Lucene排序取TopN源码分析--PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue 实现一优先队列框架,实例非常简单,只需实现lessThan(Object a, Object b)方法即可,通过该方法可以控制大优先或小优先
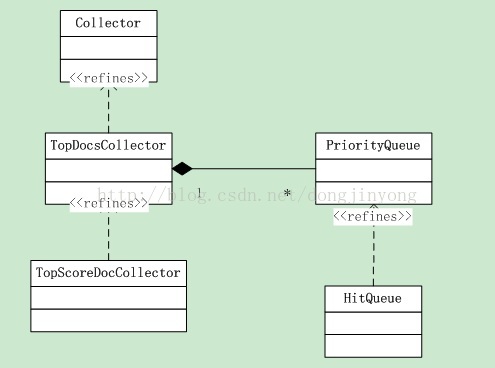
通过分析lucene源码可知,lucene每命中一个结果,就调用一次collector.collect(doc)方法,由Collector把结果保存到一个PriorityQueue中。对于常见的取TopN的情况,通常实例化一个org.apache.lucene.search.TopDocsCollector的子类对象A,这些类之间的关系如下:
PriorityQueue是抽象类,hitqueue是其具体实现
org.apache.lucene.util.PriorityQueue的内部实现
这个优先级队列被用来实现堆排序。堆用一个一位数组表示,长为size()+1,第0个元素没有实际用途,第1个元素就是堆顶元素。每次出堆,要把堆顶元素移出(按堆排序原理,pop后可以放数组后面,从后往前放,最终使数组有序;但lucene提供的这个类没这么做,只是把堆尾置null,size--,数组是private的,外部无法直接访问)。如果需要获取N个元素从大到小的序列,只需把它们全部入堆,再全部出堆,使用小顶堆比较合适。特别需要注意的是,除了add()方法之外,还有一个方法insertWithOverflow():
public T insertWithOverflow(T element) {
if (size < maxSize) {
add(element);
returnnull;
} elseif (size > 0 && !lessThan(element, heap[1])) {
T ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = element;
updateTop();
return ret;
} else {
return element;
}
}
这个方法很重要,它把想要入堆的元素和堆顶元素做比较,决定是否该入堆,从而使取topN时,堆的空间复杂度控制在O(N),降低了开销。
到底该使用大顶堆还是小顶堆呢?分析如下:
小顶堆:如果按从大到小取topN的话,只需初始化堆大小为N,入堆时调用insertWithOverflow()方法。这个方法非常重要,它把想要入堆的元素和堆顶元素做比较,决定是否该入堆,从而使堆空间复杂度降低。堆空间复杂度降低,会使堆的深度降低,对时间性能上也有提升。为获得TopN,最后还需要先把堆中所有元素弹出。需要注意的是:最先弹出的是topN里的最小值,最后弹出的才是最大值。
大顶堆:如果按从大到小取TopN的话,初始化的对大小必须为元素的总个数,只能add。堆占用的数组空间比小顶堆要大,建堆性能劣于小顶堆。出堆时,最先出的就是最大值。可见,取TopN,小顶堆优于大顶堆。但如果取lastN(按从大到小,排在最后面的N个元素),则大顶堆更有优势,这时大顶堆可以实现一个insertWithOverflow()方法。
PriorityQueue有两种模式:
1. pre-populate=false,不用重写getSentinelObject()方法,堆的size()方法可以直接用。初始化堆的大小应该根据实际需求来设置,使用时需注意区分add()和insertWithOverflow()方法,如果错误使用add()有数组下标越界的可能。
2. pre-populate=true。该类的源码注释很清楚:关于入堆、出堆、size都有特殊用法,size需要自己来维护,使用者应自己知道堆里有多少元素,知道每一步操作到底使堆发生哪些变化。相比之下,pre-populate=true的性能应该更优,它会在初始化堆数组的时候,一次性全部初始化数组里的所有元素,集中创建对象。所以看lucene的默认实现,基本都采用了pre-populate=true的用法。这种模式下,必须重写protected T getSentinelObject()方法,以便初始化堆数组
public abstract class PriorityQueue<T> {
private int size = 0;
private final int maxSize;
private final T[] heap;
public PriorityQueue(int maxSize) {
this(maxSize, true);
}
//该队列是维护一个大小固定的小顶堆,每次有新入doc'先和堆顶比较,小于堆顶直接舍弃,否则替换堆顶,然后重构该堆
//而在最初阶段,堆是空的,如果 prepopulate=true,lucene会用最小的几个元素填充该堆
public PriorityQueue(int maxSize, boolean prepopulate) {
final int heapSize;
if (0 == maxSize) {
// We allocate 1 extra to avoid if statement in top()
heapSize = 2;
} else {
// NOTE: we add +1 because all access to heap is
// 1-based not 0-based. heap[0] is unused.
heapSize = maxSize + 1;
if (heapSize > ArrayUtil.MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH) {
// Throw exception to prevent confusing OOME:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize must be <= " + (ArrayUtil.MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH-1) + "; got: " + maxSize);
}
}
// T is unbounded type, so this unchecked cast works always:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final T[] h = (T[]) new Object[heapSize];
this.heap = h;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
if (prepopulate) {
// If sentinel objects are supported, populate the queue with them
T sentinel = getSentinelObject();
if (sentinel != null) {
heap[1] = sentinel;
for (int i = 2; i < heap.length; i++) {
heap[i] = getSentinelObject();
}
size = maxSize;
}
}
}
/** Determines the ordering of objects in this priority queue. Subclasses
* must define this one method.
* @return <code>true</code> iff parameter <tt>a</tt> is less than parameter <tt>b</tt>.
*/
protected abstract boolean lessThan(T a, T b);
/**
* This method can be overridden by extending classes to return a sentinel
* object which will be used by the {@link PriorityQueue#PriorityQueue(int,boolean)}
* constructor to fill the queue, so that the code which uses that queue can always
* assume it's full and only change the top without attempting to insert any new
* object.<br>
*
* Those sentinel values should always compare worse than any non-sentinel
* value (i.e., {@link #lessThan} should always favor the
* non-sentinel values).<br>
*
* By default, this method returns false, which means the queue will not be
* filled with sentinel values. Otherwise, the value returned will be used to
* pre-populate the queue. Adds sentinel values to the queue.<br>
*
* If this method is extended to return a non-null value, then the following
* usage pattern is recommended:
*
* <pre class="prettyprint">
* // extends getSentinelObject() to return a non-null value.
* PriorityQueue<MyObject> pq = new MyQueue<MyObject>(numHits);
* // save the 'top' element, which is guaranteed to not be null.
* MyObject pqTop = pq.top();
* <...>
* // now in order to add a new element, which is 'better' than top (after
* // you've verified it is better), it is as simple as:
* pqTop.change().
* pqTop = pq.updateTop();
* </pre>
*
* <b>NOTE:</b> if this method returns a non-null value, it will be called by
* the {@link PriorityQueue#PriorityQueue(int,boolean)} constructor
* {@link #size()} times, relying on a new object to be returned and will not
* check if it's null again. Therefore you should ensure any call to this
* method creates a new instance and behaves consistently, e.g., it cannot
* return null if it previously returned non-null.
*
* @return the sentinel object to use to pre-populate the queue, or null if
* sentinel objects are not supported.
*/
protected T getSentinelObject() {
return null;
}
/**
* Adds an Object to a PriorityQueue in log(size) time. If one tries to add
* more objects than maxSize from initialize an
* {@link ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException} is thrown.
*
* @return the new 'top' element in the queue.
*/
public final T add(T element) {
size++;
heap[size] = element;
upHeap();
return heap[1];
}
/**
* Adds an Object to a PriorityQueue in log(size) time.
* It returns the object (if any) that was
* dropped off the heap because it was full. This can be
* the given parameter (in case it is smaller than the
* full heap's minimum, and couldn't be added), or another
* object that was previously the smallest value in the
* heap and now has been replaced by a larger one, or null
* if the queue wasn't yet full with maxSize elements.
*/
//数据加入队列
public T insertWithOverflow(T element) {
//堆未满,直接加入元素
if (size < maxSize) {
add(element);
return null;
//堆满,并且比堆顶值大,则替换掉堆顶值,并且重新构建堆
//如果score相同,取docid小的,认为其socre值大
} else if (size > 0 && !lessThan(element, heap[1])) {
T ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = element;
updateTop();
return ret;
} else {//堆满,并且比堆顶值小,抛弃
return element;
}
}
/** Returns the least element of the PriorityQueue in constant time. */
public final T top() {
// We don't need to check size here: if maxSize is 0,
// then heap is length 2 array with both entries null.
// If size is 0 then heap[1] is already null.
return heap[1];
}
/** Removes and returns the least element of the PriorityQueue in log(size)
time. */
//最后最小堆推出数据,每次吐出这个最小堆里最小的数据,然后将堆尾放到堆顶,然后重构堆
//该方法是在结果输出时使用一次,在收集文档的过程中不会使用,和堆排序略有不同
public final T pop() {
if (size > 0) {
T result = heap[1]; // save first value
heap[1] = heap[size]; // move last to first
heap[size] = null; // permit GC of objects
size--;
downHeap(); // adjust heap
return result;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Should be called when the Object at top changes values. Still log(n) worst
* case, but it's at least twice as fast to
*
* <pre class="prettyprint">
* pq.top().change();
* pq.updateTop();
* </pre>
*
* instead of
*
* <pre class="prettyprint">
* o = pq.pop();
* o.change();
* pq.push(o);
* </pre>
*
* @return the new 'top' element.
*/
public final T updateTop() {
downHeap();
return heap[1];
}
/** Returns the number of elements currently stored in the PriorityQueue. */
public final int size() {
return size;
}
/** Removes all entries from the PriorityQueue. */
public final void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
heap[i] = null;
}
size = 0;
}
//如果prepopulate=true,则该方法不会用到
private final void upHeap() {
int i = size;
T node = heap[i]; // save bottom node
int j = i >>> 1;
while (j > 0 && lessThan(node, heap[j])) {
heap[i] = heap[j]; // shift parents down
i = j;
j = j >>> 1;
}
heap[i] = node; // install saved node
}
//该方法是,针对一个规范堆,有且仅有一个节点改变(这里是堆顶)改变了,修复堆的方法,
// 而不是从一个乱序中重构堆,关于乱序中构建一个堆的方法可以参见https://blog.csdn.net/asdfsadfasdfsa/article/details/80643651
private final void downHeap() {
int i = 1;
T node = heap[i]; // save top node
int j = i << 1; // find smaller child
int k = j + 1; //一个元素乘2 代表它的左子节点,再加1代表右子节点; 注意这里节点从1开始而不是0!!!!!!
if (k <= size && lessThan(heap[k], heap[j])) {
j = k;//该if保证了j代表是左子节点和右子节点间最小的那个
}
while (j <= size && lessThan(heap[j], node)) {//如果子节点中有比这个堆顶元素小,则调换两个节点,如果是
//左子节点和堆顶调换则下次循环处理处理以左子节点为堆顶的子堆,如果是右子节点和堆顶调换则下次循环处理以右子节点为堆顶的子堆
heap[i] = heap[j]; // shift up child
i = j;
j = i << 1;
k = j + 1;
if (k <= size && lessThan(heap[k], heap[j])) {
j = k;
}
}
heap[i] = node; // install saved node
}
/** This method returns the internal heap array as Object[].
* @lucene.internal
*/
protected final Object[] getHeapArray() {
return (Object[]) heap;
}
}