C# 最基础知识介绍(五)——方法、封装、继承、多态
C# 最基础知识介绍(五)——方法、封装、继承、多态
前言👻
有个名词叫 "OOP思想" —— " 面向对象编程"(Object Oriented Programming,OOP,面向对象程序设计)是一种计算机编程架构。OOP 的一条基本原则是计算机程序是由单个能够起到子程序作用的单元或对象组合而成。OOP 达到了软件工程的三个主要目标:重用性、灵活性和扩展性。为了实现整体运算,每个对象都能够接收信息、处理数据和向其它对象发送信息
核心思想:封装,继承,多态.
方法❄️
一个方法是把一些相关的语句组织在一起,用来执行一个任务的语句块。每一个 C# 程序至少有一个带有 Main 方法的类。
要使用一个方法,您需要:
- 定义方法
- 调用方法
C# 中定义方法
当定义一个方法时,从根本上说是在声明它的结构的元素。在 C# 中,定义方法的语法如下:
1 <Access Specifier> <Return Type> <Method Name>(Parameter List) 2 { 3 Method Body 4 }
下面是方法的各个元素:
- Access Specifier:访问修饰符,这个决定了变量或方法对于另一个类的可见性。
- Return type:返回类型,一个方法可以返回一个值。返回类型是方法返回的值的数据类型。如果方法不返回任何值,则返回类型为 void。
- Method name:方法名称,是一个唯一的标识符,且是大小写敏感的。它不能与类中声明的其他标识符相同。
- Parameter
- list:参数列表,使用圆括号括起来,该参数是用来传递和接收方法的数据。参数列表是指方法的参数类型、顺序和数量。参数是可选的,也就是说,一个方法可能不包含参数。
- Method body:方法主体,包含了完成任务所需的指令集。
实例
下面的代码片段显示一个函数 FindMax,它接受两个整数值,并返回两个中的较大值。它有 public 访问修饰符,所以它可以使用类的实例从类的外部进行访问。
1 实例 2 class NumberManipulator 3 { 4 public int FindMax(int num1, int num2) 5 { 6 /* 局部变量声明 */ 7 int result; 8 9 if (num1 > num2) 10 result = num1; 11 else 12 result = num2; 13 14 return result; 15 } 16 }
C# 中调用方法
您可以使用方法名调用方法。下面的实例演示了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace CalculatorApplication 5 { 6 class NumberManipulator 7 { 8 public int FindMax(int num1, int num2) 9 { 10 /* 局部变量声明 */ 11 int result; 12 13 if (num1 > num2) 14 result = num1; 15 else 16 result = num2; 17 18 return result; 19 } 20 static void Main(string[] args) 21 { 22 /* 局部变量定义 */ 23 int a = 100; 24 int b = 200; 25 int ret; 26 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 27 28 //调用 FindMax 方法 29 ret = n.FindMax(a, b); 30 Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret ); 31 Console.ReadLine(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
最大值是: 200
也可以使用类的实例从另一个类中调用其他类的公有方法。例如,方法 FindMax 属于 NumberManipulator 类,可以从另一个类 Test 中调用它。
1 using System; 2 3 namespace CalculatorApplication 4 { 5 class NumberManipulator 6 { 7 public int FindMax(int num1, int num2) 8 { 9 /* 局部变量声明 */ 10 int result; 11 12 if (num1 > num2) 13 result = num1; 14 else 15 result = num2; 16 17 return result; 18 } 19 } 20 class Test 21 { 22 static void Main(string[] args) 23 { 24 /* 局部变量定义 */ 25 int a = 100; 26 int b = 200; 27 int ret; 28 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 29 //调用 FindMax 方法 30 ret = n.FindMax(a, b); 31 Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret ); 32 Console.ReadLine(); 33 34 } 35 } 36 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
最大值是: 200
递归方法调用
一个方法可以自我调用。这就是所谓的 递归。下面的实例使用递归函数计算一个数的阶乘:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace CalculatorApplication 5 { 6 class NumberManipulator 7 { 8 public int factorial(int num) 9 { 10 /* 局部变量定义 */ 11 int result; 12 13 if (num == 1) 14 { 15 return 1; 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 result = factorial(num - 1) * num; 20 return result; 21 } 22 } 23 24 static void Main(string[] args) 25 { 26 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 27 //调用 factorial 方法 28 Console.WriteLine("6 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(6)); 29 Console.WriteLine("7 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(7)); 30 Console.WriteLine("8 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(8)); 31 Console.ReadLine(); 32 33 } 34 } 35 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
6 的阶乘是: 720 7 的阶乘是: 5040 8 的阶乘是: 40320
参数传递
当调用带有参数的方法时,您需要向方法传递参数。在 C# 中,有三种向方法传递参数的
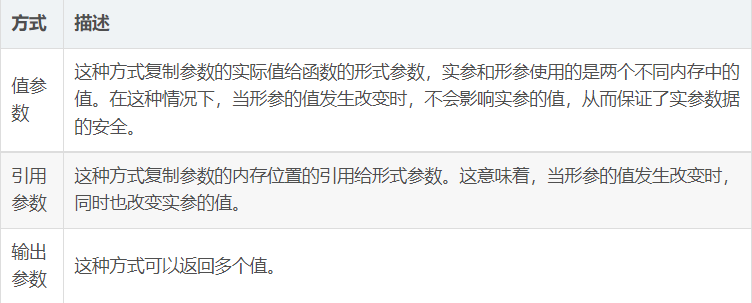
按值传递参数
这是参数传递的默认方式。在这种方式下,当调用一个方法时,会为每个值参数创建一个新的存储位置。
实际参数的值会复制给形参,实参和形参使用的是两个不同内存中的值。所以,当形参的值发生改变时,不会影响实参的值,从而保证了实参数据的安全。下面的实例演示了这个概念:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace CalculatorApplication 4 { 5 class NumberManipulator 6 { 7 public void swap(int x, int y) 8 { 9 int temp; 10 11 temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */ 12 x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */ 13 y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */ 14 } 15 16 static void Main(string[] args) 17 { 18 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 19 /* 局部变量定义 */ 20 int a = 100; 21 int b = 200; 22 23 Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a); 24 Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b); 25 26 /* 调用函数来交换值 */ 27 n.swap(a, b); 28 29 Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a); 30 Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b); 31 32 Console.ReadLine(); 33 } 34 } 35 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
在交换之前,a 的值:100 在交换之前,b 的值:200 在交换之后,a 的值:100 在交换之后,b 的值:200
结果表明,即使在函数内改变了值,值也没有发生任何的变化。
按引用传递参数
引用参数是一个对变量的内存位置的引用。当按引用传递参数时,与值参数不同的是,它不会为这些参数创建一个新的存储位置。引用参数表示与提供给方法的实际参数具有相同的内存位置。
在 C# 中,使用 按引用传递参数
引用参数是一个对变量的内存位置的引用。当按引用传递参数时,与值参数不同的是,它不会为这些参数创建一个新的存储位置。引用参数表示与提供给方法的实际参数具有相同的内存位置。
在 C# 中,使用 ref 关键字声明引用参数。下面的实例演示了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace CalculatorApplication 4 { 5 class NumberManipulator 6 { 7 public void swap(ref int x, ref int y) 8 { 9 int temp; 10 11 temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */ 12 x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */ 13 y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */ 14 } 15 16 static void Main(string[] args) 17 { 18 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 19 /* 局部变量定义 */ 20 int a = 100; 21 int b = 200; 22 23 Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a); 24 Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b); 25 26 /* 调用函数来交换值 */ 27 n.swap(ref a, ref b); 28 29 Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a); 30 Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b); 31 32 Console.ReadLine(); 33 34 } 35 } 36 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
在交换之前,a 的值:100 在交换之前,b 的值:200 在交换之后,a 的值:200 在交换之后,b 的值:100
结果表明,swap 函数内的值改变了,且这个改变可以在 Main 函数中反映出来。
按输出传递参数
return 语句可用于只从函数中返回一个值。但是,可以使用 输出参数 来从函数中返回两个值。输出参数会把方法输出的数据赋给自己,其他方面与引用参数相似。
下面的实例演示了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace CalculatorApplication 5 { 6 class NumberManipulator 7 { 8 public void getValue(out int x ) 9 { 10 int temp = 5; 11 x = temp; 12 } 13 14 static void Main(string[] args) 15 { 16 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 17 /* 局部变量定义 */ 18 int a = 100; 19 20 Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之前,a 的值: {0}", a); 21 22 /* 调用函数来获取值 */ 23 n.getValue(out a); 24 25 Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a); 26 Console.ReadLine(); 27 28 } 29 } 30 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
在方法调用之前,a 的值: 100 在方法调用之后,a 的值: 5
提供给输出参数的变量不需要赋值。当需要从一个参数没有指定初始值的方法中返回值时,输出参数特别有用。请看下面的实例,来理解这一点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace CalculatorApplication 5 { 6 class NumberManipulator 7 { 8 public void getValues(out int x, out int y ) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个值: "); 11 x = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); 12 Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个值: "); 13 y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); 14 } 15 16 static void Main(string[] args) 17 { 18 NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator(); 19 /* 局部变量定义 */ 20 int a , b; 21 22 /* 调用函数来获取值 */ 23 n.getValues(out a, out b); 24 25 Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a); 26 Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,b 的值: {0}", b); 27 Console.ReadLine(); 28 } 29 } 30 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果(取决于用户输入):
请输入第一个值: 7 请输入第二个值: 8 在方法调用之后,a 的值: 7 在方法调用之后,b 的值: 8
C# 封装⛄️
封装 被定义为"把一个或多个项目封闭在一个物理的或者逻辑的包中"。在面向对象程序设计方法论中,封装是为了防止对实现细节的访问。
抽象和封装是面向对象程序设计的相关特性。抽象允许相关信息可视化,封装则使开发者实现所需级别的抽象。
C# 封装根据具体的需要,设置使用者的访问权限,并通过 访问修饰符 来实现。
一个 访问修饰符 定义了一个类成员的范围和可见性。C# 支持的访问修饰符如下所示:
- public:所有对象都可以访问;
- private:对象本身在对象内部可以访问;
- protected:只有该类对象及其子类对象可以访问
- internal:同一个程序集的对象可以访问;
- protected internal:访问限于当前程序集或派生自包含类的类型。
Public 访问修饰符
Public 访问修饰符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数暴露给其他的函数和对象。任何公有成员可以被外部的类访问。
下面的实例说明了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace RectangleApplication 5 { 6 class Rectangle 7 { 8 //成员变量 9 public double length; 10 public double width; 11 12 public double GetArea() 13 { 14 return length * width; 15 } 16 public void Display() 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length); 19 Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width); 20 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea()); 21 } 22 }// Rectangle 结束 23 24 class ExecuteRectangle 25 { 26 static void Main(string[] args) 27 { 28 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); 29 r.length = 4.5; 30 r.width = 3.5; 31 r.Display(); 32 Console.ReadLine(); 33 } 34 } 35 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
长度: 4.5 宽度: 3.5 面积: 15.75
在上面的实例中,成员变量 length 和 width 被声明为 public,所以它们可以被函数 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问。
成员函数 Display() 和 GetArea() 可以直接访问这些变量。
成员函数 Display() 也被声明为 public,所以它也能被 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问。
Private 访问修饰符
Private 访问修饰符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数对其他的函数和对象进行隐藏。只有同一个类中的函数可以访问它的私有成员。即使是类的实例也不能访问它的私有成员。
下面的实例说明了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace RectangleApplication 5 { 6 class Rectangle 7 { 8 //成员变量 9 private double length; 10 private double width; 11 12 public void Acceptdetails() 13 { 14 Console.WriteLine("请输入长度:"); 15 length = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine()); 16 Console.WriteLine("请输入宽度:"); 17 width = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine()); 18 } 19 public double GetArea() 20 { 21 return length * width; 22 } 23 public void Display() 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length); 26 Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width); 27 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea()); 28 } 29 }//end class Rectangle 30 class ExecuteRectangle 31 { 32 static void Main(string[] args) 33 { 34 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); 35 r.Acceptdetails(); 36 r.Display(); 37 Console.ReadLine(); 38 } 39 } 40 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
请输入长度: 4.4 请输入宽度: 3.3 长度: 4.4 宽度: 3.3 面积: 14.52
在上面的实例中,成员变量 length 和 width 被声明为 private,所以它们不能被函数 Main() 访问。
成员函数 AcceptDetails() 和 Display() 可以访问这些变量。
由于成员函数 AcceptDetails() 和 Display() 被声明为 public,所以它们可以被 Main() 使用 Rectangle 类的实例 r 访问。
Protected 访问修饰符
Protected 访问修饰符允许子类访问它的基类的成员变量和成员函数。这样有助于实现继承。将在继承的内容部分详细讨论这个。
Internal 访问修饰符
Internal 访问说明符允许一个类将其成员变量和成员函数暴露给当前程序中的其他函数和对象。换句话说,带有 internal 访问修饰符的任何成员可以被定义在该成员所定义的应用程序内的任何类或方法访问。
下面的实例说明了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace RectangleApplication 5 { 6 class Rectangle 7 { 8 //成员变量 9 internal double length; 10 internal double width; 11 12 double GetArea() 13 { 14 return length * width; 15 } 16 public void Display() 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length); 19 Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width); 20 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea()); 21 } 22 }//end class Rectangle 23 class ExecuteRectangle 24 { 25 static void Main(string[] args) 26 { 27 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); 28 r.length = 4.5; 29 r.width = 3.5; 30 r.Display(); 31 Console.ReadLine(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
长度: 4.5 宽度: 3.5 面积: 15.75
在上面的实例中,请注意成员函数 GetArea() 声明的时候不带有任何访问修饰符。如果没有指定访问修饰符,则使用类成员的默认访问修饰符,即为 private。
Protected Internal 访问修饰符
Protected Internal 访问修饰符允许在本类,派生类或者包含该类的程序集中访问。这也被用于实现继承。
C# 继承⚡️
继承是面向对象程序设计中最重要的概念之一。继承允许我们根据一个类来定义另一个类,这使得创建和维护应用程序变得更容易。同时也有利于重用代码和节省开发时间。
当创建一个类时,程序员不需要完全重新编写新的数据成员和成员函数,只需要设计一个新的类,继承了已有的类的成员即可。这个已有的类被称为的基类,这个新的类被称为派生类。
继承的思想实现了 属于 (IS-A) 关系。例如,哺乳动物 属于 (IS-A) 动物,狗 属于 (IS-A) 哺乳动物,因此狗 属于 (IS-A) 动物。
基类和派生类
一个类可以派生自多个类或接口,这意味着它可以从多个基类或接口继承数据和函数。
C# 中创建派生类的语法如下:
1 <访问修饰符符> class <基类> 2 { 3 ... 4 } 5 class <派生类> : <基类> 6 { 7 ... 8 }
假设,有一个基类 Shape,它的派生类是 Rectangle:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace InheritanceApplication 4 { 5 class Shape 6 { 7 public void setWidth(int w) 8 { 9 width = w; 10 } 11 public void setHeight(int h) 12 { 13 height = h; 14 } 15 protected int width; 16 protected int height; 17 } 18 19 // 派生类 20 class Rectangle: Shape 21 { 22 public int getArea() 23 { 24 return (width * height); 25 } 26 } 27 28 class RectangleTester 29 { 30 static void Main(string[] args) 31 { 32 Rectangle Rect = new Rectangle(); 33 34 Rect.setWidth(5); 35 Rect.setHeight(7); 36 37 // 打印对象的面积 38 Console.WriteLine("总面积: {0}", Rect.getArea()); 39 Console.ReadKey(); 40 } 41 } 42 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
总面积: 35
基类的初始化
派生类继承了基类的成员变量和成员方法。因此父类对象应在子类对象创建之前被创建。您可以在成员初始化列表中进行父类的初始化。
下面的程序演示了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace RectangleApplication 4 { 5 class Rectangle 6 { 7 // 成员变量 8 protected double length; 9 protected double width; 10 public Rectangle(double l, double w) 11 { 12 length = l; 13 width = w; 14 } 15 public double GetArea() 16 { 17 return length * width; 18 } 19 public void Display() 20 { 21 Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length); 22 Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width); 23 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea()); 24 } 25 }//end class Rectangle 26 class Tabletop : Rectangle 27 { 28 private double cost; 29 public Tabletop(double l, double w) : base(l, w) 30 { } 31 public double GetCost() 32 { 33 double cost; 34 cost = GetArea() * 70; 35 return cost; 36 } 37 public void Display() 38 { 39 base.Display(); 40 Console.WriteLine("成本: {0}", GetCost()); 41 } 42 } 43 class ExecuteRectangle 44 { 45 static void Main(string[] args) 46 { 47 Tabletop t = new Tabletop(4.5, 7.5); 48 t.Display(); 49 Console.ReadLine(); 50 } 51 } 52 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
长度: 4.5 宽度: 7.5 面积: 33.75 成本: 2362.5
C# 多重继承
多重继承指的是一个类别可以同时从多于一个父类继承行为与特征的功能。与单一继承相对,单一继承指一个类别只可以继承自一个父类。
C# 不支持多重继承。但是,您可以使用接口来实现多重继承。下面的程序演示了这点:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace InheritanceApplication 4 { 5 class Shape 6 { 7 public void setWidth(int w) 8 { 9 width = w; 10 } 11 public void setHeight(int h) 12 { 13 height = h; 14 } 15 protected int width; 16 protected int height; 17 } 18 19 // 基类 PaintCost 20 public interface PaintCost 21 { 22 int getCost(int area); 23 24 } 25 // 派生类 26 class Rectangle : Shape, PaintCost 27 { 28 public int getArea() 29 { 30 return (width * height); 31 } 32 public int getCost(int area) 33 { 34 return area * 70; 35 } 36 } 37 class RectangleTester 38 { 39 static void Main(string[] args) 40 { 41 Rectangle Rect = new Rectangle(); 42 int area; 43 Rect.setWidth(5); 44 Rect.setHeight(7); 45 area = Rect.getArea(); 46 // 打印对象的面积 47 Console.WriteLine("总面积: {0}", Rect.getArea()); 48 Console.WriteLine("油漆总成本: ${0}" , Rect.getCost(area)); 49 Console.ReadKey(); 50 } 51 } 52 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
总面积: 35 油漆总成本: $2450
C# 多态性🎄
多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力。
多态性意味着有多重形式。在面向对象编程范式中,多态性往往表现为"一个接口,多个功能"。
多态性可以是静态的或动态的。在静态多态性中,函数的响应是在编译时发生的。在动态多态性中,函数的响应是在运行时发生的。
在 C# 中,每个类型都是多态的,因为包括用户定义类型在内的所有类型都继承自 Object。
多态就是同一个接口,使用不同的实例而执行不同操作,如图所示: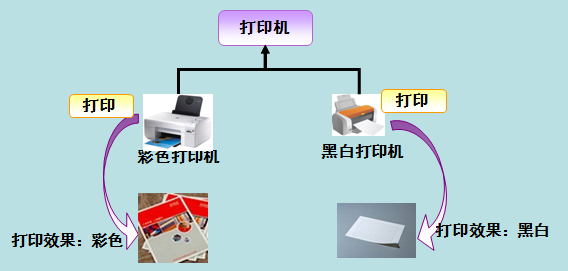
现实中,比如我们按下 F1 键这个动作:
- 如果当前在 Flash 界面下弹出的就是 AS 3 的帮助文档;
- 如果当前在 Word 下弹出的就是 Word 帮助;
- 在 Windows 下弹出的就是 Windows 帮助和支持。
- 同一个事件发生在不同的对象上会产生不同的结果。
静态多态性
在编译时,函数和对象的连接机制被称为早期绑定,也被称为静态绑定。C# 提供了两种技术来实现静态多态性。分别为:
- 函数重载
- 运算符重载
函数重载
可以在同一个范围内对相同的函数名有多个定义。函数的定义必须彼此不同,可以是参数列表中的参数类型不同,也可以是参数个数不同。不能重载只有返回类型不同的函数声明。
下面的实例演示了几个相同的函数 Add(),用于对不同个数参数进行相加处理:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace PolymorphismApplication 4 { 5 public class TestData 6 { 7 public int Add(int a, int b, int c) 8 { 9 return a + b + c; 10 } 11 public int Add(int a, int b) 12 { 13 return a + b; 14 } 15 } 16 class Program 17 { 18 static void Main(string[] args) 19 { 20 TestData dataClass = new TestData(); 21 int add1 = dataClass.Add(1, 2); 22 int add2 = dataClass.Add(1, 2, 3); 23 24 Console.WriteLine("add1 :" + add1); 25 Console.WriteLine("add2 :" + add2); 26 } 27 } 28 }
下面的实例演示了几个相同的函数 print(),用于打印不同的数据类型:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace PolymorphismApplication 4 { 5 class Printdata 6 { 7 void print(int i) 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine("输出整型: {0}", i ); 10 } 11 12 void print(double f) 13 { 14 Console.WriteLine("输出浮点型: {0}" , f); 15 } 16 17 void print(string s) 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine("输出字符串: {0}", s); 20 } 21 static void Main(string[] args) 22 { 23 Printdata p = new Printdata(); 24 // 调用 print 来打印整数 25 p.print(1); 26 // 调用 print 来打印浮点数 27 p.print(1.23); 28 // 调用 print 来打印字符串 29 p.print("Hello Runoob"); 30 Console.ReadKey(); 31 } 32 } 33 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
输出整型: 1 输出浮点型: 1.23 输出字符串: Hello Runoob
C# 运算符重载
您可以重定义或重载 C# 中内置的运算符。因此,程序员也可以使用用户自定义类型的运算符。重载运算符是具有特殊名称的函数,是通过关键字 operator 后跟运算符的符号来定义的。与其他函数一样,重载运算符有返回类型和参数列表。
例如,请看下面的函数:
1 public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c) 2 { 3 Box box = new Box(); 4 box.length = b.length + c.length; 5 box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth; 6 box.height = b.height + c.height; 7 return box; 8 }
上面的函数为用户自定义的类 Box 实现了加法运算符(+)。它把两个 Box 对象的属性相加,并返回相加后的 Box 对象。
运算符重载的实现
下面的程序演示了完整的实现:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace OperatorOvlApplication 5 { 6 class Box 7 { 8 private double length; // 长度 9 private double breadth; // 宽度 10 private double height; // 高度 11 12 public double getVolume() 13 { 14 return length * breadth * height; 15 } 16 public void setLength( double len ) 17 { 18 length = len; 19 } 20 21 public void setBreadth( double bre ) 22 { 23 breadth = bre; 24 } 25 26 public void setHeight( double hei ) 27 { 28 height = hei; 29 } 30 // 重载 + 运算符来把两个 Box 对象相加 31 public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c) 32 { 33 Box box = new Box(); 34 box.length = b.length + c.length; 35 box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth; 36 box.height = b.height + c.height; 37 return box; 38 } 39 40 } 41 42 class Tester 43 { 44 static void Main(string[] args) 45 { 46 Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box 47 Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box 48 Box Box3 = new Box(); // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box 49 double volume = 0.0; // 体积 50 51 // Box1 详述 52 Box1.setLength(6.0); 53 Box1.setBreadth(7.0); 54 Box1.setHeight(5.0); 55 56 // Box2 详述 57 Box2.setLength(12.0); 58 Box2.setBreadth(13.0); 59 Box2.setHeight(10.0); 60 61 // Box1 的体积 62 volume = Box1.getVolume(); 63 Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume); 64 65 // Box2 的体积 66 volume = Box2.getVolume(); 67 Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume); 68 69 // 把两个对象相加 70 Box3 = Box1 + Box2; 71 72 // Box3 的体积 73 volume = Box3.getVolume(); 74 Console.WriteLine("Box3 的体积: {0}", volume); 75 Console.ReadKey(); 76 } 77 } 78 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Box1 的体积: 210 Box2 的体积: 1560 Box3 的体积: 5400
可重载和不可重载运算符
下表描述了 C# 中运算符重载的能力:

实例
针对上述讨论,让我们扩展上面的实例,重载更多的运算符:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace OperatorOvlApplication 5 { 6 class Box 7 { 8 private double length; // 长度 9 private double breadth; // 宽度 10 private double height; // 高度 11 12 public double getVolume() 13 { 14 return length * breadth * height; 15 } 16 public void setLength( double len ) 17 { 18 length = len; 19 } 20 21 public void setBreadth( double bre ) 22 { 23 breadth = bre; 24 } 25 26 public void setHeight( double hei ) 27 { 28 height = hei; 29 } 30 // 重载 + 运算符来把两个 Box 对象相加 31 public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c) 32 { 33 Box box = new Box(); 34 box.length = b.length + c.length; 35 box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth; 36 box.height = b.height + c.height; 37 return box; 38 } 39 40 public static bool operator == (Box lhs, Box rhs) 41 { 42 bool status = false; 43 if (lhs.length == rhs.length && lhs.height == rhs.height 44 && lhs.breadth == rhs.breadth) 45 { 46 status = true; 47 } 48 return status; 49 } 50 public static bool operator !=(Box lhs, Box rhs) 51 { 52 bool status = false; 53 if (lhs.length != rhs.length || lhs.height != rhs.height 54 || lhs.breadth != rhs.breadth) 55 { 56 status = true; 57 } 58 return status; 59 } 60 public static bool operator <(Box lhs, Box rhs) 61 { 62 bool status = false; 63 if (lhs.length < rhs.length && lhs.height 64 < rhs.height && lhs.breadth < rhs.breadth) 65 { 66 status = true; 67 } 68 return status; 69 } 70 71 public static bool operator >(Box lhs, Box rhs) 72 { 73 bool status = false; 74 if (lhs.length > rhs.length && lhs.height 75 > rhs.height && lhs.breadth > rhs.breadth) 76 { 77 status = true; 78 } 79 return status; 80 } 81 82 public static bool operator <=(Box lhs, Box rhs) 83 { 84 bool status = false; 85 if (lhs.length <= rhs.length && lhs.height 86 <= rhs.height && lhs.breadth <= rhs.breadth) 87 { 88 status = true; 89 } 90 return status; 91 } 92 93 public static bool operator >=(Box lhs, Box rhs) 94 { 95 bool status = false; 96 if (lhs.length >= rhs.length && lhs.height 97 >= rhs.height && lhs.breadth >= rhs.breadth) 98 { 99 status = true; 100 } 101 return status; 102 } 103 public override string ToString() 104 { 105 return String.Format("({0}, {1}, {2})", length, breadth, height); 106 } 107 108 } 109 110 class Tester 111 { 112 static void Main(string[] args) 113 { 114 Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box 115 Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box 116 Box Box3 = new Box(); // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box 117 Box Box4 = new Box(); 118 double volume = 0.0; // 体积 119 120 // Box1 详述 121 Box1.setLength(6.0); 122 Box1.setBreadth(7.0); 123 Box1.setHeight(5.0); 124 125 // Box2 详述 126 Box2.setLength(12.0); 127 Box2.setBreadth(13.0); 128 Box2.setHeight(10.0); 129 130 // 使用重载的 ToString() 显示两个盒子 131 Console.WriteLine("Box1: {0}", Box1.ToString()); 132 Console.WriteLine("Box2: {0}", Box2.ToString()); 133 134 // Box1 的体积 135 volume = Box1.getVolume(); 136 Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume); 137 138 // Box2 的体积 139 volume = Box2.getVolume(); 140 Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume); 141 142 // 把两个对象相加 143 Box3 = Box1 + Box2; 144 Console.WriteLine("Box3: {0}", Box3.ToString()); 145 // Box3 的体积 146 volume = Box3.getVolume(); 147 Console.WriteLine("Box3 的体积: {0}", volume); 148 149 //comparing the boxes 150 if (Box1 > Box2) 151 Console.WriteLine("Box1 大于 Box2"); 152 else 153 Console.WriteLine("Box1 不大于 Box2"); 154 if (Box1 < Box2) 155 Console.WriteLine("Box1 小于 Box2"); 156 else 157 Console.WriteLine("Box1 不小于 Box2"); 158 if (Box1 >= Box2) 159 Console.WriteLine("Box1 大于等于 Box2"); 160 else 161 Console.WriteLine("Box1 不大于等于 Box2"); 162 if (Box1 <= Box2) 163 Console.WriteLine("Box1 小于等于 Box2"); 164 else 165 Console.WriteLine("Box1 不小于等于 Box2"); 166 if (Box1 != Box2) 167 Console.WriteLine("Box1 不等于 Box2"); 168 else 169 Console.WriteLine("Box1 等于 Box2"); 170 Box4 = Box3; 171 if (Box3 == Box4) 172 Console.WriteLine("Box3 等于 Box4"); 173 else 174 Console.WriteLine("Box3 不等于 Box4"); 175 176 Console.ReadKey(); 177 } 178 } 179 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Box1: (6, 7, 5) Box2: (12, 13, 10) Box1 的体积: 210 Box2 的体积: 1560 Box3:(18, 20, 15) Box3 的体积: 5400 Box1 不大于 Box2 Box1 小于 Box2 Box1 不大于等于 Box2 Box1 小于等于 Box2 Box1 不等于 Box2 Box3 等于 Box4
动态多态性
C# 允许您使用关键字 abstract 创建抽象类,用于提供接口的部分类的实现。当一个派生类继承自该抽象类时,实现即完成。抽象类包含抽象方法,抽象方法可被派生类实现。派生类具有更专业的功能。
请注意,下面是有关抽象类的一些规则:
- 不能创建一个抽象类的实例。
- 不能在一个抽象类外部声明一个抽象方法。
- 通过在类定义前面放置关键字 sealed,可以将类声明为密封类。当一个类被声明为 sealed 时,它不能被继承。抽象类不能被声明为
- sealed。
下面的程序演示了一个抽象类:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace PolymorphismApplication 4 { 5 abstract class Shape 6 { 7 abstract public int area(); 8 } 9 class Rectangle: Shape 10 { 11 private int length; 12 private int width; 13 public Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0) 14 { 15 length = a; 16 width = b; 17 } 18 public override int area () 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine("Rectangle 类的面积:"); 21 return (width * length); 22 } 23 } 24 25 class RectangleTester 26 { 27 static void Main(string[] args) 28 { 29 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 7); 30 double a = r.area(); 31 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}",a); 32 Console.ReadKey(); 33 } 34 } 35 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Rectangle 类的面积: 面积: 70
当有一个定义在类中的函数需要在继承类中实现时,可以使用虚方法。
虚方法是使用关键字 virtual 声明的。
虚方法可以在不同的继承类中有不同的实现。
对虚方法的调用是在运行时发生的。
动态多态性是通过 抽象类 和 虚方法 实现的。
以下实例创建了 Shape 基类,并创建派生类 Circle、 Rectangle、Triangle, Shape 类提供一个名为 Draw 的虚拟方法,在每个派生类中重写该方法以绘制该类的指定形状。
1 实例 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 5 public class Shape 6 { 7 public int X { get; private set; } 8 public int Y { get; private set; } 9 public int Height { get; set; } 10 public int Width { get; set; } 11 12 // 虚方法 13 public virtual void Draw() 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("执行基类的画图任务"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 class Circle : Shape 20 { 21 public override void Draw() 22 { 23 Console.WriteLine("画一个圆形"); 24 base.Draw(); 25 } 26 } 27 class Rectangle : Shape 28 { 29 public override void Draw() 30 { 31 Console.WriteLine("画一个长方形"); 32 base.Draw(); 33 } 34 } 35 class Triangle : Shape 36 { 37 public override void Draw() 38 { 39 Console.WriteLine("画一个三角形"); 40 base.Draw(); 41 } 42 } 43 44 class Program 45 { 46 static void Main(string[] args) 47 { 48 // 创建一个 List<Shape> 对象,并向该对象添加 Circle、Triangle 和 Rectangle 49 var shapes = new List<Shape> 50 { 51 new Rectangle(), 52 new Triangle(), 53 new Circle() 54 }; 55 56 // 使用 foreach 循环对该列表的派生类进行循环访问,并对其中的每个 Shape 对象调用 Draw 方法 57 foreach (var shape in shapes) 58 { 59 shape.Draw(); 60 } 61 62 Console.WriteLine("按下任意键退出。"); 63 Console.ReadKey(); 64 } 65 66 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
- 画一个长方形
- 执行基类的画图任务
- 画一个三角形
- 执行基类的画图任务
- 画一个圆形
- 执行基类的画图任务
- 按下任意键退出。
下面的程序演示通过虚方法 area() 来计算不同形状图像的面积:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace PolymorphismApplication 4 { 5 class Shape 6 { 7 protected int width, height; 8 public Shape( int a=0, int b=0) 9 { 10 width = a; 11 height = b; 12 } 13 public virtual int area() 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("父类的面积:"); 16 return 0; 17 } 18 } 19 class Rectangle: Shape 20 { 21 public Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0): base(a, b) 22 { 23 24 } 25 public override int area () 26 { 27 Console.WriteLine("Rectangle 类的面积:"); 28 return (width * height); 29 } 30 } 31 class Triangle: Shape 32 { 33 public Triangle(int a = 0, int b = 0): base(a, b) 34 { 35 36 } 37 public override int area() 38 { 39 Console.WriteLine("Triangle 类的面积:"); 40 return (width * height / 2); 41 } 42 } 43 class Caller 44 { 45 public void CallArea(Shape sh) 46 { 47 int a; 48 a = sh.area(); 49 Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", a); 50 } 51 } 52 class Tester 53 { 54 55 static void Main(string[] args) 56 { 57 Caller c = new Caller(); 58 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 7); 59 Triangle t = new Triangle(10, 5); 60 c.CallArea(r); 61 c.CallArea(t); 62 Console.ReadKey(); 63 } 64 } 65 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Rectangle 类的面积: 面积:70 Triangle 类的面积: 面积:25






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术