图解排序算法(四)之归并排序
基本思想
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治(conquer)的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案"修补"在一起,即分而治之)。
分而治之

可以看到这种结构很像一棵完全二叉树,本文的归并排序我们采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程,递归深度为log2n。
合并相邻有序子序列
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。
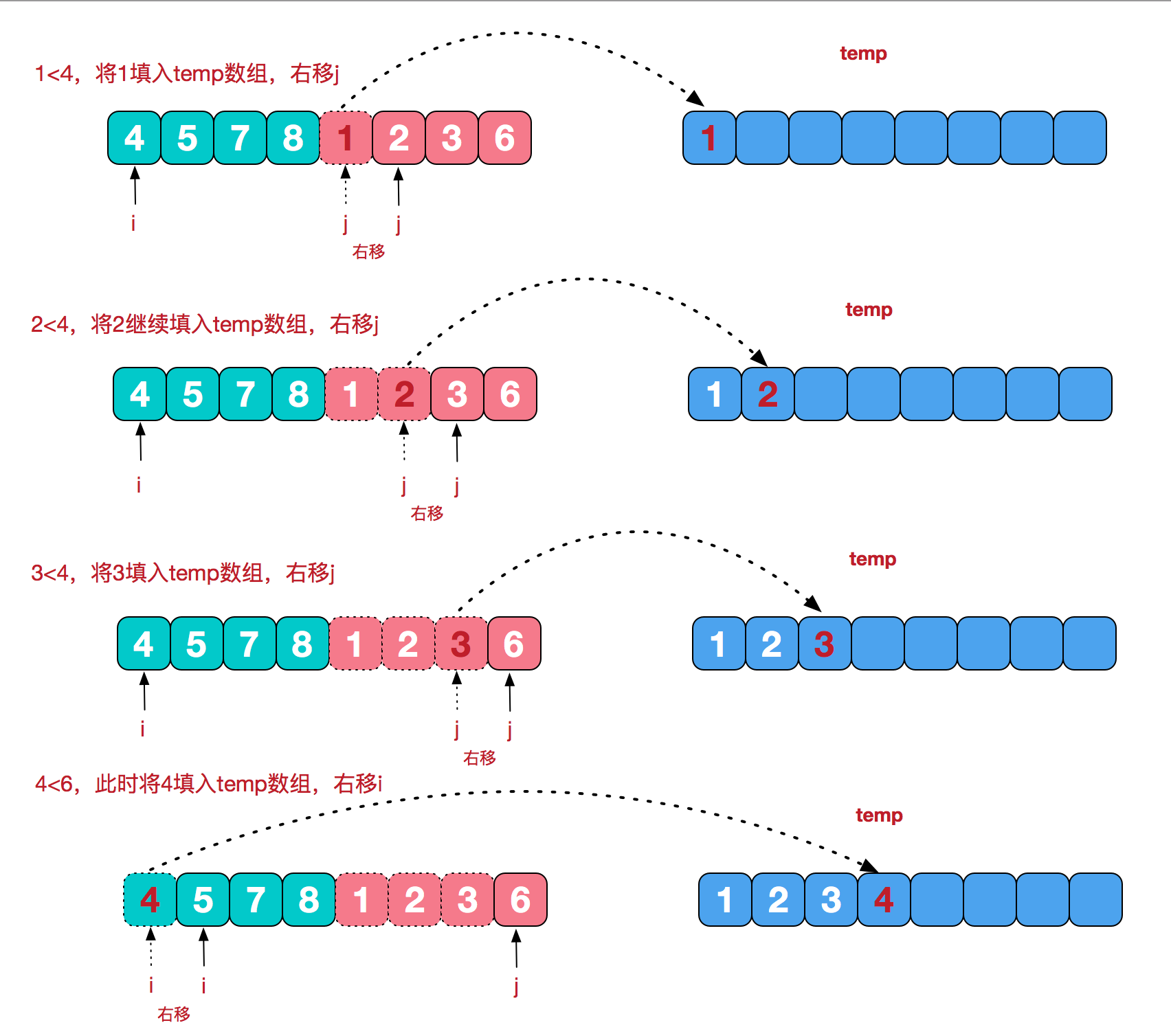
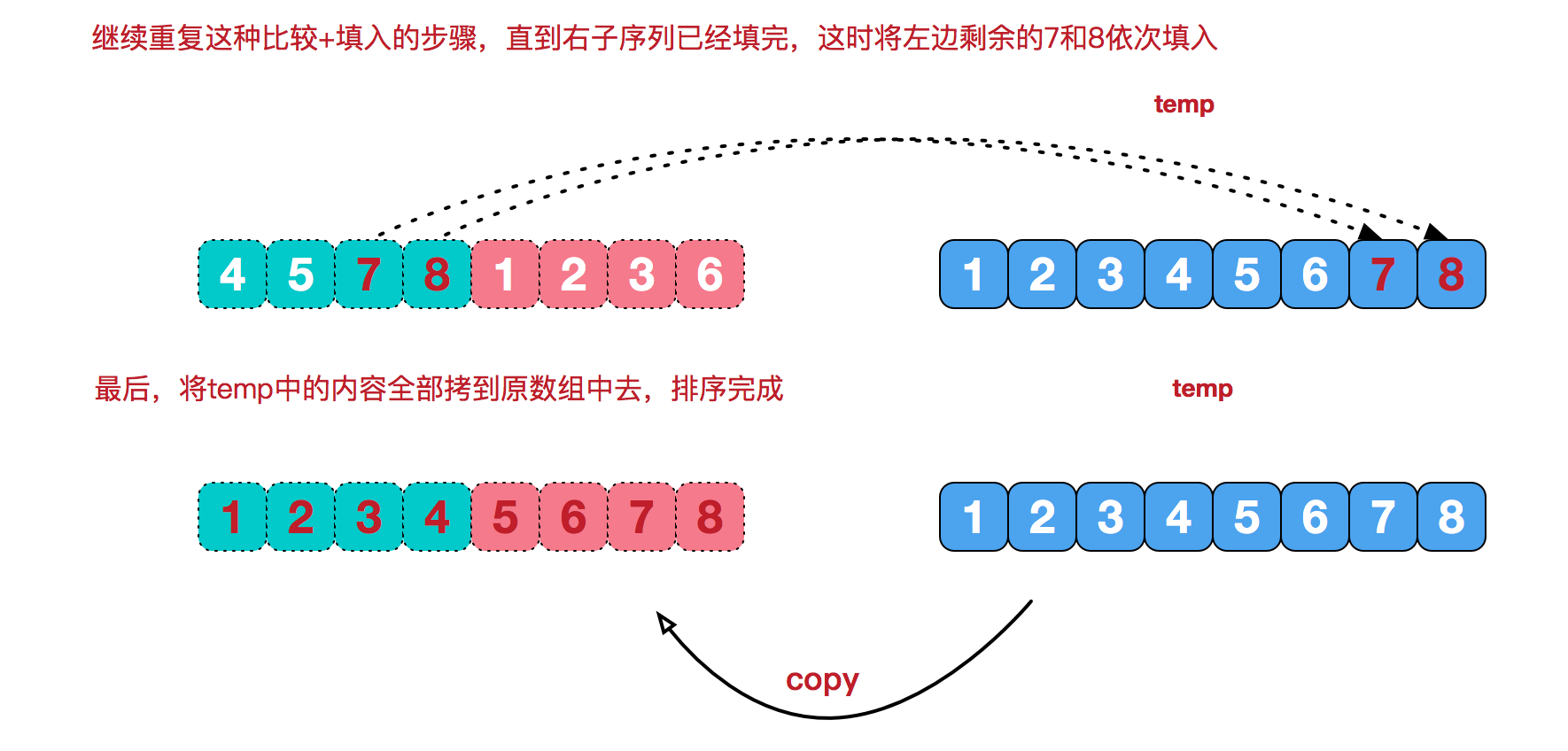
代码实现
import java.util.Arrays; /** * Created by chengxiao on 2016/12/8. */ public class MergeSort { public static void main(String []args){ int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1}; sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } public static void sort(int []arr){ int []temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间 sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp); } private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){ if(left<right){ int mid = (left+right)/2; sort(arr,left,mid,temp);//左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序 sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序 merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);//将两个有序子数组合并操作 } } private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){ int i = left;//左序列指针 int j = mid+1;//右序列指针 int t = 0;//临时数组指针 while (i<=mid && j<=right){ if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){ temp[t++] = arr[i++]; }else { temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } } while(i<=mid){//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[i++]; } while(j<=right){//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } t = 0; //将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中 while(left <= right){ arr[left++] = temp[t++]; } } }
单向链表的归并排序:
ListNode *sortList(ListNode *head) { if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr) return head; //采用快慢指针找到中间节点 ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head; while(fast!=nullptr&&fast->next!=nullptr&&fast->next->next!=nullptr){ fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; } //断开 fast=slow; slow=slow->next; fast->next=nullptr; fast=sortList(head); slow=sortList(slow); return merge(fast,slow); } ListNode* merge(ListNode* sub1,ListNode* sub2){ if(sub1==nullptr)return sub2; if(sub2==nullptr)return sub1; ListNode* head=nullptr; if(sub1->val<sub2->val){ head=sub1; sub1=sub1->next; } else{ head=sub2; sub2=sub2->next; } ListNode* p=head; while(sub1!=nullptr&&sub2!=nullptr){ if(sub1->val<sub2->val){ p->next=sub1; sub1=sub1->next; } else{ p->next=sub2; sub2=sub2->next; } p=p->next; } if(sub1!=nullptr) p->next=sub1; if(sub2!=nullptr) p->next=sub2; return head; }
最后
归并排序是稳定排序,它也是一种十分高效的排序,能利用完全二叉树特性的排序一般性能都不会太差。java中Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本。从上文的图中可看出,每次合并操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),而完全二叉树的深度为|log2n|。总的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。而且,归并排序的最好,最坏,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号