jmeter学习记录--05--Beanshell2
学习beanshell时有不少的例子、遇到不少问题。在此记录下。
测试实例列表
A1:使用Beanshell请求作为测试请求
一个打包的Jar包,直接对其内的方法进行测试。
第一步:将接口jar包要放到%JMETER_HOME%\lib目录
第二步:编写请求。
A2:共享线程变量
JMeter中线程间共享变量可以通过定义属性值来完成,JMeter启动时会读取一些属性文件,比如jmeter.properties、user.properties,这些属性值是可以增加的,也可以修改的,通过BeanShell可以对其进行更改。
定义变量:以BeanShell Sampler为例,在其中通过props.put()来增加属性,props.get()来获取属性。如:props.put("param_a","root");
使用变量:在后续请求如Java请求中通过 ${__property(【属性名称】,,)}来获取。如:${__property(param_a,,)} 来使用。
示例:
在线程组1中使用__setProperty定义属性值(全局变量),将所需变量值${param_A}设置为属性值。
String token = bsh.args[0];//输入值为assfd //第一种写法,测试时token与${token}两种写法都无法调用变量 ${__setProperty(param_A,${token},)}; //第二种写法 props.put("param_B",token);
debug请求中,打开属性与变量。查看结果树中,属性值结果为:
param_A=${token}
param_B=assfd
在线程组2,beanshell中输入
${__property(param_A,GROUP2_A,)};
${__property(param_B,GROUP2_B,)};
debug请求中,打开属性与变量。查看结果树中,变量值结果为:
GROUP2_A=${token}
GROUP2_B=assfd
疑问:1)${__setProperty(param_A,token,)}; 这里token是变量,但是实际是将这个字符串拷贝存到param_A属性里的了。换成${token}也是如此。
2)props.put添加的属性值,不会写到jmeter.properties文件里,只在当前测试计划中生效。比如当前加了一个属性A,执行过后在当前测试计划中会一直存在,即使beanshell文件中已无这个属性值的定义也是如此。重新打开一个测试计划,属性A就不存在了。
A3:使用 BeanShell 断言判断用例成功与否
用beanshell做断言结果判断

log.info(SampleResult.getResponseDataAsString()); boolean result = false; String uid = vars.get("uid"); String token = vars.get("token"); if (SampleResult.getResponseCode().equals("200") && token.contains(uid)) { result = true; } else { result = false; } SampleResult.setSuccessful(result);
http://www.cnblogs.com/xxyBlogs/p/5966194.html
A4:处理请求或结果,如对base64加解密,URL转码等(jmeter 3.2)
base64加解密,使用函数助手中的两个函数。
在beanshell中添加
//加密,encode为加密后字符串变量 ${__base64Encode(“haishizi”,encode)}; //解密,对加密胡变量做解密处理 ${__base64Decode(${encode},decode)};
debug sampler对应测试结果为:
decode="haishizi"
encode=ImhhaXNoaXppIg==
如果加密函数中${__base64Encode(“haishizi”,encode)};修改为${__base64Encode(haishizi,encode)};
对应测试结果为:
decode=haishizi
encode=aGFpc2hpemk=
A5:自定义时间格式 Jmeter-BeanShell的使用介绍
普通方式获取时间戳
在Jmeter中,可以利用${__time(,)}时间戳函数来获取十位的时间戳:
{
"time":"${__time(yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss,)}"
}
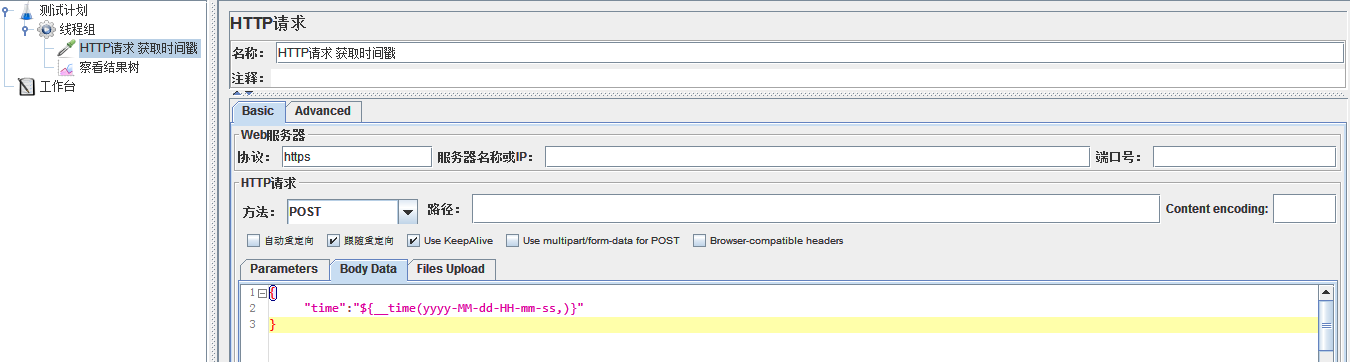
直接执行后,在“查看结果树”中显示的是:

BeanShell自定义
但是在具体使用中,有时候需要传送较为复杂的时间格式,如“2016-07-31T21:24:07.581Z”此时不能直接调用time函数,因此可以利用BeanShell获取当前时间。

import java.util.*; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; String str1 = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd")).format(new Date()); String str2 = (new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss.SSS")).format(new Date()); String str3 = (new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss")).format(new Date()); vars.put("str_A",str1+"T"+str2+"2"); vars.put("str_B",str1+"T"+str3+".000"+"2"); log.info("\n"+str_A);//直接获取不生效,日志打印为void log.info("\n"+${str_A});//直接获取不生效,日志打印为空
若使用该程序段,在Jmeter中调用变量${str_A}可以获得yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ格式的时间,调用变量${str_B}可以获得yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ格式的时间。
http请求中输入,选择post方法。
{ "time":"${__time(yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss,)}" "time2":${str_A} "time3":${str_B} "time4":${str1} }
查看结果树中结果为:
POST data:
{
"time":"2017-07-26-18-23-56"
"time2":2017-07-26T18:23:56.8692
"time3":2017-07-26T18:23:56.0002
"time4":${str1}
}
疑问:为何str1字符串直接日志输出或使用变量不可以,将其转化为内置变量就可正常使用?
A6:把测试结果放到一个excel文件中


FileWriter fstream = new FileWriter("d:\\a.csv",true); BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fstream); out.write("uid"+","+vars.get("uid")+","); out.write("mobileNumber"+","+vars.get("mobileNumber")+","); out.write("inviteCode"+","+vars.get("inviteCode")+","); out.write("\n"); //out.write(vars.get("inviteCode")); //out.write(System.getProperty("line.separator")); out.close(); fstream.close();
A7: 对redis的操作

import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; try{ Jedis jedis = new Jedis("${host}",${port},10000); if (jedis != null) { System.out.println("connect to redis server sucessfully"); } String hostCount = jedis.get("api_index_ACount"); String videoCount = jedis.get("api_index_BCount"); System.out.println(ACount); System.out.println(BCount); vars.put("hostCount",ACount); vars.put("videoCount",BCount); jedis.close(); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); }

import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; Jedis jedis = new Jedis("${host}",${port},10000); String ACount = jedis.get("api_index_ACount"); String BCount = jedis.get("api_index_BCount"); jedis.close(); String response_data = prev.getResponseDataAsString(); if(response_data.contains(ACount)&&response_data.contains(BCount)){ FailureMessage="success"; } else{ Failure=true; FailureMessage="fail:"+ACount+""+BCount; }
问题列表
Q1:自定义函数的变量赋值时报错(jmeter 3.2)---未解决
变量定义有3种情况:
第一种:param_A,直接通过vars.put来定义参数值;
第二种:param_B,通过bsh.args[0]获取到传入的参数值123,将其赋值。
第三种:通过函数变量来实现,将字符串abc变量的值赋值给unique_id。
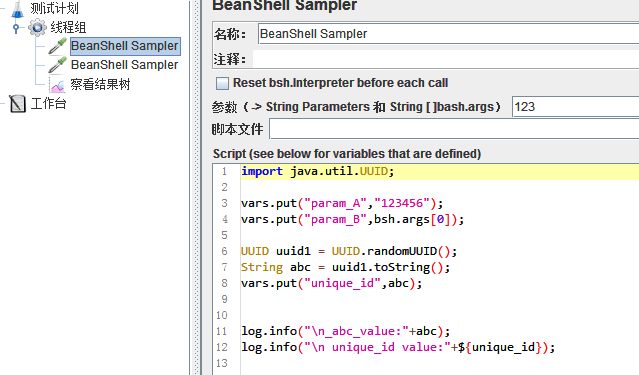

import java.util.UUID; vars.put("param_A","123456"); vars.put("param_B",bsh.args[0]); UUID uuid1 = UUID.randomUUID(); String abc = uuid1.toString(); vars.put("unique_id",abc); log.info("\n_abc_value:"+abc); log.info("\n unique_id value:"+${unique_id});
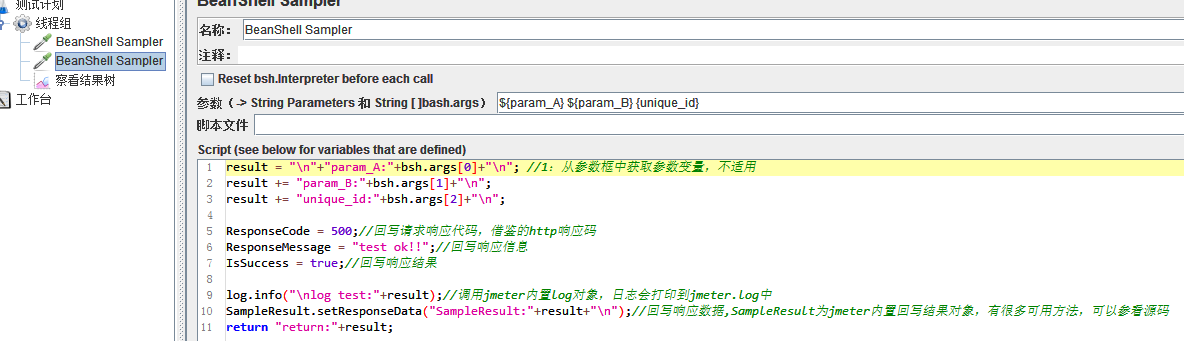

result = "\n"+"param_A:"+bsh.args[0]+"\n"; //1:从参数框中获取参数变量,不适用 result += "param_B:"+bsh.args[1]+"\n"; result += "unique_id:"+bsh.args[2]+"\n"; ResponseCode = 500;//回写请求响应代码,借鉴的http响应码 ResponseMessage = "test ok!!";//回写响应信息 IsSuccess = true;//回写响应结果 log.info("\nlog test:"+result);//调用jmeter内置log对象,日志会打印到jmeter.log中 SampleResult.setResponseData("SampleResult:"+result+"\n");//回写响应数据,SampleResult为jmeter内置回写结果对象,有很多可用方法,可以参看源码 return "return:"+result;
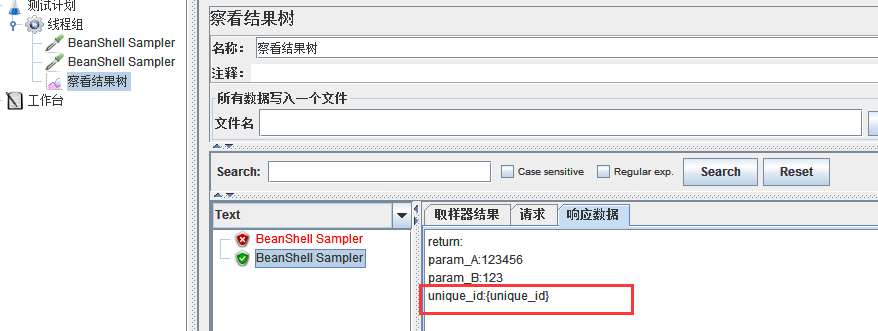
{unique_id}值并未取实际的参数值。看log日志:
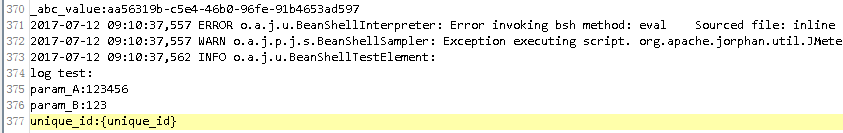
2017-07-12 09:00:53,939 ERROR o.a.j.u.BeanShellInterpreter: Error invoking bsh method: eval Sourced file: inline evaluation of: ``import java.util.UUID; vars.put("param_A","123456"); vars.put("param_B",bsh.arg . . . '' : Attempt to access property on undefined variable or class name
可看到abc字符串取值还是正常的,但是将其赋值unique_id后报错。
vars:即JMeterVariables,操作jmeter变量,这个变量实际引用了JMeter线程中的局部变量容器(本质上是Map),常用方法:
a) vars.get(String key):从jmeter中获得变量值
b) vars.put(String key,String value):只能用String类型的参数,数据存到jmeter变量中,其作用可简单理解为赋值操作:key=value,更多方法可参考:org.apache.jmeter.threads.JMeterVariables
Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
其中有这行代码时总会提示:
2019-01-30 16:04:54,702 ERROR o.a.j.u.BeanShellInterpreter: Error invoking bsh method: eval In file: inline evaluation of: ``import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils; //导入md5加密的包 import java. . . . '' Encountered "," at line 12, column 11.
2019-01-30 16:04:54,702 WARN o.a.j.p.j.s.BeanShellSampler: Exception executing script. org.apache.jorphan.util.JMeterException: Error invoking bsh method: eval In file: inline evaluation of: ``import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils; //导入md5加密的包 import java. . . . '' Encountered "," at line 12, column 11.
将这行修改为:Map paramMap = new HashMap(); 后解决
后续用put方法将信息存到paramMap中。但是如果引入的jar中有代码也是使用的map传参,而beanshell中如果调用这个方法时也会报错。
beanshell调用:
String sign = MD5Util.proSign(paramMap,secret);
jar包中源码: public String proSign(Map<String, String> params, String secret)
报错: 2019-01-30 16:38:53,914 ERROR o.a.j.u.BeanShellInterpreter: Error invoking bsh method: eval Sourced file: inline evaluation of: ``import com.chain.*; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; import java . . . '' : Typed variable declaration : Cannot reach instance method: proSign( java.util.Map, java.lang.String ) from static context: com.test.MD5Util 2019-01-30 16:38:53,914 WARN o.a.j.p.j.s.BeanShellSampler: Exception executing script. org.apache.jorphan.util.JMeterException: Error invoking bsh method: eval Sourced file: inline evaluation of: ``import com.test.*; '' : Typed variable declaration : Cannot reach instance method: proSign( java.util.Map, java.lang.String ) from static context: com.test.MD5Util
这种调用方式,没有解决。用其他方式暂时规避了。
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/linbo3168/p/9288926.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35304570/article/details/80858494




