N维整形向量类的c++实现
题目如下:
N维整型向量类
【问题描述】
线性代数里面我们学习过n维向量,请用类vector_N来封装n维整型向量,成员如下;
私有数据成员:
² 向量维数n, int型
² 指针 p,int型
公有函数成员:
- 无参默认构造函数,在该函数中,将n置0,将p置null;
- 重载输入输出运算符,输入运算符,先指定向量维数,若输入为非正整数,则提示错误信息,“Error Length!”然后退出程序,若维数输入正确则分配长度为n的动态内存,并用指针p指向该内存,输出运算符依次输出向量各元素即可;
- 重载向量的加法+、减法-、数乘*(乘数在前,乘数为int型)这三运算符;
- 重载[]运算,例如,向量a=(1,2,3,4),a[0]的值为1,若下标越界,则输出“Error Index”,然后退出程序;
- 返回向量维数的函数;
- 将两个向量的内积运算定义为vector_N的友元函数;
在主函数中定义两个vector_N类对象v1,v2,均不带参数,之后对两个对象进行输入赋值,输入数乘运算的乘数,输入待取元素的下标,对两个向量进行加、减、数乘和内积运算,并将结果输出,输出v1中对应下标对应的元素。加法、减法和内积运算先判断两向量维数是否一致,若一致则输出运算结果,否则输出错误提示信息“Mismatch Length!”
提示:1.此类需要用到动态内存的分配,所以在析构函数中应释放空间,并将指针置null,将维数n置0
2.需要显式定义复制构造函数vector_N(vector_N &)
3.需要重载复制运算符 vector_N operator= (vector_N &)
4.退出程序用函数 _exit(0)
5.返回值类型需要为引用的形式,另一方面,在使用时就要考虑不能返回临时变量的引用
显然,
这道题私有成员的n,p的建立并不困难,第一个难点就在于n维向量中,n个坐标该如何储存,其实也不难解决,;题目中提示给了整形指针p,因此我们可以用new申请一个大小为n的空间,然后在这些空间中自然就可以储存这些坐标,而有new就要有delete,所以不要忘记在析构函数中使用delete释放空间.第一个难点解决之后,之后运算符中针对n维坐标的运算问题自然就迎刃而解,用for循环对数组中每一个数字进行处理便可以解决.
具体流程:
先创建一个vector_N类,私有成员为整形n,和整形指针p,公有函数建立默认的无参函数,内容是n=0,p=NULL,接下来重载运算符和输入输出符,其中输入符复制输入n,p,输出符则需要输出以(x,y,z)类型的n维坐标,其他函数按照题目构建即可
流程图:
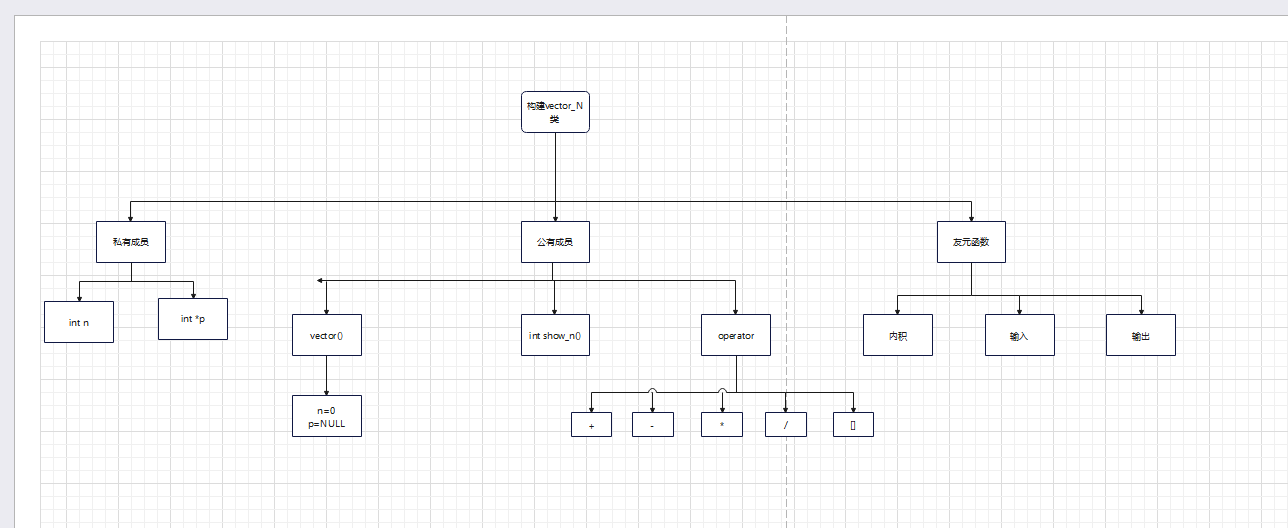
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
class vector_N
{
private:
int n;
int* p;
public:
vector_N();
vector_N(vector_N &B);
bool check(vector_N B);
int show_N();
friend istream& operator>>(istream& input, vector_N &B);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, vector_N &B);
friend vector_N neiji(vector_N A, vector_N B);
vector_N operator+(vector_N B);
vector_N operator-(vector_N B);
int operator*(vector_N B);
int operator[](int B);
};
istream& operator>>(istream& input, vector_N &B)
{
cout << "请输入维数" << endl;
input >> B.n;
if (B.n <= 0)
{
cout << "Error Length!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
else
{
B.p = new int[B.n];
cout << "请分别输入各个坐标" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < B.n; i++)
{
input >> B.p[i];
}
}
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, vector_N &B)
{
for (int i = 0; i < B.n; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
output << "(";
}
cout << B.p[i];
if (i != B.n - 1)
{
output << ",";
}
else
{
output << ")" << endl;
}
}
return output;
}
vector_N neiji(vector_N A, vector_N B)
{
if (A.n == B.n)
{
vector_N C(A);
for (int i = 0; i <= A.n; i++)
{
C.p[i] = A.p[i] * B.p[i];
}
return C;
}
else
{
cout << "error" << endl;
}
}
vector_N::vector_N()
{
n = 0;
p = NULL;
}
vector_N::vector_N(vector_N &B)
{
n = B.n;
p = new int[B.n];
for (int i = 0; i < B.n; i++)
{
p[i] = B.p[i];
}
}
bool vector_N::check(vector_N B)
{
if (n == B.n) return true;
else
{
cout << "Mismatch Length!" << endl;
return false;
}
}
int vector_N::show_N()
{
return n;
}
vector_N vector_N::operator + (vector_N B)
{
vector_N A(B);
if (check(B))
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
A.p[i] = p[i] + B.p[i];
}
return A;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
vector_N vector_N::operator - (vector_N B)
{
vector_N A(B);
cout << B;
if (check(B))
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
A.p[i] = p[i] - B.p[i];
}
return A;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
int vector_N:: operator*(vector_N B)
{
if (check(B))
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum += p[i] * B.p[i];
}
return sum;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
int vector_N:: operator[](int B)
{
if (B>=0)
return p[B];
else
{
cout << "Error Index" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
vector_N a, b;
cin >> a;
cin.sync();
cin >> b;
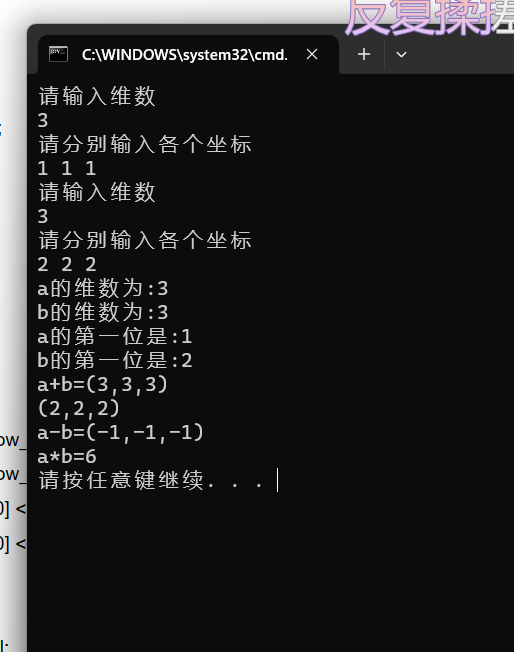
cout << "a的维数为:" << a.show_N() << endl;
cout << "b的维数为:" << b.show_N() << endl;
cout << "a的第一位是:" << a[0] << endl;
cout << "b的第一位是:" << b[0] << endl;
cout << "a+b=" << a + b;
cout << "a-b=" << a - b;
cout << "a*b=" << a*b << endl;
}
实验结果:
发现的问题:
在构造复制函数的时候注意,不要简单地使用n=B.n,p=B.p;
否则就会导致之后运算的过程中对参数运算改变了主参数中的运算数.



