【深度学习pytorch】softmax回归
数据集
图像分类数据集Fashion-MNIST
import torch import torchvision from torch.utils import data from torchvision import transforms from d2l import torch as d2l # 读取数据集 def get_dataloader_workers(): """使用4个进程来读取数据""" return 4 def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None): """获取和读取Fashion-MNIST数据集。 这个函数返回训练集和验证集的数据迭代器。 此外,这个函数还接受一个可选参数resize,用来将图像大小调整为另一种形状。""" trans = [transforms.ToTensor()] if resize: trans.insert(0, transforms.Resize(resize)) trans = transforms.Compose(trans) mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="../data", train=True, transform=trans, download=True) mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="../data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True) return (data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=get_dataloader_workers()), data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=get_dataloader_workers())) def get_fashion_mnist_labels(labels): """返回Fashion-MNIST数据集的文本标签""" text_labels = ['t-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover', 'dress', 'coat', 'sandal', 'shirt', 'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot'] return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels] batch_size = 256 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
softmax回归的从零开始实现
# 初始化参数 input_nums = 784 output_nums = 10 W = torch.normal(0, 0.1, (input_nums, output_nums), requires_grad=True) b = torch.zeros(output_nums, requires_grad=True) # 定义softmax函数 def softmax(X): X_exp = torch.exp(X) partition = X_exp.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True) return X_exp / partition # 定义模型 def net(X): return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape(-1, input_nums), W) + b) # 定义损失函数 def cross_entropy(y_hat, y): return - torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y)), y]) # 定义优化算法————小批量梯度下降 def sgd(paras, lr, batch_size): with torch.no_grad(): for para in paras: para -= lr * para.grad / batch_size para.grad.zero_() lr = 0.1 def updater(batch_size): return sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size) # 计算精度 def accuracy(y_hat, y): """计算预测正确的数量""" if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1: y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1) cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum()) class Accumulator: """在n个变量上累加""" def __init__(self, n): self.data = [0.0] * n def add(self, *args): self.data = [a + float(b) for a, b in zip(self.data, args)] def reset(self): self.data = [0.0] * len(self.data) def __getitem__(self, idx): return self.data[idx] def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter): """计算在指定数据集上模型的精度""" if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module): net.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式 metric = Accumulator(2) # 正确预测数、预测总数 with torch.no_grad(): for X, y in data_iter: metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel()) return metric[0] / metric[1] # 绘制曲线 class Animator: """在动画中绘制数据""" def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None, ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear', fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(3.5, 2.5)): # 增量地绘制多条线 if legend is None: legend = [] d2l.use_svg_display() self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize) if nrows * ncols == 1: self.axes = [self.axes, ] # 使用lambda函数捕获参数 self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes( self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend) self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts def add(self, x, y): # 向图表中添加多个数据点 if not hasattr(y, "__len__"): y = [y] n = len(y) if not hasattr(x, "__len__"): x = [x] * n if not self.X: self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)] if not self.Y: self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)] for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)): if a is not None and b is not None: self.X[i].append(a) self.Y[i].append(b) self.axes[0].cla() for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts): self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt) self.config_axes() display.display(self.fig) display.clear_output(wait=True) # 训练数据 def train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater): #@save """训练模型一个迭代周期(定义见第3章)""" # 将模型设置为训练模式 if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module): net.train() # 训练损失总和、训练准确度总和、样本数 metric = Accumulator(3) for X, y in train_iter: # 计算梯度并更新参数 y_hat = net(X) l = cross_entropy(y_hat, y) if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer): # 使用PyTorch内置的优化器和损失函数 updater.zero_grad() l.sum().backward() updater.step() else: # 使用定制的优化器和损失函数 l.sum().backward() updater(X.shape[0]) metric.add(float(l.sum()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel()) # 返回训练损失和训练精度 return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2] def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): """训练模型(定义见第3章)""" animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9], legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc']) for epoch in range(num_epochs): train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater) test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter) animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,)) train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc # test and predict num_epochs = 10 train(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater) def predict_ch3(net, test_iter, n=6): """预测标签(定义见第3章)""" for X, y in test_iter: break trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y) preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1)) titles = [true +'\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)] d2l.show_images( X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n]) predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
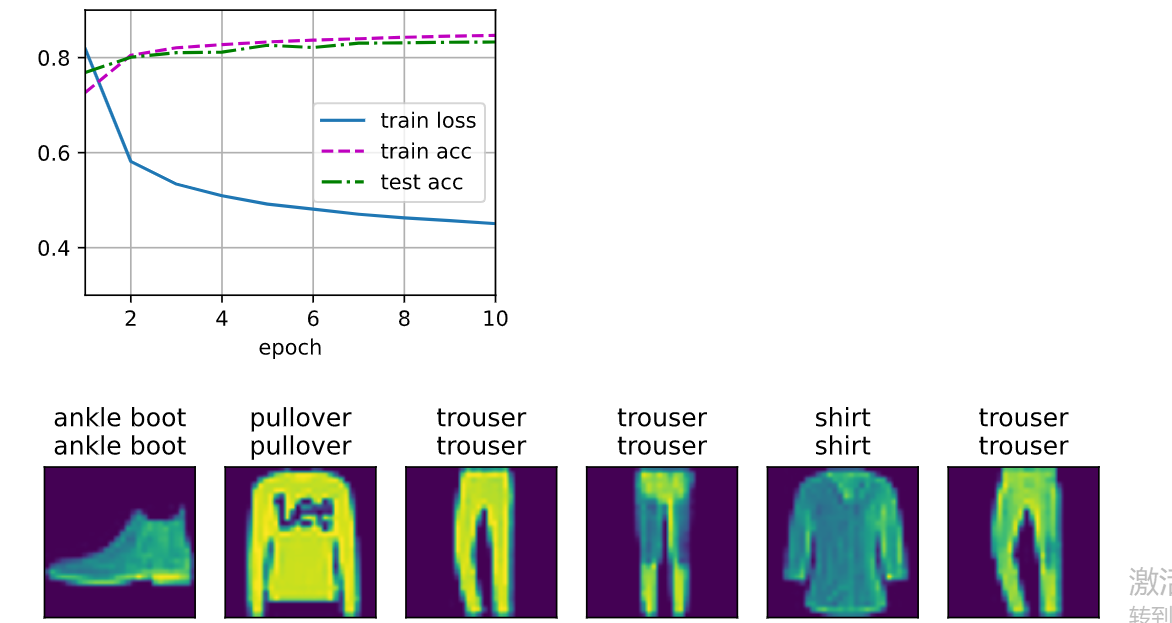
softmax回归的简洁实现
import torch from torch import nn from d2l import torch as d2l batch_size = 256 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 10)) def init_weights(m): if type(m) == nn.Linear: nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01) net.apply(init_weights) loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none') trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1) num_epochs = 10 d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本