abc246(D-F)
D:
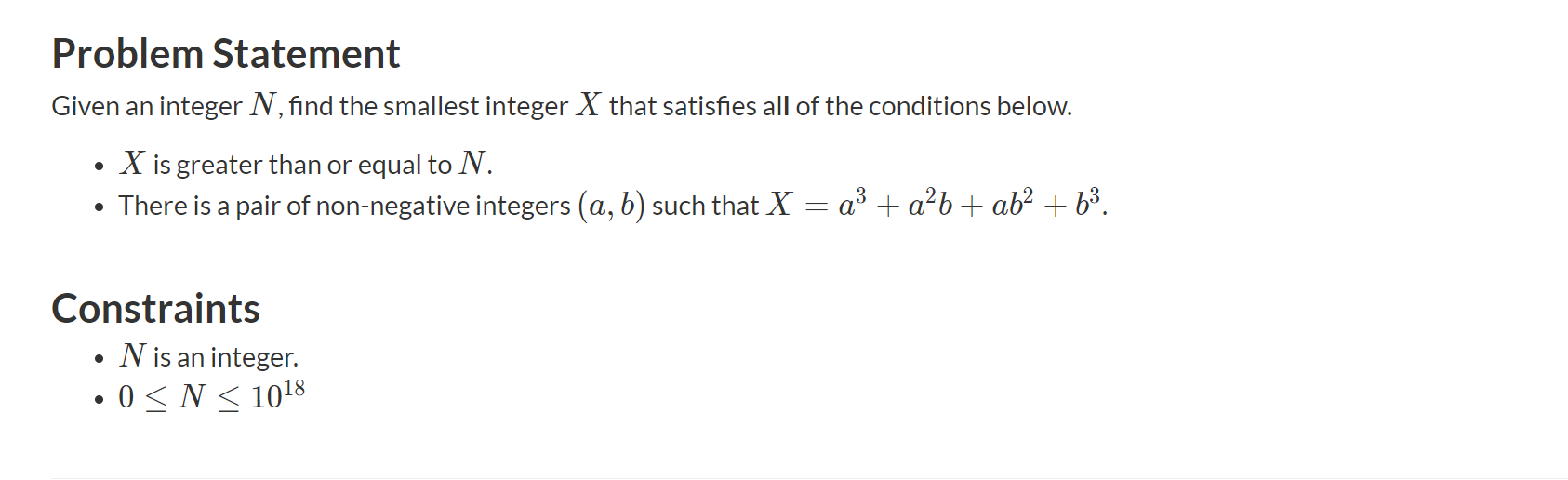
枚举a,二分b,更新最小值
code:
void solve(int Case) {
int n;
int x;
cin >> n;
int ans = 2e18;
auto check = [&](int a, int b) {
int x = a * a * a + a * a * b + a * b * b + b * b * b;
if (x < 0) return true;
return x - n >= 0;
};
auto cal = [](int a, int b) {
int x = a * a * a + a * a * b + a * b * b + b * b * b;
return x;
};
for (x = 0; x * x * x <= n; x++);
for (int i = 0; i <= x; i++) {
int l = 0, r = 1e6;
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(i,mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
ans = min(cal(i, r), ans);
}
cout << ans << nline;
}
E

大致题意是从a到b每次都可以选择一条斜着的直线走,问a到b的最短距离
从一个点每次都有n种选择,显然时间复杂度过高,可以考虑每次更换方向算作一次操作边权做1,不更换方向边权为0,所以需要再扩展一维存储扩展到这个点时的方向
code:
const int N = 2010;
char s[N][N];
int dist[N][N][5];
int vis[N][N][5];
int n;
struct T {
int x, y, w, d;
};
int ax, ay, bx, by;
int dx[4] = {1, 1, -1, -1}, dy [4] = {1, -1, 1, -1};
void bfs(int x, int y) {
deque<T> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];
if (tx >= 1 and ty >= 1 and tx <= n and ty <= n) {
if (s[tx][ty] == '#') continue;
q.push_front({x, y, 1, i});
}
}
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
while (q.size()) {
auto [x, y, w, d] = q.front();
q.pop_front();
if (vis[x][y][d]) continue;
vis[x][y][d] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];
if (tx >= 1 and ty >= 1 and tx <= n and ty <= n) {
if (s[tx][ty] == '#') continue;
int nw = (d != i);
if (dist[tx][ty][i] > w + nw) {
dist[tx][ty][i] = w + nw;
if (nw) {
q.push_back({tx, ty, w + nw, i});
} else {
q.push_front({tx, ty, w + nw, i});
}
}
}
}
}
int res = 1e18;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
res = min(res, dist[bx][by][i]);
}
if (res == 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f or res == 1e18) res = -1;
cout << res << nline;
}
void solve(int Case) {
cin >> n;
cin >> ax >> ay >> bx >> by;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> (s[i] + 1);
}
bfs(ax, ay);
}
F:

每个字符集可以扩展的有\(s[i]^{l}\),然后按照容斥原理减去相同的部分
code:
int qmi(int a, int b, int p) {
int res = 1 % p;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % p;
a = a * a % p;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void solve(int Case) {
int n, l;
cin >> n >> l;
int res=0;
vector<string> s(n);
for (auto &i : s) {
cin >> i;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 1 << n; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
vector<int> v(26);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i >> j & 1) {
for (auto it : s[j]) {
v[it-'a']++;
}
}
cnt += (i >> j & 1);
}
int sum = 0;
for (auto j : v) if (j == cnt) sum++;
sum = qmi(sum, l, mod);
if (cnt & 1) {
res += sum;
res %= mod;
} else {
res -= sum;
res = (res % mod + mod) % mod;
}
}
cout << res%mod << nline;
}


