netty的基本介绍
一、什么是netty?为什么要用netty
netty是jboss提供的一个java开源框架,netty提供异步的、事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具,用以快速开发高性能、高可用性的网络服务器和客户端程序。也就是说netty是一个基于nio的编程框架,使用netty可以快速的开发出一个网络应用。
由于java 自带的nio api使用起来非常复杂,并且还可能出现 Epoll Bug,这使得我们使用原生的nio来进行网络编程存在很大的难度且非常耗时。但是netty良好的设计可以使开发人员快速高效的进行网络应用开发。
二、netty的功能特性和架构思想
如下图所示:netty的核心是支持零拷贝的bytebuf缓冲对象、通用通信api和可扩展的事件模型;它支持多种传输服务并且支持HTTP、Protobuf、二进制、文本、WebSocket 等一系列常见协议,也支持自定义协议。

netty的模型是基于reactor多线程模型,其中mainReactor用于接收客户端请求并转发给subReactor。SubReactor负责通道的读写请求,非 IO 请求(具体逻辑处理)的任务则会直接写入队列,等待 worker threads 进行处理。

三、netty中的一些核心的概念
1、bootstrap、serverBootstrap:bootstrap的意思是引导,其主要作用是配置整个netty程序,将各个组件整合起来。serverBootstrap是服务器端的引导类。bootstrap用于连接远程主机它有一个EventLoopGroup ;serverBootstrap用于监听本地端口有两个EventLoopGroup。
2、eventLoop:eventLoop维护了一个线程和任务队列,支持异步提交执行任务。
3、eventLoopGroup:eventLoopGroup 主要是管理eventLoop的生命周期,可以将其看作是一个线程池,其内部维护了一组eventLoop,每个eventLoop对应处理多个Channel,而一个Channel只能对应一个eventLoop。
4、channelPipeLine:是一个包含channelHandler的list,用来设置channelHandler的执行顺序。
5、Channel:Channel代表一个实体(如一个硬件设备、一个文件、一个网络套接字或者一个能够执行一个或者多个不同的IO操作的程序组件)的开放链接,如读操作和写操作。
6、Futrue、ChannelFuture :Future提供了另一种在操作完成时通知应用程序的方式。这个对象可以看作是一个异步操作结果的占位符;它将在未来的某个时刻完成,并提供对其结果的访问。netty的每一个出站操作都会返回一个ChannelFuture。future上面可以注册一个监听器,当对应的事件发生后会出发该监听器。
7、ChannelInitializer:它是一个特殊的ChannelInboundHandler,当channel注册到eventLoop上面时,对channel进行初始化
8、ChannelHandler:用来处理业务逻辑的代码,ChannelHandler是一个父接口,ChannelnboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler都继承了该接口,它们分别用来处理入站和出站。
9、ChannelHandlerContext:允许与其关联的ChannelHandler与它相关联的ChannlePipeline和其它ChannelHandler来进行交互。它可以通知相同ChannelPipeline中的下一个ChannelHandler,也可以对其所属的ChannelPipeline进行动态修改。
四、netty中常用的自带解码器和编码器(编解码器名字对应的只列举一个)
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder :分隔符解码器,以设定的符号作为消息的结束解决粘包问题
FixedLengthFrameDecoder :定长解码器,作用于定长的消息
LineBasedFrameDecoder :按照每一行进行分割,也就是特殊的分隔符解码器,它的分割符为\n或者\r\n。
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder :通过消息中设置的长度字段来进行粘包处理。该解码器总共有5个参数
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength, 单个包的最大大小
int lengthFieldOffset, 定义长度的字段的相对包开始的偏移量
int lengthFieldLength, 定义长度字段所占字节数
int lengthAdjustment, lengthAdjustment = 数据长度字段之后剩下包的字节数 - 数据长度取值(也就是长度字段之后的所有非数据的其他信息)
int initialBytesToStrip) 从包头开始,要忽略的字节数
HttpRequestDecoder :将字节解码为HttpRequest、HttpContent和LastHttpContent消息
HttpResponseDecoder :将字节解码为HttpResponse、HttpContent和LastHttpContent消息
ReplayingDecoder :一个特殊的ByteToMessageDecoder ,可以在阻塞的i/o模式下实现非阻塞的解码。 ReplayingDecoder 和ByteToMessageDecoder 最大的不同就是ReplayingDecoder 允许你实现decode()和decodeLast()就像所有的字节已经接收到一样,不需要判断可用的字节
Base64Decoder :Base64编码器
StringDecoder :将接收到的ByteBuf转化为String
ByteArrayDecoder :将接收到的ByteBuf转化为byte 数组
DatagramPacketDecoder :运用指定解码器来对接收到的DatagramPacket进行解码
MsgpackDecoder :用于Msgpack序列化的解码器
ProtobufDecoder :用于Protobuf协议传输的解码器
HttpObjectAggregator :将http消息的多个部分聚合起来形成一个FullHttpRequest或者FullHttpResponse消息。
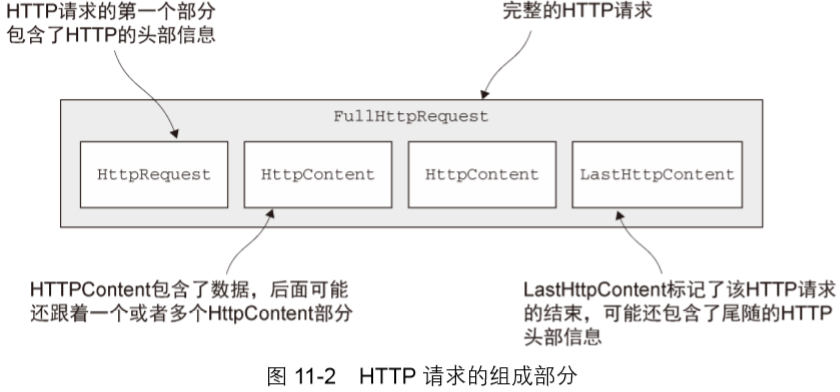
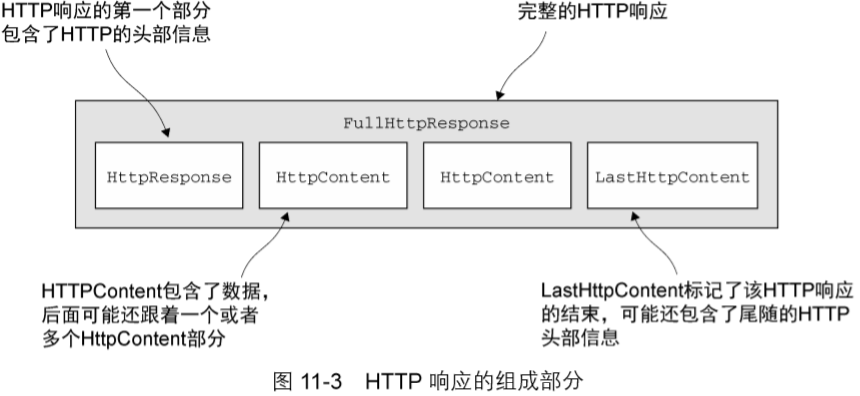
LengthFieldPrepender :将消息的长度添加到消息的前端的编码器,一般是和LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder搭配使用
HttpServerCodec :相当于HttpRequestDecoder和HttpResponseEncoder
HttpClientCodec :相当于HttpRequestEncoder和HttpResponseDecoder
ChunkedWriteHandler :在进行大文件传输的时候,一次将文件的全部内容映射到内存中,很有可能导致内存溢出,ChunkedWriteHandler可以解决大文件或者码流传输过程中可能发生的内存溢出问题
五、netty的简单使用
public class MyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try{ Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0,4,0,4)) .addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4)) .addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)) .addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)) .addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+": "+msg); ctx.writeAndFlush("来自客户端的信息"); } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ ctx.writeAndFlush("客户端第"+i+"条消息"); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }); } }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 9999).sync(); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally{ nioEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } }
public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try{ ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline() .addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4,0,4)) .addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4)) .addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)) .addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)) .addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+":"+msg); ctx.writeAndFlush("from server: "+UUID.randomUUID()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }); } }); ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync(); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally{ bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号