Sentinel源码分析二 之 流控算法-滑动时间窗口
记录Sentinel中使用的滑动时间窗口之前,先说明下简单的滑动时间窗口是怎样的。
对于限流的算法假如时间窗口不滑动,限流qps 100。如果在0.5~1s之间发生了80个请求量,会认为在0~1s内qps是不会达到限流阈值的。在1~1.5s内达到80的请求量,也会认为在1-2s内的qps为80没有达到阈值。
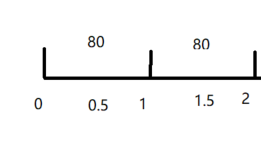 但是在0.5~1.5秒的请求量却达到160已经超过了阈值。这就出现了问题。
但是在0.5~1.5秒的请求量却达到160已经超过了阈值。这就出现了问题。
有了滑动时间时间窗口之后的统计变成下面的样子。把1s分成四个bucket,每个是250ms间隔。
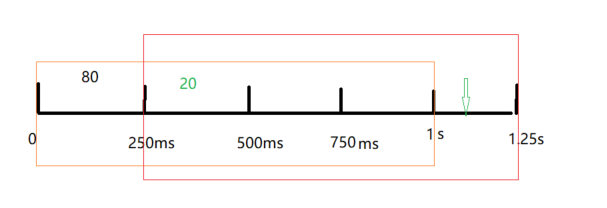
假如750ms~1s之间,来了一个请求,统计当前bucket和前面三个bucket中的请求量总和101,大于阈值,就会把当前这个请求进行限流。
假如1s~1.25s之间,来了一个请求,统计当前bucket和前面三个bucket中的请求量总和21,小于阈值,就会正常放行。这里请求总量统计去掉了0~250ms之间的bucket,就是体现了时间窗口的滑动。
但是这里需要注意的一点,时间滑动时间窗口的统计也不是百分百精准的,比如上图中在绿色箭头的地方来了一个请求之后,统计的bucket是250ms 到绿色箭头之间的bucket,但是这个时间区间并没有1s,
因为去掉了0~250ms的bucket统计,所以可能出现偏差,当然这个bucket区间细分的越小就越精准。
下面分析Sentinel中怎么利用滑动时间窗口进行流控的。
Metric :是一个记录保护资源的调用指标的基础结构。里面规定了被保护的资源有那些调用指标需要被统计。看一些关键指标。

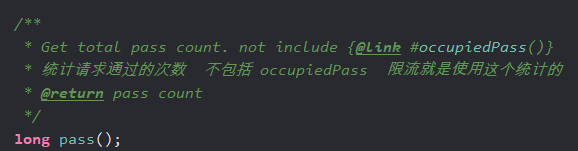
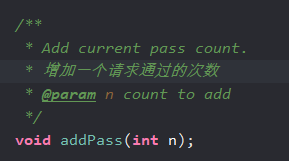
源码:

public interface Metric extends DebugSupport { /** * Get total success count. * 统计所有成功的次数 * @return success count */ long success(); /** * Get max success count. * * @return max success count */ long maxSuccess(); /** * Get total exception count. * 统计所有异常的次数 * @return exception count */ long exception(); /** * Get total block count. * * @return block count */ long block(); /** * Get total pass count. not include {@link #occupiedPass()} * 统计请求通过的次数 不包括 occupiedPass 限流就是使用这个统计的 * @return pass count */ long pass(); /** * Get total response time. * * @return total RT */ long rt(); /** * Get the minimal RT. * * @return minimal RT */ long minRt(); /** * Get aggregated metric nodes of all resources. * * @return metric node list of all resources */ List<MetricNode> details(); /** * Generate aggregated metric items that satisfies the time predicate. * * @param timePredicate time predicate * @return aggregated metric items * @since 1.7.0 */ List<MetricNode> detailsOnCondition(Predicate<Long> timePredicate); /** * Get the raw window array. * * @return window metric array */ MetricBucket[] windows(); /** * Add current exception count. * * @param n count to add */ void addException(int n); /** * Add current block count. * * @param n count to add */ void addBlock(int n); /** * Add current completed count. * * @param n count to add */ void addSuccess(int n); /** * Add current pass count. * 增加一个请求通过的次数 * @param n count to add */ void addPass(int n); /** * Add given RT to current total RT. * * @param rt RT */ void addRT(long rt); /** * Get the sliding window length in seconds. * * @return the sliding window length */ double getWindowIntervalInSec(); /** * Get sample count of the sliding window. * * @return sample count of the sliding window. */ int getSampleCount(); /** * Note: this operation will not perform refreshing, so will not generate new buckets. * * @param timeMillis valid time in ms * @return pass count of the bucket exactly associated to provided timestamp, or 0 if the timestamp is invalid * @since 1.5.0 */ long getWindowPass(long timeMillis); // Occupy-based (@since 1.5.0) /** * Add occupied pass, which represents pass requests that borrow the latter windows' token. * * @param acquireCount tokens count. * @since 1.5.0 */ void addOccupiedPass(int acquireCount); /** * Add request that occupied. * * @param futureTime future timestamp that the acquireCount should be added on. * @param acquireCount tokens count. * @since 1.5.0 */ void addWaiting(long futureTime, int acquireCount); /** * Get waiting pass account * * @return waiting pass count * @since 1.5.0 */ long waiting(); /** * Get occupied pass count. * * @return occupied pass count * @since 1.5.0 */ long occupiedPass(); // Tool methods. long previousWindowBlock(); long previousWindowPass(); }
ArrayMetric 是上面接口的一个实现类。它维护了一个局部变量 LeapArray<MetricBucket> data 来具体计算被保护资源的调用指标.
部分源码如下:
public class ArrayMetric implements Metric { // 滑动时间窗口算法的实现 private final LeapArray<MetricBucket> data; public ArrayMetric(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
// 使用的这个具体类,sampleCount :时间窗口的bucket数量 默认 2个, intervalInMs: 时间窗口的时间间隔 默认 1000ms 也就是每个bucket是500ms this.data = new OccupiableBucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs); } @Override public long pass() {
// 更新最新的时间窗口 data.currentWindow(); long pass = 0;
// 得到所有的统计窗口 List<MetricBucket> list = data.values(); // 每个窗口中的统计量累加起来 for (MetricBucket window : list) { pass += window.pass(); } return pass; } @Override public void addPass(int count) {
// 向当前时间窗口中增加一个请求数量 这个方法会在StatisticSlot 统计qps的时候使用到
// 时间窗口每个bucket都被WindowWrap包装了下,而且一个MetricBucket 里面可以统计好多维度的数据,使用MetricEvent区分的。 WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow(); wrap.value().addPass(count); } public void add(MetricEvent event, long count) { data.currentWindow().value().add(event, count); } @Override public double getWindowIntervalInSec() { return data.getIntervalInSecond(); } @Override public int getSampleCount() { return data.getSampleCount(); } }
LeapArray:
public abstract class LeapArray<T> {
// 滑动时间窗口每个bucket的时间长度 protected int windowLengthInMs;
// 滑动时间窗口 一共有多少个bucket protected int sampleCount;
// 滑动时间窗口 总的时间窗口 单位 毫秒 protected int intervalInMs;
// 滑动时间窗口 总的时间窗口 单位 秒 private double intervalInSecond;
// 每个时间窗口bucket 的存储实例WindowWrap array 就相当于是整个滑动时间窗口 protected final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>> array; /** * The conditional (predicate) update lock is used only when current bucket is deprecated.
更新滑动时间窗口的时候使用 */ private final ReentrantLock updateLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** * The total bucket count is: {@code sampleCount = intervalInMs / windowLengthInMs}. * * @param sampleCount bucket count of the sliding window * @param intervalInMs the total time interval of this {@link LeapArray} in milliseconds */ public LeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) { AssertUtil.isTrue(sampleCount > 0, "bucket count is invalid: " + sampleCount); AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs > 0, "total time interval of the sliding window should be positive"); AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs % sampleCount == 0, "time span needs to be evenly divided"); this.windowLengthInMs = intervalInMs / sampleCount; this.intervalInMs = intervalInMs; this.intervalInSecond = intervalInMs / 1000.0; this.sampleCount = sampleCount; this.array = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(sampleCount); } /** * Get the bucket at current timestamp. * 计算当前时间的bucket实例 每次请求过来都会计算处于那个bucket位置 * @return the bucket at current timestamp */ public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow() {
return currentWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } /** * Create a new statistic value for bucket. * * @param timeMillis current time in milliseconds * @return the new empty bucket */ public abstract T newEmptyBucket(long timeMillis); /** * Reset given bucket to provided start time and reset the value. * * @param startTime the start time of the bucket in milliseconds * @param windowWrap current bucket * @return new clean bucket at given start time */ protected abstract WindowWrap<T> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<T> windowWrap, long startTime);
// 计算当前时间处于滑动时间窗口数组中的索引位置 private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) { long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs; // Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array. return (int)(timeId % array.length()); } // 计算时间窗口bucket的起始时间 protected long calculateWindowStart(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) { return timeMillis - timeMillis % windowLengthInMs; } /** * Get bucket item at provided timestamp. * * @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds * @return current bucket item at provided timestamp if the time is valid; null if time is invalid */ public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) { if (timeMillis < 0) { return null; } // 计算当前时间 在滑动时间窗口array中的索引位置 int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis); // Calculate current bucket start time.
// 计算当前时间在时间窗口bucket中的开始时间
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis); /* * Get bucket item at given time from the array. * * (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array. * (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket. * (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket and clean all deprecated buckets. */ while (true) {
// 根据当前时间计算的bucket 索引值 在array的数据 WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx); if (old == null) { /* * B0 B1 B2 NULL B4 * ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp * ^ * time=888 * bucket is empty, so create new and update * * If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart}, * then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can * succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice.
这个图解就很好理解了,比如当前时间计算的bucket 所在的位置在上面的800~1000之间的时候,array是空的,就新建一个时间窗口bucket WindowWrap
通过cas更新到array中 如果cas失败了就让出时间片 */ WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis)); if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) { // Successfully updated, return the created bucket. return window; } else { // Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available. Thread.yield(); } } else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
/* * B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 * ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp * ^ * time=888 * startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date * * If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket, * that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.
如果当前时间计算出来的索引位置已经有了WindowWrap bucket 而且存在的bucket的开始时间和当前计算的开始相等,就返回已经存在的这个WindowWrap
在StatisticSlot增加请求数量的时候就会使用这个bucket 中的请求数量进行累加 */ return old; } else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) { /* * (old) * B0 B1 B2 NULL B4 * |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp * ^ * time=1676 * startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset * * If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means * the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}. * Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic, * so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update. * * The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when * bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss.
这个时候就表明 时间窗口要向前滑动了 就是把存在的时间窗口内容进行重置 重置包括开始时间更新 窗口内的计数清零
使用加锁操作 */ if (updateLock.tryLock()) { try { // Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.
// 具体逻辑在的子类 OccuiableBucketLeapArray中
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart); } finally { updateLock.unlock(); } } else { // Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available. Thread.yield(); } } else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) { // Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind. return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis)); } } } public List<T> values() { return values(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } public List<T> values(long timeMillis) {
// 把当前时间窗口中的bucket WindowWrap 都返回出去 用来统计时间窗口总的请求数量 if (timeMillis < 0) { return new ArrayList<T>(); } int size = array.length(); List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i); if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)) { continue; } result.add(windowWrap.value()); } return result; }
上面滑动时间窗口用了WindowWrap 来表示bucket,但是这个类里又包了一个泛型,使用泛型的目的是为了让这个bucket 可以统计更多类型的数据。比如上面的泛型是MetricBucket。
WindowWrap :
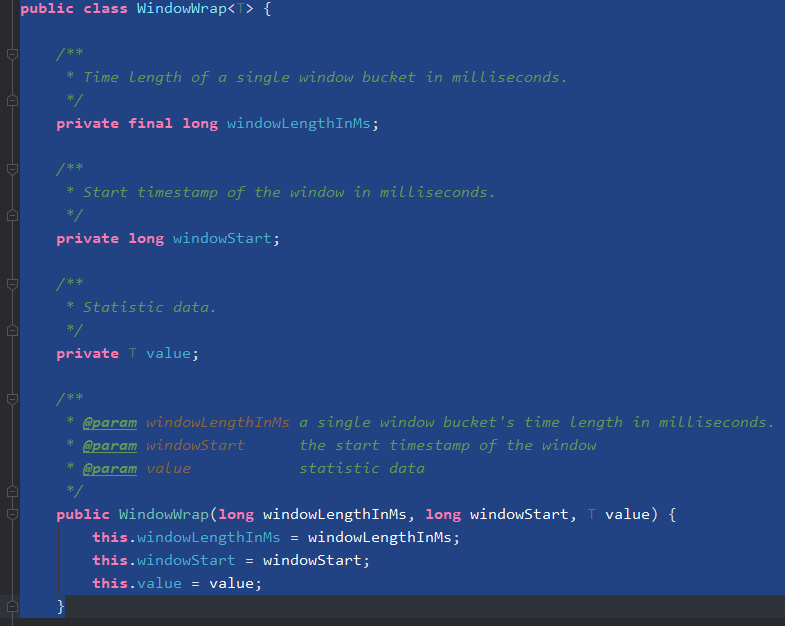
MetricBucket:

public class MetricBucket { // 可以存储自己想统计的数据维度 LongAdder是比Atomic类性能更高的类 private final LongAdder[] counters; private volatile long minRt; public MetricBucket() { // 用一个枚举值来记录想统计的数据维度 MetricEvent[] events = MetricEvent.values(); this.counters = new LongAdder[events.length]; for (MetricEvent event : events) { // 数据中不同的位置表示不同的数据维度 counters[event.ordinal()] = new LongAdder(); } initMinRt(); } public MetricBucket reset(MetricBucket bucket) { for (MetricEvent event : MetricEvent.values()) { counters[event.ordinal()].reset(); counters[event.ordinal()].add(bucket.get(event)); } initMinRt(); return this; } private void initMinRt() { this.minRt = SentinelConfig.statisticMaxRt(); } /** * Reset the adders. * * @return new metric bucket in initial state */ public MetricBucket reset() { for (MetricEvent event : MetricEvent.values()) { counters[event.ordinal()].reset(); } initMinRt(); return this; } public long get(MetricEvent event) { return counters[event.ordinal()].sum(); } public MetricBucket add(MetricEvent event, long n) { counters[event.ordinal()].add(n); return this; } public long pass() { return get(MetricEvent.PASS); } public long occupiedPass() { return get(MetricEvent.OCCUPIED_PASS); } public long block() { return get(MetricEvent.BLOCK); } public long exception() { return get(MetricEvent.EXCEPTION); } public long rt() { return get(MetricEvent.RT); } public long minRt() { return minRt; } public long success() { return get(MetricEvent.SUCCESS); } public void addPass(int n) { add(MetricEvent.PASS, n); } public void addOccupiedPass(int n) { add(MetricEvent.OCCUPIED_PASS, n); } public void addException(int n) { add(MetricEvent.EXCEPTION, n); } public void addBlock(int n) { add(MetricEvent.BLOCK, n); } public void addSuccess(int n) { add(MetricEvent.SUCCESS, n); } public void addRT(long rt) { add(MetricEvent.RT, rt); // Not thread-safe, but it's okay. if (rt < minRt) { minRt = rt; } } @Override public String toString() { return "p: " + pass() + ", b: " + block() + ", w: " + occupiedPass(); } }
统计的维度枚举类:MetricEvent
public enum MetricEvent { /** * Normal pass. */ PASS, /** * Normal block. */ BLOCK, EXCEPTION, SUCCESS, RT, /** * Passed in future quota (pre-occupied, since 1.5.0). */ OCCUPIED_PASS }
Sentinel中 qps的统计和限流控制主要是在StatisticSlot,FlowSlot里面完成的。

先执行StatisticSlot的entry. fireEntry就是执行下一个slot的。从这里看出,在正向执行的时候它并没有处理什么内容。但是在下面责任链上的entry方法执行完后。
调用了node.increaseThreadNum(); node.addPassRequest(count); 这里就是统计请求通过的线程数量和请求数量。
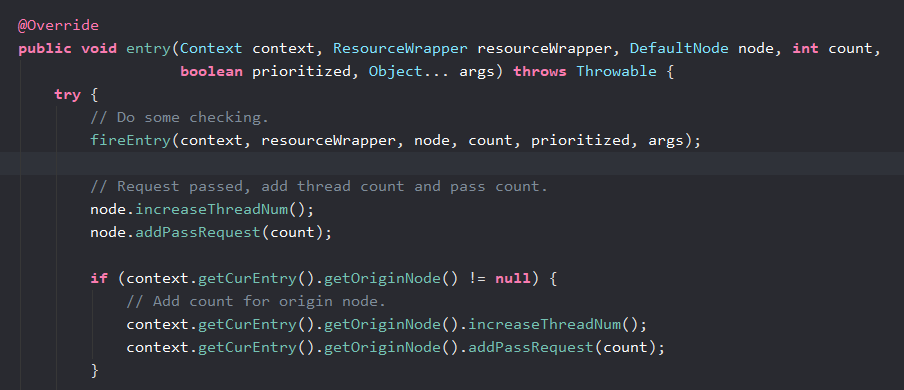
我们这里跟踪下node.addPassRequest(count); 用到了时间滑动窗口。node是DefaultNode实例。
DefaultNode#addPassRequest(count)
@Override public void addPassRequest(int count) {
//调用父类 StatisticNode super.addPassRequest(count);
// 集群模式下使用的 this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count); }
这里看单机限流模式,跟随StatisticNode#addPassRequest(count);
@Override public void addPassRequest(int count) {
// 秒级别的滑动时间窗口 看这个就可以了 rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);
// 分钟级别的滑动时间窗口 rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(count); }
秒级别的滑动时间窗口:
// 两个参数分别是:2 1000 这里就是构建了一个时间滑动窗口长度 1s,分了两个bucket,一个bucket长度是500ms
private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT, IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
ArrayMetric的部分源码上面有贴出来。
rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count); 这个是调用下面这端逻辑。
@Override public void addPass(int count) {
// 首先获取当前时间的时间窗口,然后向窗口中增加请求量。 // 向当前时间窗口中增加一个请求数量 这个方法会在StatisticSlot 统计qps的时候使用到 // 时间窗口每个bucket都被WindowWrap包装了下,而且一个MetricBucket 里面可以统计好多维度的数据,使用MetricEvent区分的。 WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow(); wrap.value().addPass(count); }data.currentWindow();
data.currentWindow()会调用到LeapArray#currentWindow(long timeMills);的方法上面源码也有分析。
得到窗口之后 wrap.value().addPass(count); 会调用MetricBucket#appPass(int n); 方法
public void addPass(int n) {
// 时间窗口bucket 中也是有一个 LongAdder[] counter来存储计数统计的,因为可以统计不同维度的数据,比如这里就是统计PASS的数量 add(MetricEvent.PASS, n); }
至于为什么使用LongAdder,因为它的效率比Atomic类的性能更好些。至于为什么就不说了这里。
public MetricBucket add(MetricEvent event, long n) {
// event.ordinal() 就是获取枚举值在枚举类中的位置,就是索引值 这个操作是cas的 性能更好些。 counters[event.ordinal()].add(n); return this; }
上面分析的就是StatisticSlot 统计qps的过程。
下面看下FlowSlot中怎么做流控限制的。
FlowSlot#entry中
@Override public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 根据配置的限流规则进行校验 checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized); fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); }
FlowSlot#checkFlow
void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {
// checker 是 FlowRuleChecker checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized); }
FlowRuleChecker#checkFlow
public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException { if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) { return; } Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName()); if (rules != null) { for (FlowRule rule : rules) {
// 开始调用配置的限流规则
if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) { throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule); } } } }
private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node); if (selectedNode == null) { return true; } // 不同的流控效果,对应不同的rater 这里主要看快速失败DefaultController return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized); }
流控效果分为下面三种。分别对应:DefaultController,WarmUpController,RateLimiterController
![]()
DefaultController@canPass
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {
// 计算时间窗口内已经通过的请求数量 int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
// acquireCount一般就是 1 ,count就是配置的单机阈值 如果条件满足就是达到阈值 直接返回false if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {
// prioritized 默认是false if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) { long currentTime; long waitInMs; currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count); if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) { node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount); node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount); sleep(waitInMs); // PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}. throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs); } } return false; } return true; }
如果通过,说明没有达到阈值,然后走到StatisticSlot逻辑的时候进行addPass。这样整个流程就串起来了。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
2021-05-10 web项目使用maven插件直接本地启动