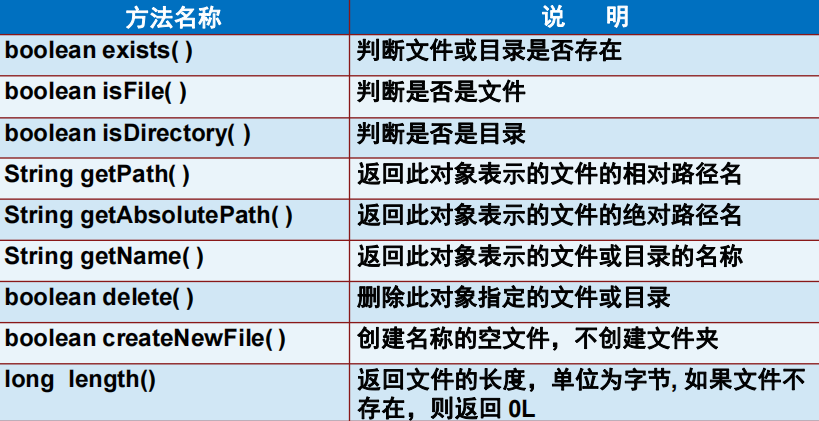
20、File类、io流(字节流\字符流\输入流\输出流\标准输入\标准输出\打印流)
一、File类
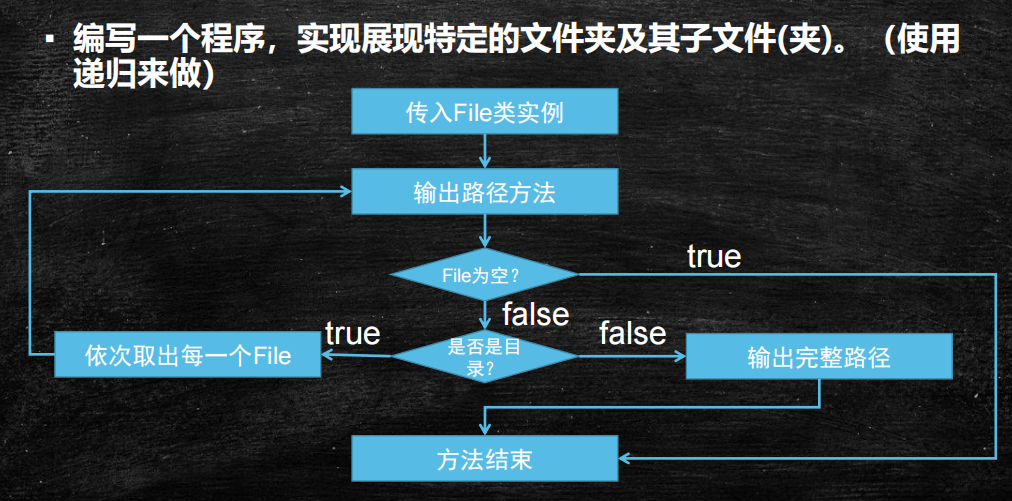
public class FileDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("src/abc.txt"); //创建文件 try { file.createNewFile(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //判断文件的属性,都会返回boolean类型的值 file.canExecute(); file.canRead(); file.canWrite(); //判断当前文件是否存在 System.out.println(file.exists()); //获取文件的名称 System.out.println(file.getName()); //获取文件的绝对路径 System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); //获取文件的父路径名称,如果文件的路径中只包含文件名称,则显示空 System.out.println(file.getParent()); //返回文件绝对路径的规范格式 System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath()); //返回操作系统的文件分割符 System.out.println(File.separator); //无论当前文件是否存在,只要给定具体的路径,都可以返回相应的路径名称 File file2 = new File("c:/a/b/c"); System.out.println(file2.getAbsolutePath()); //判断文件是否是文件或者目录 System.out.println(file2.isDirectory()); System.out.println(file2.isFile()); // String[] list = file2.list(); // for(String str:list){ // System.out.println(list.toString()); // } // System.out.println("---------------"); // File[] files = file2.listFiles(); // for(File f : files){ // System.out.println(f); // } //打印当前文件系统的所有盘符 File[] files1 = File.listRoots(); for(int i = 0;i<files1.length;i++){ System.out.println(files1[i]); } //创建单级目录 file2.mkdir(); //创建多级目录 file2.mkdirs(); //循环遍历输出C盘中的所有文件的绝对路径 //使用递归的方式 printFile(new File("D:\\Github\\javase")); } /** * * 文件在遍历的时候,会出现空指针的问题,原因在于当前文件系统受保护,某些文件没有访问权限,此时会报空指针异常 * @param file */ public static void printFile(File file){ if(file.isDirectory()){ File[] files = file.listFiles(); for(File f:files){ printFile(f); } }else{ System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); } } }
二、IO流的原理及概念
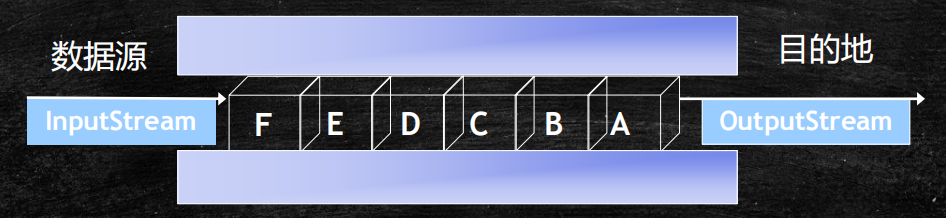
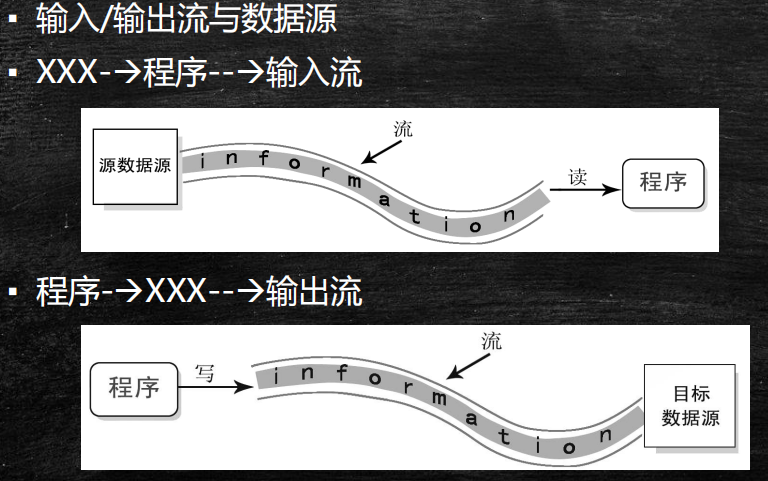
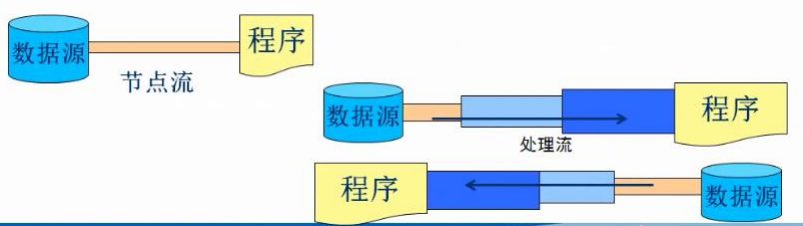
/** * 在java中需要读写文件中的数据的话,需要使用流的概念 * 流表示从一个文件将数据返送到另一个文件,包含一个流向的问题 * 最终需要选择一个参照物:当前程序作为参照物 * 从一个文件中读取数据到程序叫做输入流 * 从程序输出数据到另一个文件叫做输出流 * * 注意:当编写io流的程序的时候一定要注意关闭流 * 步骤; * 1、选择合适的io流对象 * 2、创建对象 * 3、传输数据 * 4、关闭流对象(占用系统资源) */

三、IO流的分类
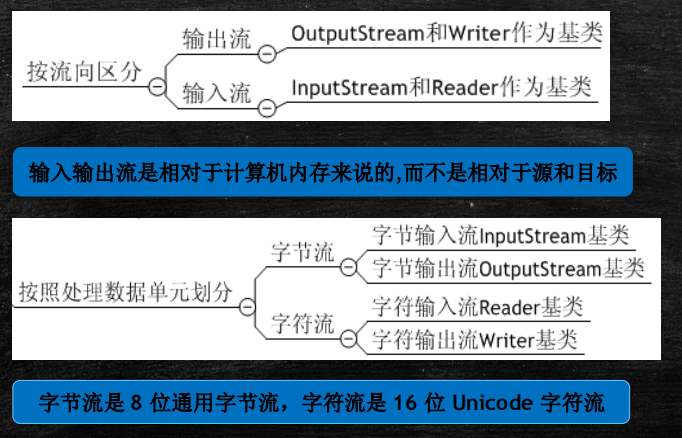
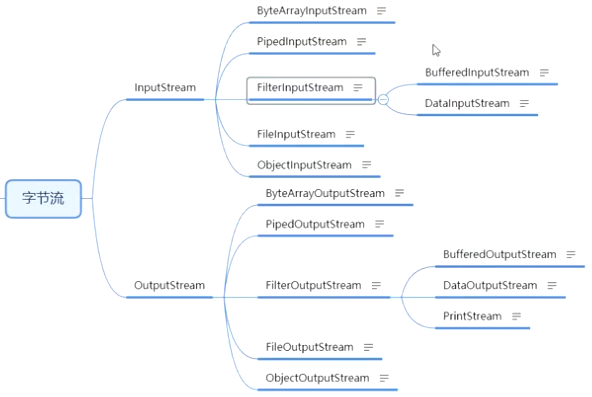
1、InputStream
public class StreamDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { InputStream inputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); int read = 0; //循环输出所有的字节, while((read = inputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)read); } // int read = inputStream.read(); // System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/* * 存在问题,每次只能读取一个字节,效率比较低,需要循环N多次 * */
缓冲区的方式
public class StreamDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { InputStream inputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); int length = 0; //添加缓冲区的方式进行读取,每次会将数据添加到缓冲区中,当缓冲区满了之后,一次 读取,而不是每一个字节进行读取 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; while((length = inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,length)); } // int read = inputStream.read(); // System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
从哪读到哪
public class StreamDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { InputStream inputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); int length = 0; //添加缓冲区的方式进行读取,每次会将数据添加到缓冲区中,当缓冲区满了之后,一次 读取,而不是每一个字节进行读取 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; while((length = inputStream.read(buffer,5,5))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(buffer,5,length)); } // int read = inputStream.read(); // System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
2、OutputStream
public class OutputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("aaa.txt"); OutputStream outputStream = null; try { outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); outputStream.write(99); outputStream.write("\r\nmashibing".getBytes()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
文件的复制代码
public class CopyFile { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义源数据文件 File src = new File("abc.txt"); //定义目的数据文件 File dest = new File("aaa.txt"); //创建输入流对象 InputStream inputStream = null; //创建输出流对象 OutputStream outputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(src); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dest); //带缓存的输入输出方式 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int length = 0; //完成数据传输的过程 while((length = inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ outputStream.write(buffer); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
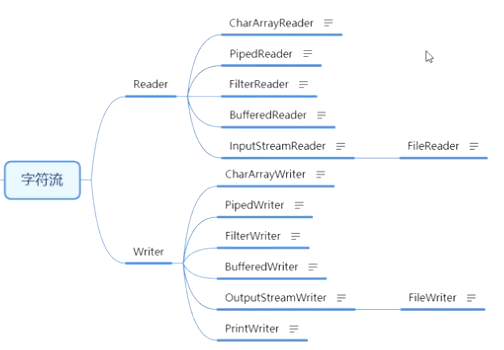
3、Reader、Writer
3.1、Reader
public class ReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Reader reader = null; try { reader = new FileReader("abc.txt"); int read = reader.read(); System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/** * 字符流可以直接读取中文汉字,而字节流在处理的时候会出现中文乱码 */
public class ReaderDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Reader reader = null; try { reader = new FileReader("abc.txt"); int read = 0; while((read = reader.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)read); } // int read = reader.read(); // System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class ReaderDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Reader reader = null; try { reader = new FileReader("abc.txt"); int length = 0; char[] chars = new char[1024]; //添加缓冲区 while((length = reader.read(chars))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(chars,0,length)); } // int read = reader.read(); // System.out.println((char)read); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3.2、Writer
/* * 什么时候需要加flush,什么时候不加flush, 两个桶通过水管连接,flush就是水管里的那部分水 * 最保险的方式,在输出流关闭之前每次都flush一下,然后再关闭 * 当某一个输出流对象中带有缓冲区的时候,就需要进行flush,不建议大家去记住每个输出流的分类 * * */
public class WriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("writer.txt"); Writer writer = null; try { writer = new FileWriter(file); writer.write("www.mashibing.com"); writer.write("马士兵教育"); writer.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3.3、读取一张图片,并复制
处理纯文本一般不会有问题,处理图片视频就不要用字符处理了,用字节处理
public class CopyPicture { public static void main(String[] args) { /* FileReader reader = null; FileWriter writer = null; try { reader = new FileReader("1.jpg"); writer = new FileWriter("2.jpg"); int length = 0; char[] chars = new char[1024]; while((length = reader.read(chars))!=-1){ writer.write(chars); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }*/ FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.jpg"); fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("3.jpg"); int length = 0; byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; while((length = fileInputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ fileOutputStream.write(buffer); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4、InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer子类


FileInputStream\FileOutputStream\FileReader\FileWriter上面说过了,看下其他的
我们可以观察到
FileInputStream\FileOutputStream属于InputStream和OutputStream
FileReader\FileWriter 不直接属于Reader和Writer 中间隔了一层
如果我知道你就是要传纯文本,就可以用下面这种处理流方式读取字节提升效率
4.1、OutputStreamWriter
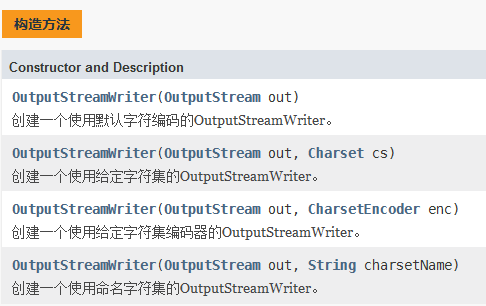
套了一层字节流,可以指定字符集 utf-8 gbk
public class OutputStreamWriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("abc.txt"); OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream,"iso8859-1"); outputStreamWriter.write(99); outputStreamWriter.write("马士兵教育"); outputStreamWriter.write("abcdefg",0,5); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end-time); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭流对象的时候,建议按照创建的顺序的逆序来进行关闭 try { outputStreamWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
是以字符为单位处理的,而不是字节了
4.2、InputStreamReader
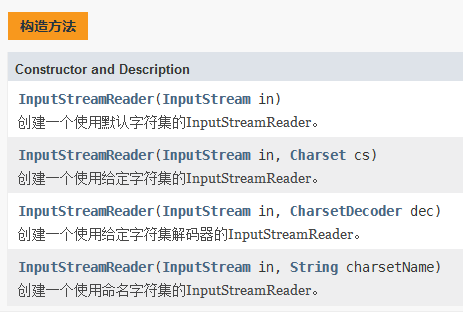
public class InputStreamReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("abc.txt"); FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream); //为什么没有用循环的方式,因为数据比较少,无法占用1024个缓存区,只需要读取一次即可 char[] chars = new char[1024]; int length = inputStreamReader.read(chars); System.out.println(new String(chars,0,length)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStreamReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
其他字节流
4.3、ByteArrayInputStream
包含一个内部缓存区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节
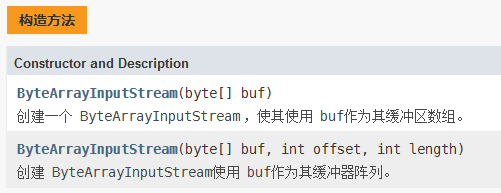
public class ByteArrayInputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "www.mashibing.com"; byte[] buffer = str.getBytes(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = null; byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer); int read = 0; while((read = byteArrayInputStream.read())!=-1){ byteArrayInputStream.skip(4); /间隔4 System.out.println((char)read); } try { byteArrayInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.4、ByteArrayOutputStream
public class ByteArrayOutputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = null; byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byteArrayOutputStream.write(123); try { byteArrayOutputStream.write("www.mashibing.com".getBytes()); System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { byteArrayOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.5、PipedInputStream\ PipedOutputStream
和PipedOutputStream一起使用, 实现多线程的管道通信
4.6、FilterInputStream下有两个BufferedInputStream和DataInputStream
BufferedInputStream: 用于为其他输入流提供缓存功能
InputStream处理比较麻烦, 因为要自己创建缓冲区, BufferedInputStream就不需要自己创建了
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("abc.txt"); FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream); int read = 0; while((read = bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){ bufferedInputStream.skip(10); System.out.print((char)read); } ; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class BufferedOutputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("123.txt"); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =null; try { fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream); bufferedOutputStream.write(98); bufferedOutputStream.write("www.baidu.com".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.7、DataInputStream\DataOutputStream
用来装饰其他输入流, 以从底层输入流中读取基本java数据类型
写入的顺序要和读取的顺序一致
public class DataDemp { public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; DataInputStream dataInputStream = null; DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { //向文件中写入数据流 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("abc.txt"); dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(fileOutputStream); dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true); dataOutputStream.writeInt(123); dataOutputStream.writeShort(344); dataOutputStream.writeDouble(3.14); dataOutputStream.writeUTF("www.mashibing.com马士兵教育"); //从文件读取数据流 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fileInputStream); System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean()); System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt()); System.out.println(dataInputStream.readShort()); System.out.println(dataInputStream.readDouble()); System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.8、ObjectInputStream\ObjectOutputStream
ObjectInputStream: 对以前使用ObjectOutputStream写入的基本数据和对象进行反序列化
ObjectOutputStream: 将java对象基本数据和图形写入OutputStream
怎么保存一个对象???
/** * 1、如果需要将对象通过io流进行传输,那么必须要实现序列化接口 * 2、当前类中必须声明一个serialVersionUID的值,值为多少无所谓,但是要有 * 3、transient:使用此关键字修饰的变量,在进行序列化的时候,不会被序列化 * */
public class Person implements Serializable { long serialVersionUID = 1L; // 写什么都行 但是必须传输 private int id; private String name; transient private String pwd; public Person() { } public Person(int id, String name, String pwd) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' + '}'; } }
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream); System.out.println(objectInputStream.readUTF()); Object object = objectInputStream.readObject(); if(object instanceof Person){ Person p = (Person) object; System.out.println(p); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { objectInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null; try { fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("abc.txt"); objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream); objectOutputStream.writeUTF("www.mashibing.com"); objectOutputStream.writeObject(new Person(1,"zhangsan","123456")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { objectOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.8.1、Person继承的序列化器代码是空的,怎么序列化?
其他字符流

4.9、CharArrayReader\CharArrayWriter
和ByteArrayInputStream差不多
public class CharArrayReaderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] chars = "马士兵教育".toCharArray(); CharArrayReader charArrayReader = new CharArrayReader(chars); try { int read = 0; while((read = charArrayReader.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)read); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { charArrayReader.close(); } } }
public class charArrayWriterTest { public static void main(String[] args) { CharArrayWriter charArrayWriter = new CharArrayWriter(); charArrayWriter.write(97); charArrayWriter.write(98); charArrayWriter.write(99); System.out.println(charArrayWriter); charArrayWriter.close(); } }
4.10、FilterReader
用于读取已过滤的字符流
4.10、BufferedReader\BufferedWriter
public class BufferedReaderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader reader = null; try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("aaa.txt")); String read = null; while((read = reader.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(read); }; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class BufferedWriterTest { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null; FileWriter fileWriter = null; try { fileWriter = new FileWriter(new File("abc.txt")); bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter); bufferedWriter.append("mashibing"); bufferedWriter.newLine(); bufferedWriter.append("马士兵教育"); bufferedWriter.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { fileWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { bufferedWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.10.1、类似于进入mysql输入exit退出实例
public class ExitTest { public static void main(String[] args) { InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(System.in); OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); try { String str = ""; while (!str.equals("exit")) { str = bufferedReader.readLine(); bufferedWriter.write(str); bufferedWriter.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStreamReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { outputStreamWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { bufferedReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { bufferedWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class ExitTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try( InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(System.in); OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);) { String str = ""; while (!str.equals("exit")) { str = bufferedReader.readLine(); bufferedWriter.write(str); bufferedWriter.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.10.1、要么从文件,要么从控制台,要么写死
访问百度,服务器返回,也会涉及到一个io流,也有写入写出的过程
java代码里能通过访问百度并且返回数据
public class BaiDuTest { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null; try { bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream(),"utf-8")); bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("baidu.html"))); String msg = null; while((msg = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){ bufferedWriter.write(msg); bufferedWriter.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { bufferedReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.11、PrintWriter
public class PrintStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { PrintStream printStream = null; try { // printStream = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("123.txt")); printStream = new PrintStream(System.out); printStream.write("hello mashibing".getBytes()); printStream.println(true); System.out.println(); //格式化输出 %s:字符串 %d:整数 %f:浮点数 System.out.printf("%s--%d---%.2f","abc",123,111.1111); System.err.println("mashibing"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } printStream.close(); } }
五、RandomAccessFile

public class RandomAccessFileTest { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("doc.txt"); //整个文件的大小 long length = file.length(); //规定块的大小 int blockSize = 1024; //文件可以被切分成多少个块 int size = (int)Math.ceil(length*1.0/blockSize); System.out.printf("要被切成《%d》个块",size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(blockSize>length?length:blockSize); for(int i = 0;i<size;i++){ //每次读取块的时候的起始偏移量 beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i==size-1){ actualSize = (int) length; // 最后一个块 }else{ actualSize = blockSize; length -=actualSize; } System.out.println(i+"---》起始位置是:"+beginPos+"---->读取的大小是:"+actualSize); // readSplit(i,beginPos,actualSize); } } public static void readSplit(int i,int beginPos,int actualSize){ RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null; try { randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(new File("doc.txt"),"r"); //表示从哪个偏移量开始读取数据 randomAccessFile.seek(beginPos); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length = 0; while((length = randomAccessFile.read(bytes))!=-1){ if(actualSize>length){ System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,length)); actualSize-=length; }else{ System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,actualSize)); break; } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { randomAccessFile.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }


