实验6
1
ABC.h
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class ADD { public: void add(int m, int n); private: int x, y, result; }; class A :public ADD { public: void reduce(int m, int n); private: int x, y, result; }; class B :public ADD { public: void multiply(int m, int n); private: int x, y, result; }; class C :public A { public: void division(int m, int n); private: int x, y,result; double result1 = 0.0; };
ABC.cpp
#include"ABC.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; void ADD::add(int m, int n) { x = m; y = n; result = x + y; cout << result << ", "; } void A::reduce(int m, int n) { x = m; y = n; result = x - y; cout << result; } void B::multiply(int m, int n) { x = m; y = n; result = x*y; cout << result; } void C::division(int m, int n) { double a = m; double b = n; result1 = a/b; cout << result1; }
main.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"ABC.h" using namespace std; int main() { int a = 0, b = 0; char c; cout << "输入两个整数" << endl; cin >> a >> b; cout << "选择ABC:" << endl; cin >> c; if (c == 'A') { A ABC; ABC.add(a, b); ABC.reduce(a, b); } else if (c == 'B') { B ABC; ABC.add(a, b); ABC.multiply(a, b); } else if (c == 'C') { C ABC; ABC.add(a, b); ABC.division(a, b); } cin >> c; if (c == 'exit') { return 0;} }
运行截图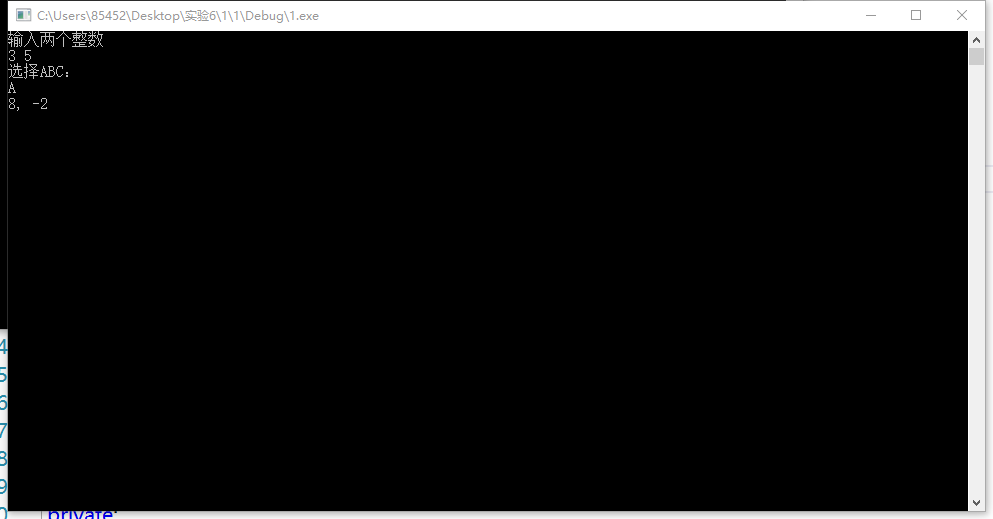
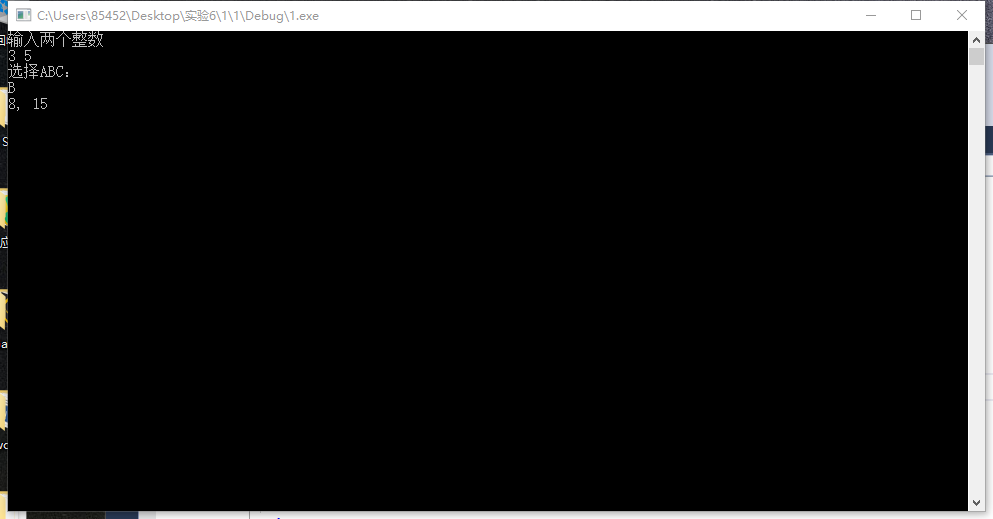
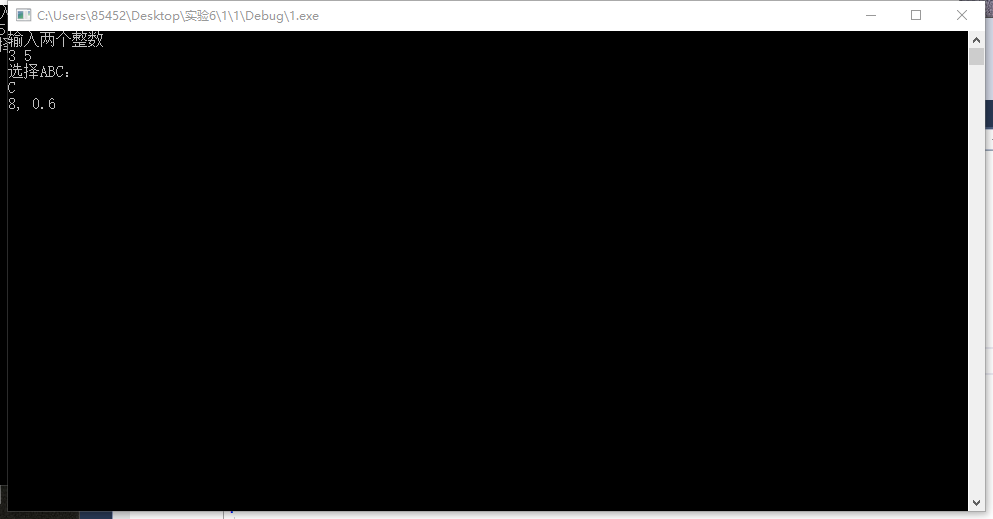
2.
vehicle.h
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class vehicle { public: vehicle(){} vehicle(int a, int b); ~vehicle(){} void run(); void stop(); private: int maxspeed, weight; }; class bicycle :virtual public vehicle { public: bicycle(){} bicycle(int a, int b, int c); ~bicycle(){} private: int height; }; class motorcar :virtual public vehicle { public: motorcar(){} motorcar(int a, int b, int d); ~motorcar(){} private: int seatnum; }; class motorcycle :public bicycle, public motorcar { public: motorcycle(){} motorcycle(int a, int b, int c, int d); ~motorcycle(){} };
vehicle.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"vehicle.h" using namespace std; vehicle::vehicle(int a, int b) { maxspeed = a; weight = b; } void vehicle::run() { cout << "run" << endl; } void vehicle::stop() { cout << "stop" << endl; } bicycle::bicycle(int a, int b, int c) { vehicle(a, b); height = c; } motorcar::motorcar(int a, int b, int d) { vehicle(a, b); seatnum = d; } motorcycle::motorcycle(int a, int b, int c, int d) { vehicle(a, b); bicycle(a, b, c); motorcar(a, b, d); cout << "maxspeed=" << a <<endl; cout<< "weight=" << b << endl; cout << "height=" << c << endl; cout << "seatnum=" << d << endl; }
main.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"vehicle.h" using namespace std; int main() { int x, y, z, r, end; cout << "输入maxspeed weight height seatnum:"; cin >> x >> y >> z >> r; motorcycle go(x,y,z,r); go.run(); go.stop(); if (cin >> end); return 0; }
运行截图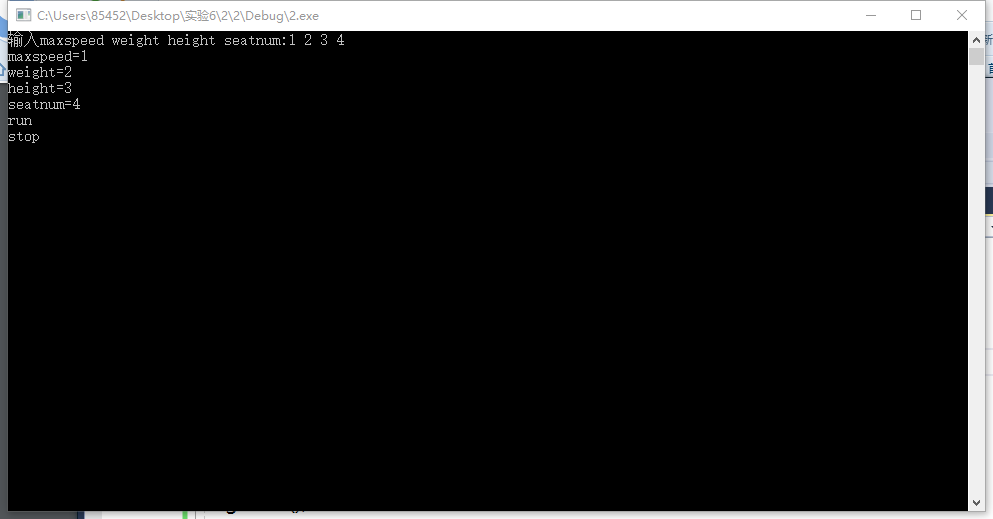
3.fraction.h
#ifndef FRACTION_H //不加这2条会报错,所以百度了 #define FRACTION_H //原理好像是防止头文件的重复包含和编译 class Fraction { public: Fraction(int a = 0, int b = 1); void operator+ ( Fraction &p) ; void operator- ( Fraction &p) ; void operator* ( Fraction &p) ; void operator/ ( Fraction &p) ; void compare(Fraction &p); void reduction(); void show(); private: int top; int bottom; }; #endif //FRACTION_H
fraction.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"fraction.h" using namespace std; Fraction::Fraction(int a, int b) :top(a), bottom(b) { } void Fraction::compare(Fraction &p) { if (p.top>top) { cout << "前者<后者" << endl; } else if (p.top <= top) { cout << "前者>=后者" << endl; } } void Fraction::reduction() { int a; if (top%bottom == 0) a = bottom; else if (bottom%top == 0) a = top; else for (int i = 1; i<(bottom / 2) && i<(top / 2); i++) { if (bottom%i == 0 && top%i == 0) a = i; } top /= a; bottom /= a; } void Fraction::show() { cout << "结果:" << top << "/" << bottom << endl; } void Fraction::operator+ (Fraction &p) { int b1 = bottom, b2 = p.bottom; top = top * b2; bottom = bottom * b2; p.top = p.top*b1; p.bottom = p.bottom*b1; top = top + p.top; } void Fraction::operator-(Fraction &p) { int b1 = bottom, b2 = p.bottom; top = top * b2; bottom = bottom * b2; p.top = p.top*b1; p.bottom = p.bottom*b1; top = top - p.top; } void Fraction::operator*(Fraction &p) { top = top * p.top; bottom = bottom * p.bottom; } void Fraction::operator/(Fraction &p) { top = top * p.bottom; bottom = bottom * p.top; }
ifraction.h
#include"fraction.h" class iFraction :public Fraction { public: iFraction(int a = 0, int b = 1); void ishow(); private: int top, bottom, side=0; };
ifraction.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"ifraction.h" using namespace std; iFraction::iFraction(int a, int b) :top(a),bottom(b){ while (top > bottom) { top = top - bottom; side = side + 1; } } void iFraction::ishow() { cout << side << " " << top << "/" << bottom << endl; }
main.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"fraction.h" #include"ifraction.h" using namespace std; int main() { int m, n, x, y; cout << "分数1:"; cin >> m >> n; Fraction a(m, n); a.show(); cout << "分数2:"; cin >> x >> y; Fraction b(x, y); b.show(); a.compare(b); char input; cout << "输入+ - * /:"; cin >> input; switch (input) { case '+': a + b; break; case '-' : a - b; break; case '*' : a * b; break; case '/' : a / b; break; default :return 0; } a.reduction(); a.show(); iFraction i(5, 3); cout << "ifraction分数为:" << "5/3" << endl << " -> "; i.ishow(); if (cin >> input); return 0; }
运行截图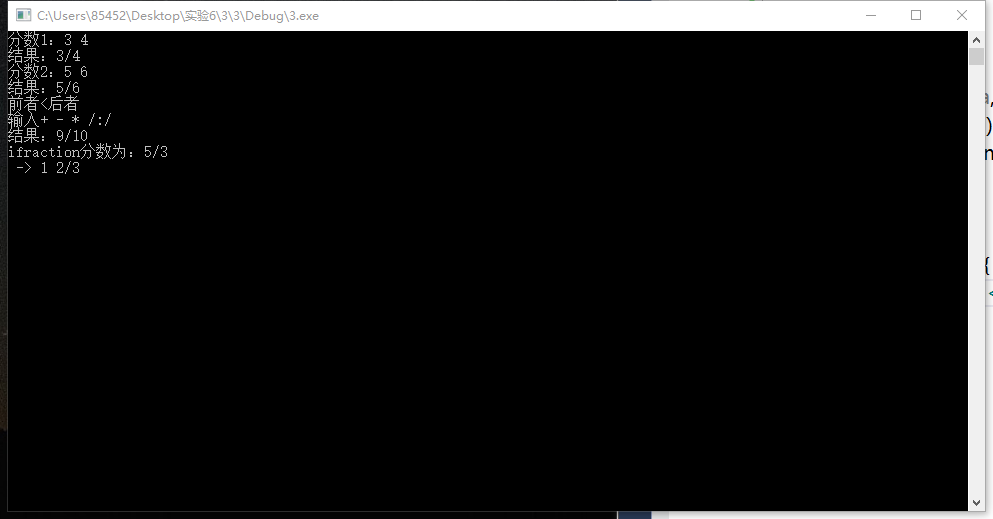



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号