Unity ugui拖动控件(地图模式与物件模式)
拖动在游戏中使用频繁,例如将装备拖动到指定的快捷栏,或者大地图中拖动以查看局部信息等。
Unity的EventSystems中可以直接继承几个接口来实现拖动功能,如下:
namespace UnityEngine.EventSystems { public interface IBeginDragHandler : IEventSystemHandler { void OnBeginDrag(PointerEventData eventData); } } namespace UnityEngine.EventSystems { public interface IDragHandler : IEventSystemHandler { void OnDrag(PointerEventData eventData); } } namespace UnityEngine.EventSystems { public interface IEndDragHandler : IEventSystemHandler { void OnEndDrag(PointerEventData eventData); } }
他们分别代表拖动开始,持续和结束时的处理方法。然而遗憾的是,每有一个要拖动的物件对象,都需要重新写一遍如何去处理它们,而大部分时候拖动的功能都相对通用,一般就是根据你鼠标或者手指滑动的方向对应的移动物体的方向,只有在拖动结束的时候可能需要额外判断一下物体的状态,例如是不是在指定的范围内不是的话可能需要复位,是的话可能增加了某项属性或者完成了一些其他功能,这时才是因情况而异。基于这样的思考,考虑将一些通用的拖动实现过程再封装一下,只留一个拖动结束后的委托用于外部调用即可,这样省去了每次都写一遍地图拖动时如何移动,拖动到边界了如何判断等。
幸运的是,Unity在EventTrigger中已经包含了拖动的事件,具体如何动态添加EventTrigger的侦听可以详细见上一篇随笔的末尾处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/koshio0219/p/12808063.html
在上面的基础上参加一个新的扩展方法:
1 public static void AddDragListener(this Canvas canvas, Component obj, DragMode mode, UnityAction complete, float speed = 1f) 2 { 3 var dragable = obj.gameObject.GetOrAddComponent<Dragable>(); 4 dragable.Init(mode,speed); 5 6 canvas.AddTriggerListener(obj, EventTriggerType.BeginDrag, dragable.OnBeginDrag); 7 canvas.AddTriggerListener(obj, EventTriggerType.Drag, dragable.OnDrag); 8 canvas.AddTriggerListener(obj, EventTriggerType.EndDrag, (x) => dragable.OnEndDrag(x, complete)); 9 } 10 11 public static void RemoveDragListener(this Canvas canvas, Component obj) 12 { 13 canvas.RemoveTriggerListener(obj); 14 }
调用时如下:
1 //添加 2 Canvas.AddDragListener(View.Map, DragMode.Map, OnDragComplete); 3 4 //处理 5 private void OnDragComplete() 6 { 7 //Do something else... 8 } 9 10 //移除 11 Canvas.RemoveDragListener(View.Map);
Dragable类就是重新封装过的一个专门用于处理拖动的类,外部使用它时不需要了解任何它的实现细节,而且使用时也简单了许多,什么都不用关心,直接添加侦听即可,不用再像原来一样还要继承三个接口分别写。
当然了,接下来就是要讨论Dragable这个类具体的实现方式,它需要处理通用的拖动操作,首先就是能让拖的物体动起来,其次就是不能乱动,到了拖动范围边缘就不能再朝那个方位动了。
值得注意的是,拖动物件和拖动地图一般是不同的,因为在拖动物件时,整个物件的轮廓范围都应该保持在拖动范围之内,而拖动地图时则完全相反,一般地图大于整个范围才需要拖动来看,所以要保证地图边缘永远大于拖动范围。
见下图:
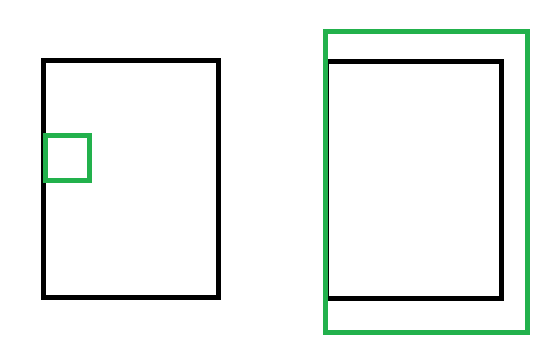
假设上图中黑色框代表拖动范围,同样贴近范围左边缘的情况下,左图的物件不能再往向左的方向拖动,而右图的地图则不能再往向右的方向拖动。
分别定义两种拖动模式如下,在初始化中可以设置模式与拖动速度:
1 public DragMode DragMode = DragMode.Map; 2 [Range(0.1f, 1.9f)] 3 public float DragSpeed = 1f; 4 5 public void Init(DragMode dragMode,float dragSpeed=1f) 6 { 7 DragMode = dragMode; 8 DragSpeed = dragSpeed > 1.9f ? 1.9f : dragSpeed < 0.1f ? 0.1f : dragSpeed; 9 }
1 public enum DragMode 2 { 3 Map, 4 Obj 5 }
拖动开始时:
1 Vector2 lastPos; 2 RectTransform rt; 3 Vector2 lastAnchorMin; 4 Vector2 lastAnchorMax; 5 6 public void OnBeginDrag(BaseEventData data) 7 { 8 //将基类的Data转化为对应子类 9 var d = data as PointerEventData; 10 //初始化屏幕位置 11 lastPos = d.position; 12 13 rt = GetComponent<RectTransform>(); 14 lastAnchorMin = rt.anchorMin; 15 lastAnchorMax = rt.anchorMax; 16 17 //将锚框设置为四周扩展类型的预设,方便后续判断和边缘范围的距离 18 rt.SetRtAnchorSafe(Vector2.zero, Vector2.one); 19 }
有一个位置需要注意,动态改变锚框时Unity并不会像是在编辑器中一样友好帮你自动计算RectTransform,而是会各种乱,位置也可能不对了,大小也可能不对了,所以这里写一个扩展方法进行安全改变锚框:
1 public static void SetRtAnchorSafe(this RectTransform rt, Vector2 anchorMin, Vector2 anchorMax) 2 { 3 if (anchorMin.x < 0 || anchorMin.x > 1 || anchorMin.y < 0 || anchorMin.y > 1 || anchorMax.x < 0 || anchorMax.x > 1 || anchorMax.y < 0 || anchorMax.y > 1) 4 return; 5 6 var lp = rt.localPosition; 7 //注意不要直接用sizeDelta因为该值会随着anchor改变而改变 8 var ls = new Vector2(rt.rect.width, rt.rect.height); 9 10 rt.anchorMin = anchorMin; 11 rt.anchorMax = anchorMax; 12 13 //动态改变anchor后size和localPostion可能会发生变化需要重新设置 14 rt.SetSizeWithCurrentAnchors(RectTransform.Axis.Horizontal, ls.x); 15 rt.SetSizeWithCurrentAnchors(RectTransform.Axis.Vertical, ls.y); 16 rt.localPosition = lp; 17 }
在拖动的过程中最重要的是要检测是否到达父物体设置的拖动范围,只有该方向上没有到达边缘才能朝这个方向移动:
1 public void OnDrag(BaseEventData data) 2 { 3 var d = data as PointerEventData; 4 //一帧内拖动的向量 5 Vector2 offse = d.position - lastPos; 6 7 //检测拖动的方向与边缘的关系 8 if (CheckDragLimit(offse)) 9 { 10 rt.anchoredPosition += offse * DragSpeed; 11 12 //极限快速拖动时单帧拖动距离超出范围的归位检测 13 ResetRtOffset(); 14 } 15 lastPos = d.position; 16 }
1 bool CheckDragLimit(Vector2 offse) 2 { 3 bool result = false; 4 if (offse.x >= 0 && offse.y >= 0) 5 { 6 //向右上拖动 7 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMin.x < 0 && rt.offsetMin.y < 0 : 8 rt.offsetMax.x < 0 && rt.offsetMax.y < 0; 9 } 10 else if (offse.x >= 0 && offse.y < 0) 11 { 12 //向右下拖动 13 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMin.x < 0 && rt.offsetMax.y > 0 : 14 rt.offsetMax.x < 0 && rt.offsetMin.y > 0; 15 16 } 17 else if (offse.x < 0 && offse.y >= 0) 18 { 19 //向左上拖动 20 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMax.x > 0 && rt.offsetMin.y < 0 : 21 rt.offsetMin.x > 0 && rt.offsetMax.y < 0; 22 } 23 else if (offse.x < 0 && offse.y < 0) 24 { 25 //向左下拖动 26 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMax.x > 0 && rt.offsetMax.y > 0 : 27 rt.offsetMin.x > 0 && rt.offsetMin.y > 0; 28 } 29 return result; 30 }
先判断拖动的方向,再根据拖动的方向结合拖动模式和相对边缘的偏移来判断是否还能朝对应方向拖动。
如果需要在全屏范围内拖动,其上的父物体层都需要四周扩展类型的锚框预设且切合屏幕边缘。
这里的offsetMin和offsetMax并不完全是对应Unity面板上的以下四个值,需要特别注意,网上的很多说法都存在一些未有考虑全面的地方:
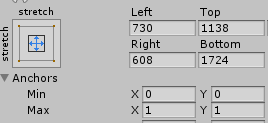
比如上面这样的数据,offsetMin实际上的(730,1724),但offsetMax则是(-608,-1138),这里不注意可能会出现很多错误。
那为什么会是这样呢,其实那就要看offsetMin和offsetMax实际代表的是什么,他们分别是以其父物体大小的范围的左下,右上为原点,右,上分别为X轴Y轴正方向得出的偏移值。
注意,无论是offsetMin还是offsetMax都是以右上为X轴和Y轴的正方向作为计算标准的,只不过原点不同。
然而恶意的是,在ugui的编辑面板中却是用的边到边的距离,故而对于左下的点不会产生任何影响,但对于右上的点就会变为其相反数。
有时检测边缘也有丢失的情况,那就是单帧拖动的速度过快了,例如上一帧还远远不到边缘,下一帧已经超出很远,这时就需要对超出的部分进行重新复位到边缘:
1 void ResetRtOffset() 2 { 3 switch (DragMode) 4 { 5 case DragMode.Map: 6 if (rt.offsetMin.x > 0) 7 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMin.x, 0); 8 9 if (rt.offsetMin.y > 0) 10 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMin.y); 11 12 if (rt.offsetMax.x < 0) 13 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMax.x, 0); 14 15 if (rt.offsetMax.y < 0) 16 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMax.y); 17 break; 18 case DragMode.Obj: 19 if (rt.offsetMin.x < 0) 20 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMin.x, 0); 21 22 if (rt.offsetMin.y < 0) 23 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMin.y); 24 25 if (rt.offsetMax.x > 0) 26 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMax.x, 0); 27 28 if (rt.offsetMax.y > 0) 29 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMax.y); 30 break; 31 } 32 }
归为操作实际就是一个平移变换,超过多少就对应方位平移多少,这样即使一帧内拖动的距离远超过了边缘,也只能到达紧紧贴合边缘的程度。
拖动完成后,复位拖动前的锚框预设,执行整个过程完成后的委托:
1 public void OnEndDrag(BaseEventData data,UnityAction complete) 2 { 3 //还原拖动之前的预设 4 rt.SetRtAnchorSafe(lastAnchorMin, lastAnchorMax); 5 complete(); 6 }
当然了,如果真的遇到拖动过程中也需要执行个性化命令,这时也可考虑自行添加其他委托。
完整Dragable脚本:

1 using UnityEngine; 2 using UnityEngine.EventSystems; 3 using UnityEngine.Events; 4 5 public enum DragMode 6 { 7 Map, 8 Obj 9 } 10 11 public class Dragable : MonoBehaviour 12 { 13 public DragMode DragMode = DragMode.Map; 14 [Range(0.1f, 1.9f)] 15 public float DragSpeed = 1f; 16 17 public void Init(DragMode dragMode,float dragSpeed=1f) 18 { 19 DragMode = dragMode; 20 DragSpeed = dragSpeed > 1.9f ? 1.9f : dragSpeed < 0.1f ? 0.1f : dragSpeed; 21 } 22 23 Vector2 lastPos; 24 RectTransform rt; 25 Vector2 lastAnchorMin; 26 Vector2 lastAnchorMax; 27 28 public void OnBeginDrag(BaseEventData data) 29 { 30 //将基类的Data转化为对应子类 31 var d = data as PointerEventData; 32 //初始化屏幕位置 33 lastPos = d.position; 34 35 rt = GetComponent<RectTransform>(); 36 lastAnchorMin = rt.anchorMin; 37 lastAnchorMax = rt.anchorMax; 38 39 //将锚框设置为四周扩展类型的预设,方便后续判断和屏幕边缘的距离 40 rt.SetRtAnchorSafe(Vector2.zero, Vector2.one); 41 } 42 43 public void OnDrag(BaseEventData data) 44 { 45 var d = data as PointerEventData; 46 //一帧内拖动的向量 47 Vector2 offse = d.position - lastPos; 48 49 //检测拖动的方向与边缘的关系 50 if (CheckDragLimit(offse)) 51 { 52 rt.anchoredPosition += offse * DragSpeed; 53 54 //极限快速拖动时单帧拖动距离超出范围的归位检测 55 ResetRtOffset(); 56 } 57 lastPos = d.position; 58 } 59 60 public void OnEndDrag(BaseEventData data,UnityAction complete) 61 { 62 //还原拖动之前的预设 63 rt.SetRtAnchorSafe(lastAnchorMin, lastAnchorMax); 64 complete(); 65 } 66 67 bool CheckDragLimit(Vector2 offse) 68 { 69 bool result = false; 70 if (offse.x >= 0 && offse.y >= 0) 71 { 72 //向右上拖动 73 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMin.x < 0 && rt.offsetMin.y < 0 : 74 rt.offsetMax.x < 0 && rt.offsetMax.y < 0; 75 } 76 else if (offse.x >= 0 && offse.y < 0) 77 { 78 //向右下拖动 79 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMin.x < 0 && rt.offsetMax.y > 0 : 80 rt.offsetMax.x < 0 && rt.offsetMin.y > 0; 81 82 } 83 else if (offse.x < 0 && offse.y >= 0) 84 { 85 //向左上拖动 86 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMax.x > 0 && rt.offsetMin.y < 0 : 87 rt.offsetMin.x > 0 && rt.offsetMax.y < 0; 88 } 89 else if (offse.x < 0 && offse.y < 0) 90 { 91 //向左下拖动 92 return DragMode == DragMode.Map ? rt.offsetMax.x > 0 && rt.offsetMax.y > 0 : 93 rt.offsetMin.x > 0 && rt.offsetMin.y > 0; 94 } 95 return result; 96 } 97 98 void ResetRtOffset() 99 { 100 switch (DragMode) 101 { 102 case DragMode.Map: 103 if (rt.offsetMin.x > 0) 104 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMin.x, 0); 105 106 if (rt.offsetMin.y > 0) 107 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMin.y); 108 109 if (rt.offsetMax.x < 0) 110 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMax.x, 0); 111 112 if (rt.offsetMax.y < 0) 113 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMax.y); 114 break; 115 case DragMode.Obj: 116 if (rt.offsetMin.x < 0) 117 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMin.x, 0); 118 119 if (rt.offsetMin.y < 0) 120 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMin.y); 121 122 if (rt.offsetMax.x > 0) 123 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(rt.offsetMax.x, 0); 124 125 if (rt.offsetMax.y > 0) 126 rt.anchoredPosition -= new Vector2(0, rt.offsetMax.y); 127 break; 128 } 129 } 130 }





