【OpenFeign 】OpenFeign 下的重试器的执行过程分析
1 前言
上节我们看了下 OpenFeign 里的重试,在从源码的角度看它的执行原理的时候,又意外的遇到了一个【OpenFeign 】OpenFeign 下未开启重试,服务却被调用了两次 的问题的分析,那本节我们就来看看重试器的一个入场以及执行的过程。
2 源码分析
首先我们要知道在默认的情况下,OpenFeign 也是有重试器的,只不过是 Retryer 接口中的 NEVER_RETRY:
// Retryer 接口 Retryer NEVER_RETRY = new Retryer() { @Override public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) { throw e; } @Override public Retryer clone() { return this; } };
并且在 FeignClientsConfiguration 配置中:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class FeignClientsConfiguration { // ... // 当没有重试器的情况下,配置默认的 Retryer.NEVER_RETRY; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Retryer feignRetryer() { return Retryer.NEVER_RETRY; } // ... }
我们在调试的时候,也可以看到:
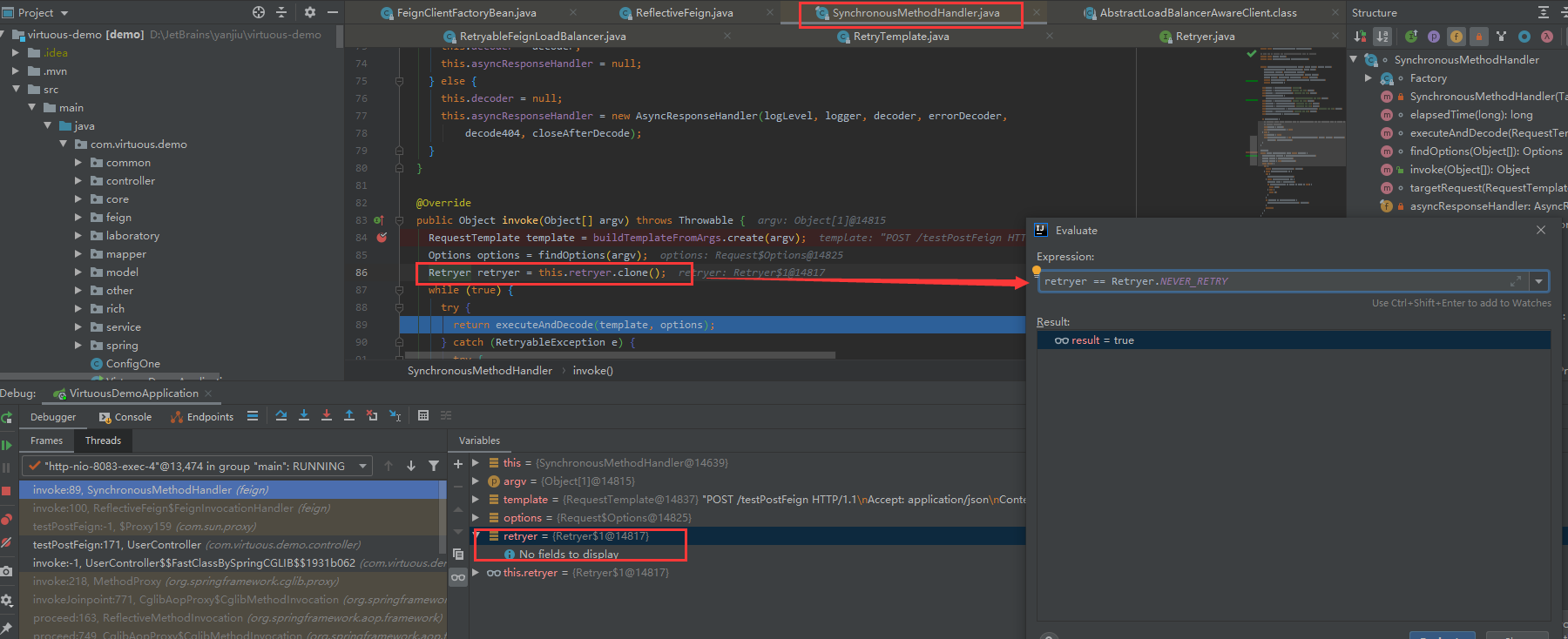
那么接下来我们要分析重试器的执行原理的话,还是要从两个角度看起,一个是创建过程或者叫入场时机,因为我们的 Feign 会被 FeignClientFactoryBean 来负责创建,创建的时候会设置重试器 二就是执行过程。
2.1 重试器的入场
我们还是从 FeignClientFactoryBean 创建 Feign 代理的入口开始看起:
// FeignClientFactoryBean @Override public Object getObject() { // 调用内部的 getTarget 方法 return getTarget(); } <T> T getTarget() { // 获取 FeignContext 这个是 feign 的上下文对象 FeignContext context = beanFactory != null ? beanFactory.getBean(FeignContext.class) : applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class); // 构建 feign 的 builder 建造器 Feign.Builder builder = feign(context); // 处理一些基础属性 // 如果没有 url 就创建负载均衡型的客户端来请求 一般我们都是用这个 if (!StringUtils.hasText(url)) { if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) { LOG.info("For '" + name + "' URL not provided. Will try picking an instance via load-balancing."); } if (!name.startsWith("http")) { url = "http://" + name; } else { url = name; } url += cleanPath(); return (T) loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(type, name, url)); } if (StringUtils.hasText(url) && !url.startsWith("http")) { url = "http://" + url; } String url = this.url + cleanPath(); // 如果你全局上下文执行了用什么型号的客户端去请求 就采用你指定的 Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class); if (client != null) { if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) { // not load balancing because we have a url, // but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient) client).getDelegate(); } if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) { // not load balancing because we have a url, // but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate(); } if (client instanceof RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) { // not load balancing because we have a url, // but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap client = ((RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client) .getDelegate(); } builder.client(client); } // 创建代理对象 Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class); return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(type, name, url)); }
我们的 Feign 代理对象的创建跟 Feign.Builder 贴合很近,所以 Feign.Builder 设置的是什么重试器,我们最后的 Feign 的执行也是用的什么重试器。为什么这么说呢?我这里就不一点点带大家看了,我简单画个主流向图:
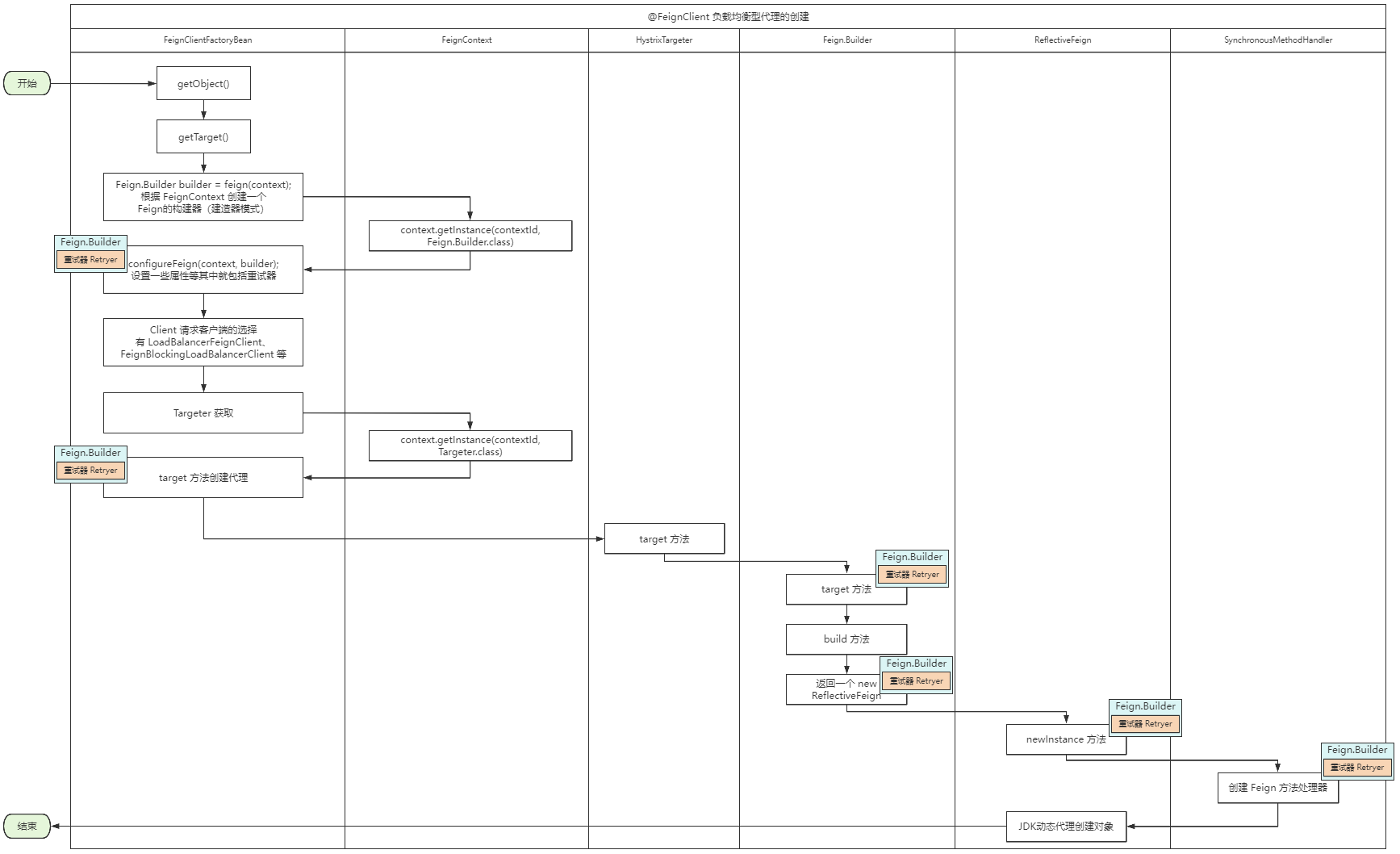
可以看到当我们的 Feign.Builder 创建并初始化重试器后,是一直向后传递的,最后交给方法的处理器 SynchronousMethodHandler。
所以我们这里看下 Feign.Builder 的重试器的设置:
// FeignClientFactoryBean protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) { // 日志相关 FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class); Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(type); // @formatter:off Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class) // required values .logger(logger) .encoder(get(context, Encoder.class)) .decoder(get(context, Decoder.class)) .contract(get(context, Contract.class)); // @formatter:on // 填充 configureFeign(context, builder); // 自定义行为 applyBuildCustomizers(context, builder); return builder; } // configureFeign // 这个配置 feign 有一个共同点就是不管是 if else 都会走向 configureUsingConfiguration protected void configureFeign(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) { FeignClientProperties properties = beanFactory != null ? beanFactory.getBean(FeignClientProperties.class) : applicationContext.getBean(FeignClientProperties.class); FeignClientConfigurer feignClientConfigurer = getOptional(context, FeignClientConfigurer.class); setInheritParentContext(feignClientConfigurer.inheritParentConfiguration()); if (properties != null && inheritParentContext) { if (properties.isDefaultToProperties()) { configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); configureUsingProperties( properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder); configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(contextId), builder); } else { configureUsingProperties( properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder); configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(contextId), builder); configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); } } else { configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); } } // configureUsingConfiguration protected void configureUsingConfiguration(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) { Logger.Level level = getInheritedAwareOptional(context, Logger.Level.class); if (level != null) { builder.logLevel(level); } // 获取重试器并放进 Builder Retryer retryer = getInheritedAwareOptional(context, Retryer.class); if (retryer != null) { builder.retryer(retryer); } // ... }
好啦,到这里重试器的入场就看到这里了。
2.2 重试器的执行
按照上边的流图,最后 Feign 执行的时候,会进入到 ReflectiveFeign 的 invoke:
// FeignInvocationHandler static class FeignInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private final Target target; private final Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch; FeignInvocationHandler(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) { this.target = checkNotNull(target, "target"); this.dispatch = checkNotNull(dispatch, "dispatch for %s", target); } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) { try { Object otherHandler = args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null; return equals(otherHandler); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { return false; } } else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) { return hashCode(); } else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) { return toString(); } // 接着走向 SynchronousMethodHandler 的 invoke return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args); } ... }
那我们继续看 SynchronousMethodHandler 的 invoke:
// SynchronousMethodHandler @Override public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable { RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv); Options options = findOptions(argv); // 每次请求都会把重试器复制一份 Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone(); // 一直循环 // 两种方式退出 // 1、return 正常请求 2、throw 抛出异常 while (true) { try { // 执行请求 return executeAndDecode(template, options); } catch (RetryableException e) { // 捕获重试异常 try { // 执行重试器的 continueOrPropagate 方法 retryer.continueOrPropagate 方法(e); } catch (RetryableException th) { Throwable cause = th.getCause(); if (propagationPolicy == UNWRAP && cause != null) { throw cause; } else { throw th; } } if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) { logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel); } continue; } } }
可以看到当请求发生异常时,会调用重试器的 continueOrPropagate 方法,那么对于默认不开启重试的 NEVER_RETRY ,就是直接抛出异常,结束调用。
Retryer NEVER_RETRY = new Retryer() { @Override public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) { throw e; } @Override public Retryer clone() { return this; } };
对于 Retryer 内部的还有一个提供的 Default 的重试器,就是根据最大重试次数以及重试间隔时间控制睡眠时间然后继续进入 while 循环,继而继续请求,当达到最大重试次数时,还是异常的话,抛出异常,执行结束。
class Default implements Retryer { private final int maxAttempts; private final long period; private final long maxPeriod; int attempt; long sleptForMillis; public Default() { this(100, SECONDS.toMillis(1), 5); } public Default(long period, long maxPeriod, int maxAttempts) { this.period = period; this.maxPeriod = maxPeriod; this.maxAttempts = maxAttempts; this.attempt = 1; } // visible for testing; protected long currentTimeMillis() { return System.currentTimeMillis(); } public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) { if (attempt++ >= maxAttempts) { throw e; } long interval; if (e.retryAfter() != null) { interval = e.retryAfter().getTime() - currentTimeMillis(); if (interval > maxPeriod) { interval = maxPeriod; } if (interval < 0) { return; } } else { interval = nextMaxInterval(); } try { Thread.sleep(interval); } catch (InterruptedException ignored) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); throw e; } sleptForMillis += interval; }
好啦,那么重试器的执行也看到这里了。
3 小结
本节我们主要看了下,FeignClient 的重试器的入场以及执行流程,有理解不对的地方,还请指正。



