Mybatis源码分析(二)Mybatis执行流程全流程跟踪
使用Mybatis
1:全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 指定数据库的配置文件 --> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!-- <mapper class="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HRMapper"></mapper>--> <mapper resource="./mapper/hr.xml"></mapper> </mappers> </configuration>
2:mapper的xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HRMapper"> <select id="selectBlog" resultType="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HR"> select name,phone,address,enabled from hr where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
测试 主代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) { HRMapper mapper = session.getMapper(HRMapper.class); List<HR> hrs = mapper.selectBlog(3L); System.out.println(hrs.get(0).getName()); } }
这样Mybatis就可以正常运行了。先来介绍下Mybatis中关键的一些概念,再看源码:
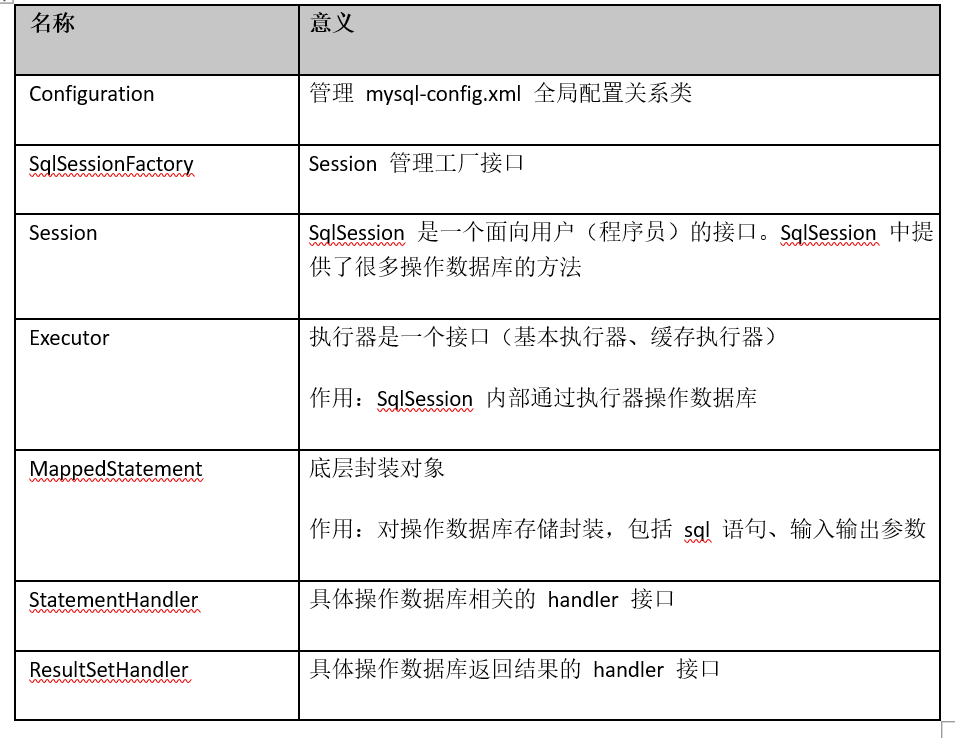
Configuration 、 SqlSessionFactory 、 Session 、 Executor 、 MappedStatement 、StatementHandler、ResultSetHandler
上面的第一步,就是根据全局配置文件,构建一个SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build
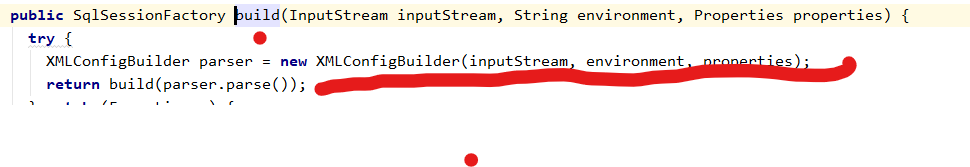
XMLConfigBuilder#parse() 就是根据全局的配置文件生成一个Configuration对象。这个对象就对应全局配置文件中的<configuration></configuration>节点,它里面有对应xml中的不同节点的对象。
public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; // 解析全局的配置文件 configuration节点 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
解析每个xml中的节点:
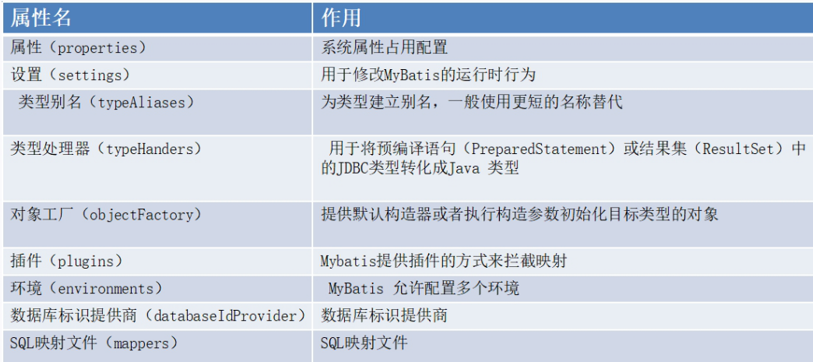
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { // issue #117 read properties first // 每一个子节点的处理,对应一个方法 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); loadCustomVfs(settings); loadCustomLogImpl(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 // 数据库信息 占位符的的填充是在构建XNode的时候设置的 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); // 解析mapper映射 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
build方法返回的是DefaultSqlSessionFactory里面保留这Configuration,DefaultSqlSessionFactory是维护sqlSession的。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
构建完DefaultSqlSessionFactory,回到主流程中,就要openSession了。
DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSession()
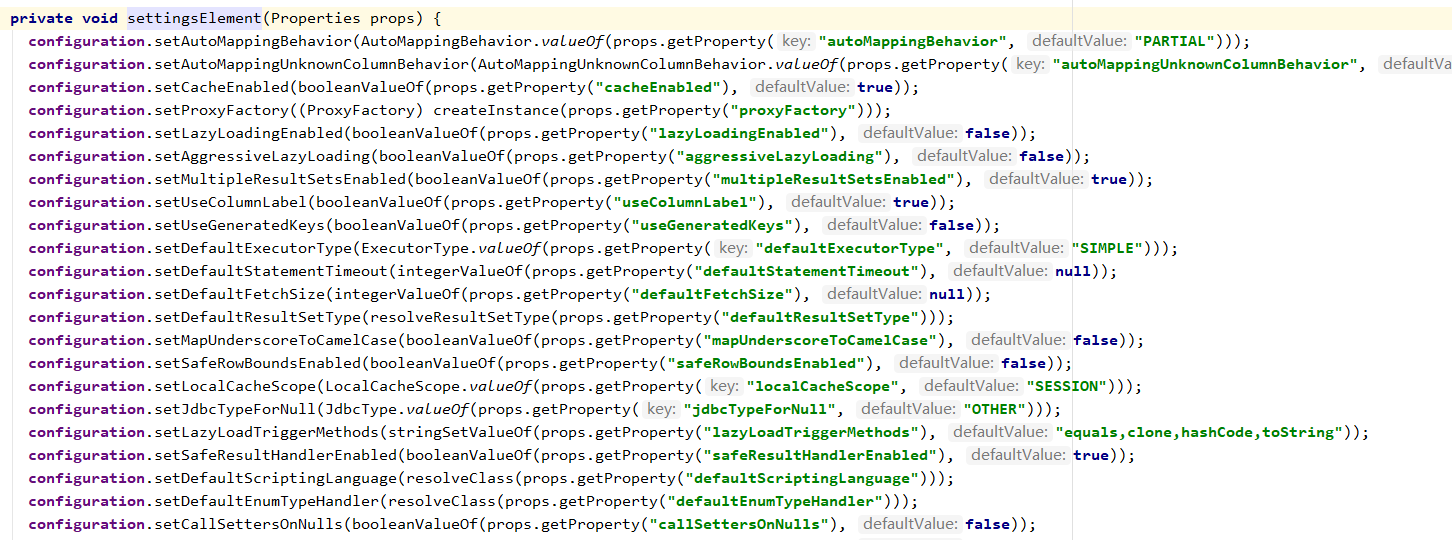
public SqlSession openSession() { // 默认的执行器类型 ExecutorType.SIMPLE,一共有三种类型,在全局配置中可以通过: // <settings> // <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="BATCH"/> // </settings> // 设置,configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(type) 是在parseConfiguration 的时候解析settings的时候设置的, // 从解析settings源码可以看出,可以设置很多属性 return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
下面的属性都可以进行设置
至于三种执行器类型:有什么区别,后面代码用到的时候再说明
public enum ExecutorType { SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH }
创建一个sqlSession
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { // 获取全局配置文件设置的属性 封装成的 Environment final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 如果全局配置文件中没有设置事务工厂 默认ManagedTransactionFactory final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 执行器 mybatis中有三种 默认ExecutorType.SIMPLE final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); // sqlSession是联系全局配置文件到数据库执行的桥梁,看到sqlSession里面持有了 configuration executor autoCommit:默认为false return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
上面我们看到重要的sqlSession是怎么创建出来的,我们看到里面都有什么方法: DefaultSqlSession 实现了接口SqlSession,里面都是一些select查询的方法

里面还有一个重要的方法: <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type); 在主流程里使用了:
HRMapper mapper = session.getMapper(HRMapper.class);
看下在DefaultSqlSession#getMapper中是怎样的
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { // Configuration中维护了一个MapperRegistry 通过它返回 HRMapper的一个动态代理 return configuration.getMapper(type, this); }
在Configuration中
MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); }
MapperRegistry
------------恢复内容结束------------
------------恢复内容开始------------
使用Mybatis
1:全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 指定数据库的配置文件 --> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!-- <mapper class="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HRMapper"></mapper>--> <mapper resource="./mapper/hr.xml"></mapper> </mappers> </configuration>
2:mapper的xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HRMapper"> <select id="selectBlog" resultType="org.apache.ibatis.demo.HR"> select name,phone,address,enabled from hr where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
测试 主代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) { HRMapper mapper = session.getMapper(HRMapper.class); List<HR> hrs = mapper.selectBlog(3L); System.out.println(hrs.get(0).getName()); } }
这样Mybatis就可以正常运行了。先来介绍下Mybatis中关键的一些概念,再看源码:
Configuration 、 SqlSessionFactory 、 Session 、 Executor 、 MappedStatement 、StatementHandler、ResultSetHandler


上面的第一步,就是根据全局配置文件,构建一个SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build

XMLConfigBuilder#parse() 就是根据全局的配置文件生成一个Configuration对象。这个对象就对应全局配置文件中的<configuration></configuration>节点,它里面有对应xml中的不同节点的对象。
public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; // 解析全局的配置文件 configuration节点 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
解析每个xml中的节点:
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { // issue #117 read properties first // 每一个子节点的处理,对应一个方法 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); loadCustomVfs(settings); loadCustomLogImpl(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 // 数据库信息 占位符的的填充是在构建XNode的时候设置的 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); // 解析mapper映射 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
build方法返回的是DefaultSqlSessionFactory里面保留这Configuration,DefaultSqlSessionFactory是维护sqlSession的。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
构建完DefaultSqlSessionFactory,回到主流程中,就要openSession了。
DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSession()
public SqlSession openSession() { // 默认的执行器类型 ExecutorType.SIMPLE,一共有三种类型,在全局配置中可以通过: // <settings> // <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="BATCH"/> // </settings> // 设置,configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(type) 是在parseConfiguration 的时候解析settings的时候设置的, // 从解析settings源码可以看出,可以设置很多属性 return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
下面的属性都可以进行设置

至于三种执行器类型:有什么区别,后面代码用到的时候再说明
public enum ExecutorType { SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH }
创建一个sqlSession
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { // 获取全局配置文件设置的属性 封装成的 Environment final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 如果全局配置文件中没有设置事务工厂 默认ManagedTransactionFactory final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 执行器 mybatis中有三种 默认ExecutorType.SIMPLE final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); // sqlSession是联系全局配置文件到数据库执行的桥梁,看到sqlSession里面持有了 configuration executor autoCommit:默认为false return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
上面我们看到重要的sqlSession是怎么创建出来的,我们看到里面都有什么方法: DefaultSqlSession 实现了接口SqlSession,里面都是一些select查询的方法

里面还有一个重要的方法: <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type); 在主流程里使用了:
HRMapper mapper = session.getMapper(HRMapper.class);
看下在DefaultSqlSession#getMapper中是怎样的
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { // Configuration中维护了一个MapperRegistry 通过它返回 HRMapper的一个动态代理 return configuration.getMapper(type, this); }
在Configuration中
MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); }
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { // 使用动态代理 返回一个代理对象 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }
MapperProxyFactory是在全局配置解析mapper的时候调用如下方法放入的 :type是mapper中class属性,或者resource配置的xml中的namespace的类
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); // It's important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try. MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } }
MapperProxyFactory中newInstance 创建一个以MapperProxy为代理逻辑的动态代理。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() { return methodCache; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }
MapperProxy 实现了 InvocationHandler,在执行mapper的方法时候执行invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { // 如果是Object中的方法 就直接执行本身的方法 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else { return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } }
里面又调用 cachedInvoker(method)得到一个 MapperMethodInvoker,默认会是 PlainMethodInvoker 它维护了一个MapperMethod,一个MapperMethod维护了mapper接口,将要调用的方法,还有全局配置Configuration
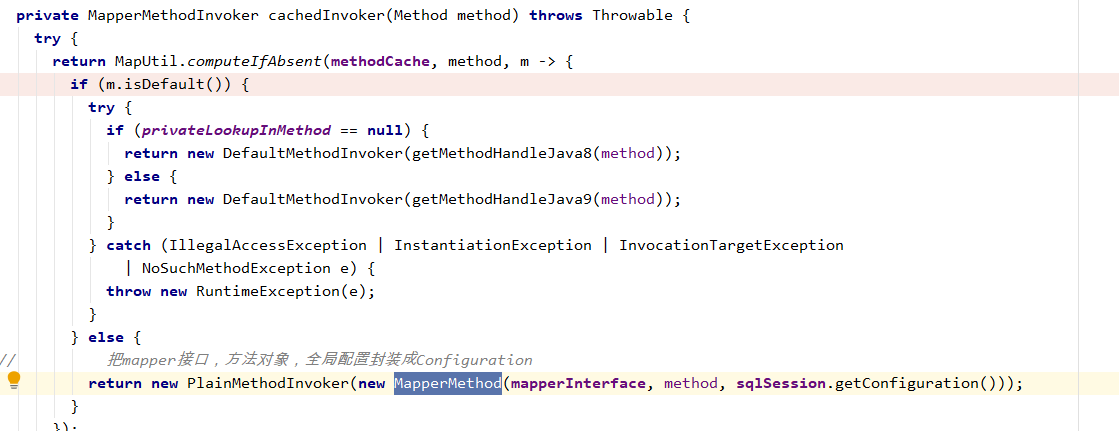
MapperMethod的构造函数中又维护了SqlCommand,MethodSignature两个对象。SqlCommand维护了当前调用的方法sql。
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) { final String methodName = method.getName(); final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass, configuration); if (ms == null) { if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) { name = null; type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH; } else { throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): " + mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName); } } else { name = ms.getId(); type = ms.getSqlCommandType(); if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) { throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name); } } }
回到PlainMethodInvoker#invoke中
调用的是MapperMethod中的execute方法。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable { return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); }
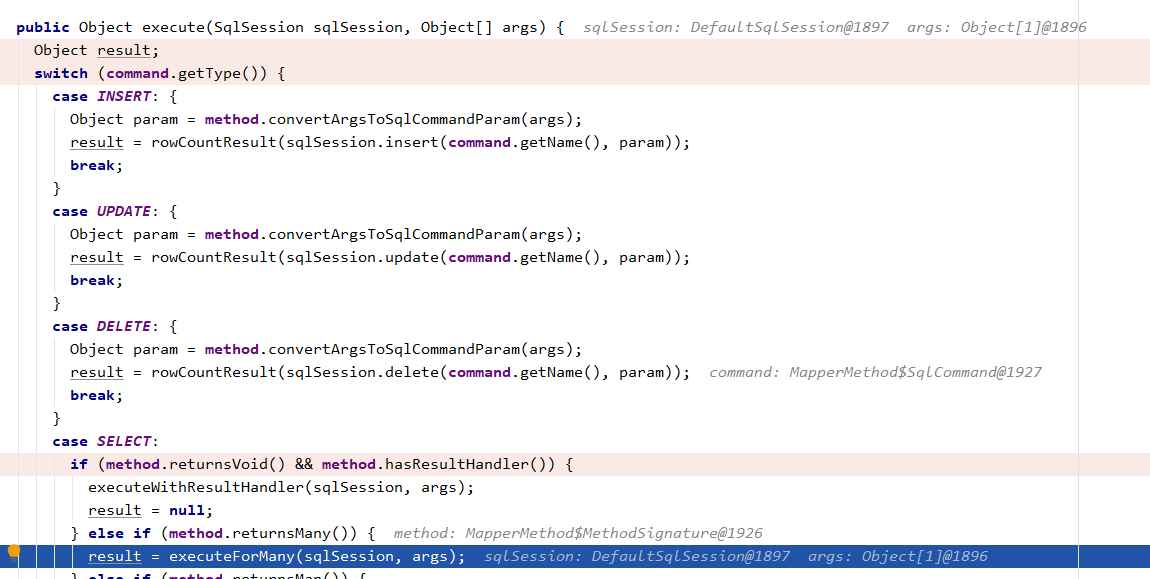
执行的时候会根据SqlCommand保存的类型,判断是哪一种
最后走到了SqlSession中的selectList方法
DefaultSqlSession#selectList
在这里把保存的 MappedStatement获取出来之后,交给了Eexecutor执行,它的实现类在configuration.getEnvironment中设置的。真正sql的执行者
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
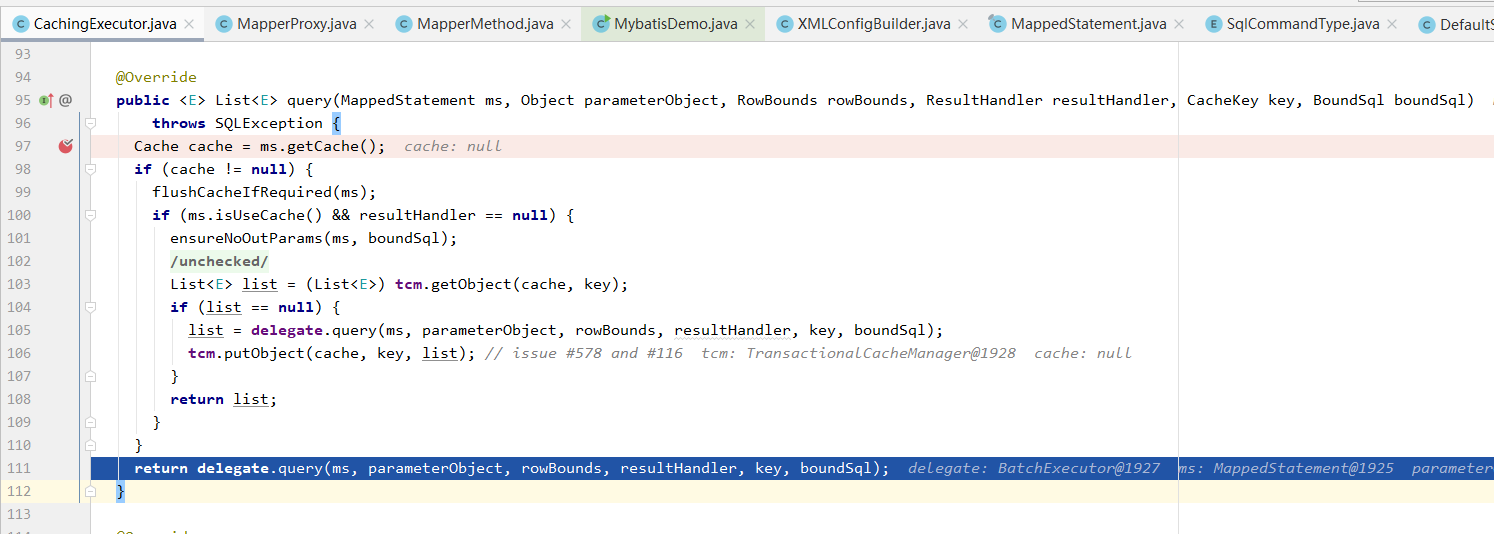
CachingExecutor#query
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 绑定的sql BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); // 缓存结果时候用到的key CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
这里用到了装饰器模式,我们看到走到的Executor是CachingExecutor,它就是一个装饰者,装饰其它Executor的实现类,比如SimpleExecutor,BatchExecutor,让他们不仅具有执行sql的功能还有缓存的功能。
delegate就是被装饰的对象BatchExecutor,它继承了BaseExecutor,这个query是在父类中的方法
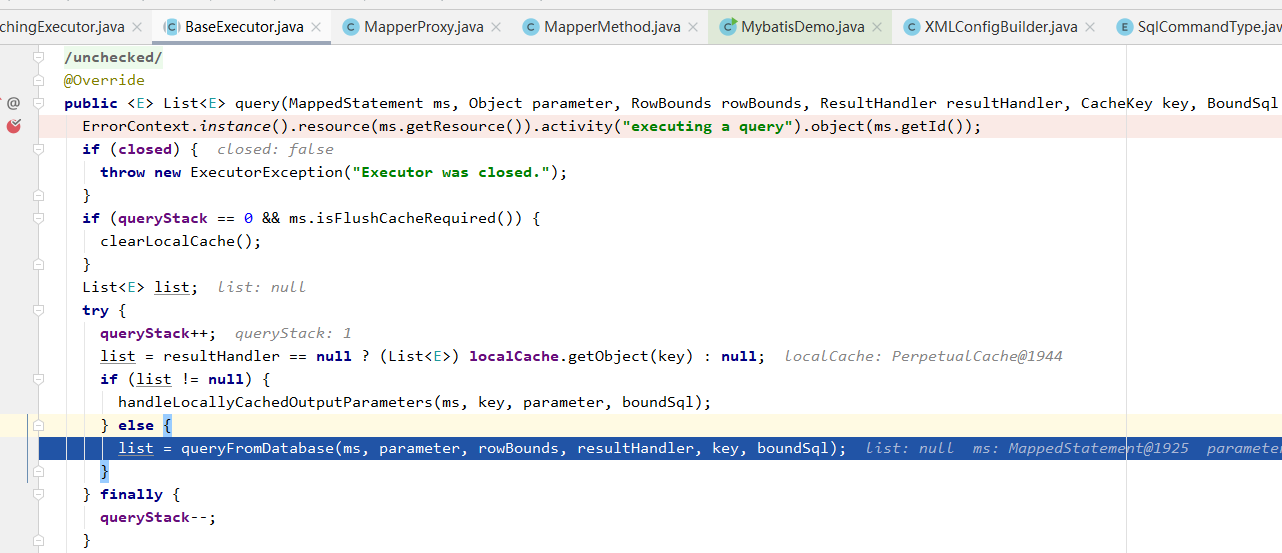
queryFromDatabase
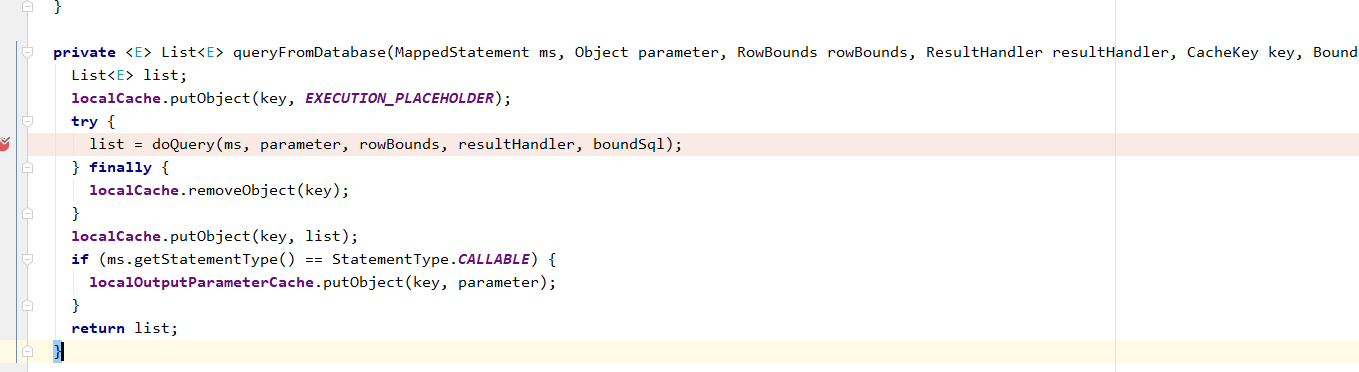
到doQuery这一步才走到子类BatchExecutor中
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { flushStatements(); Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog()); // StatementHandler 用到策略模式,这种模式可以动态的让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为,而装饰器模式有增强被装饰者的功能 具体看CachingExecutor stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
用到的StatementHandler 实现类,RoutingStatementHandler,它是使用了某种策略的类,我们看到它的构造方法中根据参数分了很多类。

现在走到的delegate是PreparedStatementHandler

prepare在父类BaseStatementHandler中
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try {// 这个调用子类的方法 statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } }
PreparedStatementHandler#instantiateStatement 准备的就是jdbc中的Statement了
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } }
回到BatchExecutor#doQuery中
handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); 准备了Statement
handler.parameterize(stmt); 设置参数
handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); 真正执行并返回结果
PreparedStatementHandler#query
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; // jdbc中的执行 ps.execute(); // 结果的处理交给了 DefaultResultSetHandler return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); }
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId()); final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>(); int resultSetCount = 0; ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt); List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps(); int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size(); validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount); while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) { ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount); handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null); rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); resultSetCount++; } String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets(); if (resultSets != null) { while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) { ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]); if (parentMapping != null) { String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId(); ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId); handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping); } rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); resultSetCount++; } } return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults); }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现