C# 最基础知识介绍(四)——数组、字符串、结构体、枚举、类
C# 最基础知识介绍(四)——数组、字符串、结构体、枚举、类
数组(Array)💚
数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组是用来存储数据的集合,通常认为数组是一个同一类型变量的集合。
声明数组变量并不是声明 number0、number1、…、number99 一个个单独的变量,而是声明一个就像 numbers 这样的变量,然后使用 numbers[0]、numbers[1]、…、numbers[99] 来表示一个个单独的变量。数组中某个指定的元素是通过索引来访问的。
所有的数组都是由连续的内存位置组成的。最低的地址对应第一个元素,最高的地址对应最后一个元素。
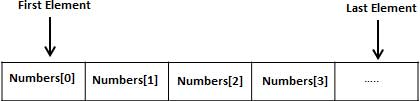
声明数组
在 C# 中声明一个数组,您可以使用下面的语法:
1 datatype[] arrayName;
其中,
- datatype 用于指定被存储在数组中的元素的类型。
- [ ]指定数组的秩(维度)。秩指定数组的大小。
- arrayName 指定数组的名称。
例如:
1 double[] balance;
初始化数组
声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组。当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组。
数组是一个引用类型,所以您需要使用 new 关键字来创建数组的实例。
例如:
1 double[] balance = new double[10];
赋值给数组
可以通过使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素,比如:
1 double[] balance = new double[10]; 2 balance[0] = 4500.0;
可以在声明数组的同时给数组赋值,比如:
1 double[] balance = { 2340.0, 4523.69, 3421.0};
也可以创建并初始化一个数组,比如:
1 int [] marks = new int[5] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
在上述情况下,你也可以省略数组的大小,比如:
1 int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
也可以赋值一个数组变量到另一个目标数组变量中。在这种情况下,目标和源会指向相同的内存位置:
1 int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95}; 2 int[] score = marks;
当创建一个数组时,C# 编译器会根据数组类型隐式初始化每个数组元素为一个默认值。例如,int 数组的所有元素都会被初始化为 0。
访问数组元素
元素是通过带索引的数组名称来访问的。这是通过把元素的索引放置在数组名称后的方括号中来实现的。例如:
1 double salary = balance[9];
下面是一个实例,使用上面提到的三个概念,即声明、赋值、访问数组:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace ArrayApplication 4 { 5 class MyArray 6 { 7 static void Main(string[] args) 8 { 9 int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */ 10 int i,j; 11 12 13 /* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */ 14 for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) 15 { 16 n[ i ] = i + 100; 17 } 18 19 /* 输出每个数组元素的值 */ 20 for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ ) 21 { 22 Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", j, n[j]); 23 } 24 Console.ReadKey(); 25 } 26 } 27 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Element[0] = 100 Element[1] = 101 Element[2] = 102 Element[3] = 103 Element[4] = 104 Element[5] = 105 Element[6] = 106 Element[7] = 107 Element[8] = 108 Element[9] = 109
使用 foreach 循环
在前面的实例中,我们使用一个 for 循环来访问每个数组元素。也可以使用一个 foreach 语句来遍历数组。
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace ArrayApplication 5 { 6 class MyArray 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */ 11 12 13 /* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */ 14 for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) 15 { 16 n[i] = i + 100; 17 } 18 19 /* 输出每个数组元素的值 */ 20 foreach (int j in n ) 21 { 22 int i = j-100; 23 Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", i, j); 24 } 25 Console.ReadKey(); 26 } 27 } 28 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Element[0] = 100 Element[1] = 101 Element[2] = 102 Element[3] = 103 Element[4] = 104 Element[5] = 105 Element[6] = 106 Element[7] = 107 Element[8] = 108 Element[9] = 109
C# 数组细节
在 C# 中,数组是非常重要的,且需要了解更多的细节。下面列出了 C# 程序员必须清楚的一些与数组相关的重要概念:
C# 字符串(String)💜
在 C# 中,您可以使用字符数组来表示字符串,但是,更常见的做法是使用 string 关键字来声明一个字符串变量。string 关键字是 System.String 类的别名。
创建 String 对象
可以使用以下方法之一来创建 string 对象:
- 通过给 String 变量指定一个字符串
- 通过使用 String 类构造函数
- 通过使用字符串串联运算符( + )
- 通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
- 通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace StringApplication 5 { 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 //字符串,字符串连接 11 string fname, lname; 12 fname = "Rowan"; 13 lname = "Atkinson"; 14 15 string fullname = fname + lname; 16 Console.WriteLine("Full Name: {0}", fullname); 17 18 //通过使用 string 构造函数 19 char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l','o' }; 20 string greetings = new string(letters); 21 Console.WriteLine("Greetings: {0}", greetings); 22 23 //方法返回字符串 24 string[] sarray = { "Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point" }; 25 string message = String.Join(" ", sarray); 26 Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", message); 27 28 //用于转化值的格式化方法 29 DateTime waiting = new DateTime(2012, 10, 10, 17, 58, 1); 30 string chat = String.Format("Message sent at {0:t} on {0:D}", 31 waiting); 32 Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", chat); 33 Console.ReadKey() ; 34 } 35 } 36 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Full Name: RowanAtkinson Greetings: Hello Message: Hello From Tutorials Point Message: Message sent at 17:58 on Wednesday, 10 October 2012
String 类的属性
String 类有以下两个属性:
序号 属性名称 & 描述
1 Chars 在当前 String 对象中获取 Char 对象的指定位置。
2 Length 在当前的 String 对象中获取字符数。
String 类的方法
String 类有许多方法用于 string 对象的操作。下面的表格提供了一些最常用的方法:

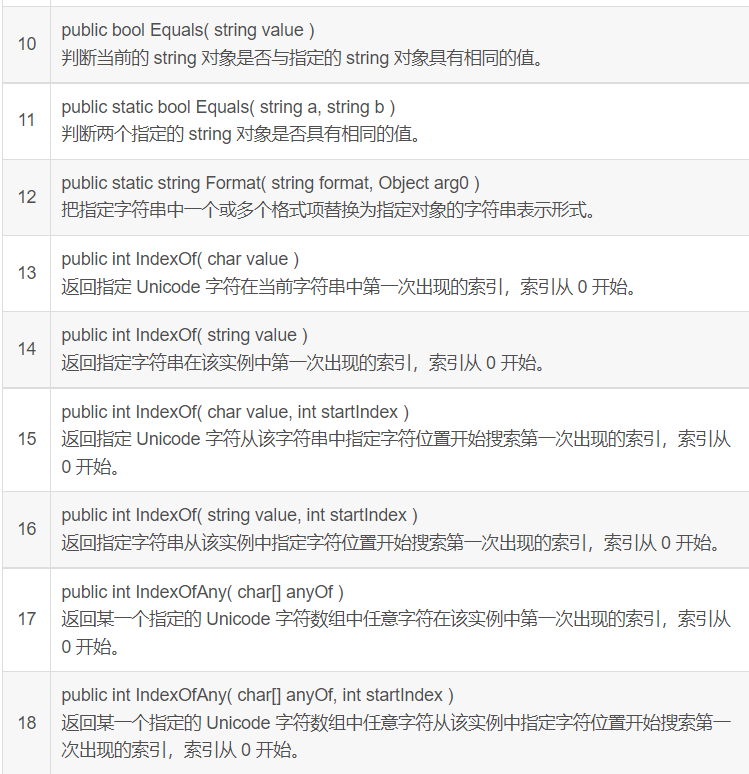

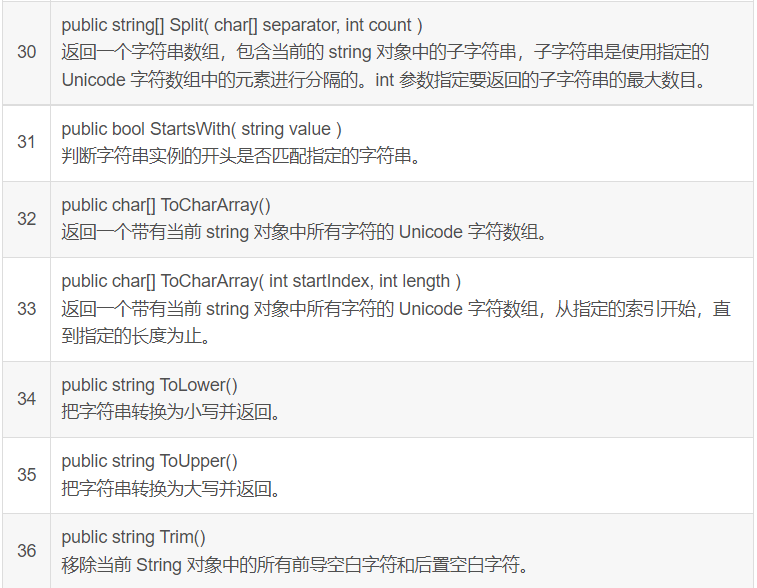
上面的方法列表并不详尽,请访问 MSDN 库,查看完整的方法列表和 String 类构造函数。
实例
下面的实例演示了上面提到的一些方法:
比较字符串
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace StringApplication 5 { 6 class StringProg 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 string str1 = "This is test"; 11 string str2 = "This is text"; 12 13 if (String.Compare(str1, str2) == 0) 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are equal."); 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are not equal."); 20 } 21 Console.ReadKey() ; 22 } 23 } 24 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
This is test and This is text are not equal.
字符串包含字符串:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace StringApplication 5 { 6 class StringProg 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 string str = "This is test"; 11 if (str.Contains("test")) 12 { 13 Console.WriteLine("The sequence 'test' was found."); 14 } 15 Console.ReadKey() ; 16 } 17 } 18 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
The sequence ‘test’ was found.
获取子字符串:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace StringApplication 4 { 5 class StringProg 6 { 7 static void Main(string[] args) 8 { 9 string str = "Last night I dreamt of San Pedro"; 10 Console.WriteLine(str); 11 string substr = str.Substring(23); 12 Console.WriteLine(substr); 13 Console.ReadKey() ; 14 } 15 } 16 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Last night I dreamt of San Pedro
San Pedro
连接字符串:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 namespace StringApplication 5 { 6 class StringProg 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 string[] starray = new string[]{"Down the way nights are dark", 11 "And the sun shines daily on the mountain top", 12 "I took a trip on a sailing ship", 13 "And when I reached Jamaica", 14 "I made a stop"}; 15 16 string str = String.Join("\n", starray); 17 Console.WriteLine(str); 18 Console.ReadKey() ; 19 } 20 } 21 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Down the way nights are dark
And the sun shines daily on the mountain top
I took a trip on a sailing ship
And when I reached Jamaica
I made a stop
结构体(Struct)💙
在 C# 中,结构体是值类型数据结构。它使得一个单一变量可以存储各种数据类型的相关数据。struct 关键字用于创建结构体。
结构体是用来代表一个记录。假设您想跟踪图书馆中书的动态。您可能想跟踪每本书的以下属性:
- Title
- Author
- Subject
- Book ID
定义结构体
为了定义一个结构体,您必须使用 struct 语句。struct 语句为程序定义了一个带有多个成员的新的数据类型。
例如,可以按照如下的方式声明 Book 结构:
1 struct Books 2 { 3 public string title; 4 public string author; 5 public string subject; 6 public int book_id; 7 };
下面的程序演示了结构的用法:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 using System.Text; 4 5 struct Books 6 { 7 public string title; 8 public string author; 9 public string subject; 10 public int book_id; 11 }; 12 13 public class testStructure 14 { 15 public static void Main(string[] args) 16 { 17 18 Books Book1; /* 声明 Book1,类型为 Books */ 19 Books Book2; /* 声明 Book2,类型为 Books */ 20 21 /* book 1 详述 */ 22 Book1.title = "C Programming"; 23 Book1.author = "Nuha Ali"; 24 Book1.subject = "C Programming Tutorial"; 25 Book1.book_id = 6495407; 26 27 /* book 2 详述 */ 28 Book2.title = "Telecom Billing"; 29 Book2.author = "Zara Ali"; 30 Book2.subject = "Telecom Billing Tutorial"; 31 Book2.book_id = 6495700; 32 33 /* 打印 Book1 信息 */ 34 Console.WriteLine( "Book 1 title : {0}", Book1.title); 35 Console.WriteLine("Book 1 author : {0}", Book1.author); 36 Console.WriteLine("Book 1 subject : {0}", Book1.subject); 37 Console.WriteLine("Book 1 book_id :{0}", Book1.book_id); 38 39 /* 打印 Book2 信息 */ 40 Console.WriteLine("Book 2 title : {0}", Book2.title); 41 Console.WriteLine("Book 2 author : {0}", Book2.author); 42 Console.WriteLine("Book 2 subject : {0}", Book2.subject); 43 Console.WriteLine("Book 2 book_id : {0}", Book2.book_id); 44 45 Console.ReadKey(); 46 47 } 48 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Book 1 title : C Programming Book 1 author : Nuha Ali Book 1 subject : C Programming Tutorial Book 1 book_id : 6495407 Book 2 title : Telecom Billing Book 2 author : Zara Ali Book 2 subject : Telecom Billing Tutorial Book 2 book_id : 6495700
C# 结构的特点
已经用了一个简单的名为 Books 的结构。在 C# 中的结构与传统的 C 或 C++ 中的结构不同。C# 中的结构有以下特点:
- 结构可带有方法、字段、索引、属性、运算符方法和事件。
- 结构可定义构造函数,但不能定义析构函数。但是,您不能为结构定义无参构造函数。无参构造函数(默认)是自动定义的,且不能被改变。
- 与类不同,结构不能继承其他的结构或类。
- 结构不能作为其他结构或类的基础结构。
- 结构可实现一个或多个接口。
- 结构成员不能指定为 abstract、virtual 或 protected。
- 当您使用 New 操作符创建一个结构对象时,会调用适当的构造函数来创建结构。与类不同,结构可以不使用 New 操作符即可被实例化。
- 如果不使用 New 操作符,只有在所有的字段都被初始化之后,字段才被赋值,对象才被使用。
类 vs 结构
类和结构有以下几个基本的不同点:
- 类是引用类型,结构是值类型。
- 结构不支持继承。
- 结构不能声明默认的构造函数。
针对上述讨论,让我们重写前面的实例:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 using System.Text; 4 5 struct Books 6 { 7 private string title; 8 private string author; 9 private string subject; 10 private int book_id; 11 public void setValues(string t, string a, string s, int id) 12 { 13 title = t; 14 author = a; 15 subject = s; 16 book_id =id; 17 } 18 public void display() 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine("Title : {0}", title); 21 Console.WriteLine("Author : {0}", author); 22 Console.WriteLine("Subject : {0}", subject); 23 Console.WriteLine("Book_id :{0}", book_id); 24 } 25 26 }; 27 28 public class testStructure 29 { 30 public static void Main(string[] args) 31 { 32 33 Books Book1 = new Books(); /* 声明 Book1,类型为 Books */ 34 Books Book2 = new Books(); /* 声明 Book2,类型为 Books */ 35 36 /* book 1 详述 */ 37 Book1.setValues("C Programming", 38 "Nuha Ali", "C Programming Tutorial",6495407); 39 40 /* book 2 详述 */ 41 Book2.setValues("Telecom Billing", 42 "Zara Ali", "Telecom Billing Tutorial", 6495700); 43 44 /* 打印 Book1 信息 */ 45 Book1.display(); 46 47 /* 打印 Book2 信息 */ 48 Book2.display(); 49 50 Console.ReadKey(); 51 52 } 53 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Title : C Programming Author : Nuha Ali Subject : C Programming Tutorial Book_id : 6495407 Title : Telecom Billing Author : Zara Ali Subject : Telecom Billing Tutorial Book_id : 6495700
枚举(Enum)💛
枚举是一组命名整型常量。枚举类型是使用 enum 关键字声明的。
C# 枚举是值类型。换句话说,枚举包含自己的值,且不能继承或传递继承。
声明 enum 变量
声明枚举的一般语法:
1 enum <enum_name> 2 { 3 enumeration list 4 };
其中,
- enum_name 指定枚举的类型名称。
- enumeration list 是一个用逗号分隔的标识符列表。
枚举列表中的每个符号代表一个整数值,一个比它前面的符号大的整数值。默认情况下,第一个枚举符号的值是 0.例如:
1 enum Days { Sun, Mon, tue, Wed, thu, Fri, Sat };
实例
下面的实例演示了枚举变量的用法:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 4 public class EnumTest 5 { 6 enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat }; 7 8 static void Main() 9 { 10 int x = (int)Day.Sun; 11 int y = (int)Day.Fri; 12 Console.WriteLine("Sun = {0}", x); 13 Console.WriteLine("Fri = {0}", y); 14 } 15 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Sun = 0 Fri = 5
类(Class)❤️
当你定义一个类时,你定义了一个数据类型的蓝图。这实际上并没有定义任何的数据,但它定义了类的名称意味着什么,也就是说,类的对象由什么组成及在这个对象上可执行什么操作。对象是类的实例。构成类的方法和变量称为类的成员。
类的定义
类的定义是以关键字 class 开始,后跟类的名称。类的主体,包含在一对花括号内。下面是类定义的一般形式:
1 <access specifier> class class_name 2 { 3 // member variables 4 <access specifier> <data type> variable1; 5 <access specifier> <data type> variable2; 6 ... 7 <access specifier> <data type> variableN; 8 // member methods 9 <access specifier> <return type> method1(parameter_list) 10 { 11 // method body 12 } 13 <access specifier> <return type> method2(parameter_list) 14 { 15 // method body 16 } 17 ... 18 <access specifier> <return type> methodN(parameter_list) 19 { 20 // method body 21 } 22 }
请注意:
- 访问标识符 指定了对类及其成员的访问规则。如果没有指定,则使用默认的访问标识符。类的默认访问标识符是
- internal,成员的默认访问标识符是 private。
- 数据类型 指定了变量的类型,返回类型 指定了返回的方法返回的数据类型。
- 如果要访问类的成员,你要使用点(.)运算符。
- 点运算符链接了对象的名称和成员的名称。
下面的实例说明了目前为止所讨论的概念:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace BoxApplication 4 { 5 class Box 6 { 7 public double length; // 长度 8 public double breadth; // 宽度 9 public double height; // 高度 10 } 11 class Boxtester 12 { 13 static void Main(string[] args) 14 { 15 Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box 16 Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box 17 double volume = 0.0; // 体积 18 19 // Box1 详述 20 Box1.height = 5.0; 21 Box1.length = 6.0; 22 Box1.breadth = 7.0; 23 24 // Box2 详述 25 Box2.height = 10.0; 26 Box2.length = 12.0; 27 Box2.breadth = 13.0; 28 29 // Box1 的体积 30 volume = Box1.height * Box1.length * Box1.breadth; 31 Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume); 32 33 // Box2 的体积 34 volume = Box2.height * Box2.length * Box2.breadth; 35 Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume); 36 Console.ReadKey(); 37 } 38 } 39 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Box1 的体积: 210 Box2 的体积: 1560
成员函数和封装
类的成员函数是一个在类定义中有它的定义或原型的函数,就像其他变量一样。作为类的一个成员,它能在类的任何对象上操作,且能访问该对象的类的所有成员。
成员变量是对象的属性(从设计角度),且它们保持私有来实现封装。这些变量只能使用公共成员函数来访问。
让我们使用上面的概念来设置和获取一个类中不同的类成员的值:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace BoxApplication 4 { 5 class Box 6 { 7 private double length; // 长度 8 private double breadth; // 宽度 9 private double height; // 高度 10 public void setLength( double len ) 11 { 12 length = len; 13 } 14 15 public void setBreadth( double bre ) 16 { 17 breadth = bre; 18 } 19 20 public void setHeight( double hei ) 21 { 22 height = hei; 23 } 24 public double getVolume() 25 { 26 return length * breadth * height; 27 } 28 } 29 class Boxtester 30 { 31 static void Main(string[] args) 32 { 33 Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box 34 Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box 35 double volume; // 体积 36 37 38 // Box1 详述 39 Box1.setLength(6.0); 40 Box1.setBreadth(7.0); 41 Box1.setHeight(5.0); 42 43 // Box2 详述 44 Box2.setLength(12.0); 45 Box2.setBreadth(13.0); 46 Box2.setHeight(10.0); 47 48 // Box1 的体积 49 volume = Box1.getVolume(); 50 Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}" ,volume); 51 52 // Box2 的体积 53 volume = Box2.getVolume(); 54 Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume); 55 56 Console.ReadKey(); 57 } 58 } 59 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Box1 的体积: 210 Box2 的体积: 1560
C# 中的构造函数
类的 构造函数 是类的一个特殊的成员函数,当创建类的新对象时执行。
构造函数的名称与类的名称完全相同,它没有任何返回类型。
下面的实例说明了构造函数的概念:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace LineApplication 4 { 5 class Line 6 { 7 private double length; // 线条的长度 8 public Line() 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("对象已创建"); 11 } 12 13 public void setLength( double len ) 14 { 15 length = len; 16 } 17 public double getLength() 18 { 19 return length; 20 } 21 22 static void Main(string[] args) 23 { 24 Line line = new Line(); 25 // 设置线条长度 26 line.setLength(6.0); 27 Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength()); 28 Console.ReadKey(); 29 } 30 } 31 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
对象已创建 线条的长度: 6
默认的构造函数没有任何参数。但是如果你需要一个带有参数的构造函数可以有参数,这种构造函数叫做参数化构造函数。这种技术可以帮助你在创建对象的同时给对象赋初始值,具体请看下面实例:
1 实例 2 3 using System; 4 namespace LineApplication 5 { 6 class Line 7 { 8 private double length; // 线条的长度 9 public Line(double len) // 参数化构造函数 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("对象已创建,length = {0}", len); 12 length = len; 13 } 14 15 public void setLength( double len ) 16 { 17 length = len; 18 } 19 public double getLength() 20 { 21 return length; 22 } 23 24 static void Main(string[] args) 25 { 26 Line line = new Line(10.0); 27 Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength()); 28 // 设置线条长度 29 line.setLength(6.0); 30 Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength()); 31 Console.ReadKey(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
对象已创建,length = 10 线条的长度: 10 线条的长度: 6
C# 中的析构函数
类的 析构函数 是类的一个特殊的成员函数,当类的对象超出范围时执行。
析构函数的名称是在类的名称前加上一个波浪形(~)作为前缀,它不返回值,也不带任何参数。
析构函数用于在结束程序(比如关闭文件、释放内存等)之前释放资源。析构函数不能继承或重载。
下面的实例说明了析构函数的概念:
1 实例 2 3 using System; 4 namespace LineApplication 5 { 6 class Line 7 { 8 private double length; // 线条的长度 9 public Line() // 构造函数 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("对象已创建"); 12 } 13 ~Line() //析构函数 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("对象已删除"); 16 } 17 18 public void setLength( double len ) 19 { 20 length = len; 21 } 22 public double getLength() 23 { 24 return length; 25 } 26 27 static void Main(string[] args) 28 { 29 Line line = new Line(); 30 // 设置线条长度 31 line.setLength(6.0); 32 Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength()); 33 } 34 } 35 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
对象已创建 线条的长度: 6 对象已删除
C# 类的静态成员
我们可以使用 static 关键字把类成员定义为静态的。当我们声明一个类成员为静态时,意味着无论有多少个类的对象被创建,只会有一个该静态成员的副本。
关键字 static 意味着类中只有一个该成员的实例。静态变量用于定义常量,因为它们的值可以通过直接调用类而不需要创建类的实例来获取。静态变量可在成员函数或类的定义外部进行初始化。你也可以在类的定义内部初始化静态变量。
下面的实例演示了静态变量的用法:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace StaticVarApplication 4 { 5 class StaticVar 6 { 7 public static int num; 8 public void count() 9 { 10 num++; 11 } 12 public int getNum() 13 { 14 return num; 15 } 16 } 17 class StaticTester 18 { 19 static void Main(string[] args) 20 { 21 StaticVar s1 = new StaticVar(); 22 StaticVar s2 = new StaticVar(); 23 s1.count(); 24 s1.count(); 25 s1.count(); 26 s2.count(); 27 s2.count(); 28 s2.count(); 29 Console.WriteLine("s1 的变量 num: {0}", s1.getNum()); 30 Console.WriteLine("s2 的变量 num: {0}", s2.getNum()); 31 Console.ReadKey(); 32 } 33 } 34 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
s1 的变量 num: 6 s2 的变量 num: 6
也可以把一个成员函数声明为 static。这样的函数只能访问静态变量。静态函数在对象被创建之前就已经存在。下面的实例演示了静态函数的用法:
1 实例 2 using System; 3 namespace StaticVarApplication 4 { 5 class StaticVar 6 { 7 public static int num; 8 public void count() 9 { 10 num++; 11 } 12 public static int getNum() 13 { 14 return num; 15 } 16 } 17 class StaticTester 18 { 19 static void Main(string[] args) 20 { 21 StaticVar s = new StaticVar(); 22 s.count(); 23 s.count(); 24 s.count(); 25 Console.WriteLine("变量 num: {0}", StaticVar.getNum()); 26 Console.ReadKey(); 27 } 28 } 29 }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
变量 num: 3





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律