heapCapability;
}
public List<T> getHeap() {
return heap;
}
synchronized public void buildHeap(List<T> sourceData) {
this.sourceData = sourceData;
//初始化堆容量
if (heap == null) {
heap = new ArrayList<>(heapCapability);
}
sourceData.forEach(x -> {
//如果堆中元素还没有达到最大值,则插入到堆尾并向上调整,否则替换根元素并向下进行调整
if (heap.size() < heapCapability) {
heapUp(x);
} else {
if (direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MAX_ROOT && x.getKey() < heap.get(0).getKey()
|| direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MIN_ROOT && x.getKey() > heap.get(0).getKey()) {
heap.set(0, x);
heapDown(0);
}
}
});
}
/**
* @param current the value to be added at the tail
*/
private void heapUp(T current) {
int i, j;
heap.add(current);
i = heap.size() - 1;
j = (i - 1) / 2; //j指向i的父结点
while (i > 0) {
if (direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MAX_ROOT && heap.get(j).getKey() >= current.getKey()
|| direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MIN_ROOT && heap.get(j).getKey() <= current.getKey()) {
break;
}
heap.set(i, heap.get(j));
i = j;
j = (i - 1) / 2;
}
heap.set(i, current);
}
/**
* @param top the location where the value will be adjusted down
*/
private void heapDown(int top) {
int j = 2 * top + 1;
T x = heap.get(top);
int heapSize = heap.size() - 1;
while (j <= heapSize) {
if (j + 1 <= heapSize && (
direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MAX_ROOT && heap.get(j + 1).getKey() > heap.get(j).getKey()
|| direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MIN_ROOT && heap.get(j + 1).getKey() < heap.get(j).getKey()))
j++;
if (direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MAX_ROOT && heap.get(j).getKey() <= x.getKey()
|| direction == HeapDirectionEnum.MIN_ROOT && heap.get(j).getKey() >= x.getKey()) {
break;
}
heap.set(top, heap.get(j));
top = j;
j = 2 * top + 1;
}
heap.set(top, x);
}
public T heapPop() {
T ret = heap.get(0);
heap.set(0, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
heapDown(0);
return ret;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号