笔记2. 堆(优先队列)
目录
堆(优先队列)
堆的概念
- 堆是满二叉树:从左到右依次变满(一般用数组下标存储)
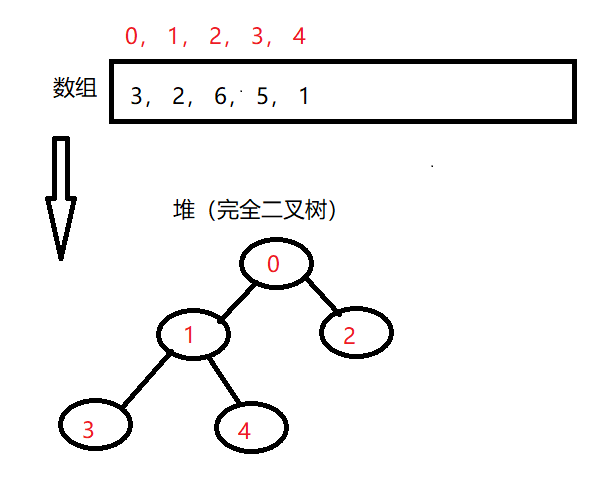
父节点和左右节点的位置
节点i位置对应的父子节点位置
父节点: (i - 1) / 2;
左子节点: 2 * i + 1
右子节点: 2 * i + 2
大根堆和小根堆
- 大根堆:每棵子树的头节点为当前树的最大值
- 小根堆:每棵子树的头节点为当前树的最小值
堆的行为:上浮(insert)、下沉(pop)
待刷的题

完全二叉树的高度
堆排序
需要两步:
- 数组array->大根堆。在这个过程中array也发生了变化,但是还未完成有序。但是大根堆的第1个元素就是array中最大的。
- 把大根堆第1个和最后一个做交换,然后heapSize--,直到heapSize为0,array中所有数据都处理完了,数组排序完成。
练习题
703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
#define Parent(i) ((i - 1) / 2)
#define Left(i) ((i * 2) + 1)
#define Right(i) ((i * 2) + 2)
/* 小根堆 */
typedef struct {
int *heap;
int heapSize;
int capacity;
} KthLargest;
int Top(KthLargest *obj)
{
return obj->heap[0];
}
void Swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void Swim(KthLargest *obj, int index)
{
int cur = index;
while (cur >= 0 && obj->heap[Parent(cur)] > obj->heap[cur]) {
Swap(&obj->heap[Parent(cur)], &obj->heap[cur]);
cur = Parent(cur);
}
}
/* 下沉:从堆的指定位置(一般是顶部),开始下沉 */
void Sink(KthLargest *obj, int index)
{
int cur = index;
int reChild = cur;
while (cur < obj->capacity) {
if (Left(cur) >= obj->capacity) {
break;
}
if (obj->heap[Left(cur)] < obj->heap[cur]) {
reChild = Left(cur);
}
if (Right(cur) < obj->capacity && obj->heap[Right(cur)] < obj->heap[Left(cur)]) {
reChild = Right(cur);
}
if (obj->heap[reChild] < obj->heap[cur]) {
Swap(&obj->heap[reChild], &obj->heap[cur]);
cur = reChild;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
void HeapAdd(KthLargest *obj, int num)
{
// printf("add num = %d, Top(obj) = %d\n", num, Top(obj));
if (obj->heapSize < obj->capacity) {
obj->heap[obj->heapSize] = num;
++(obj->heapSize);
Swim(obj, obj->heapSize - 1);
} else if (Top(obj) < num) {
obj->heap[0] = num;
Sink(obj, 0);
}
}
KthLargest* kthLargestCreate(int k, int* nums, int numsSize)
{
KthLargest *obj = malloc(sizeof(KthLargest));
obj->heap = malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
obj->heapSize = 0;
obj->capacity = k;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
HeapAdd(obj, nums[i]);
}
return obj;
}
int kthLargestAdd(KthLargest* obj, int val)
{
HeapAdd(obj, val);
return Top(obj);
}
void kthLargestFree(KthLargest* obj)
{
free(obj->heap);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your KthLargest struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest* obj = kthLargestCreate(k, nums, numsSize);
* int param_1 = kthLargestAdd(obj, val);
* kthLargestFree(obj);
*/
347. 前 K 个高频元素
#define GetParent(i) ((i - 1) / 2)
#define GetLeftChid(i) ((2 * i) + 1)
#define GetRightChild(i) ((2 * i) + 2)
// #define TopCnt(Heap *heap) ((heap)->data[0].cnt)
typedef struct HashTable {
int key; // num
int val; // 出现次数
UT_hash_handle hh;
} HashTable;
HashTable *g_hash;
typedef struct Data {
int num;
int cnt;
} Data;
typedef struct Heap {
Data *data;
int heapSize;
int capacity;
} Heap; // 小根堆
void Swap(Data *a, Data *b)
{
Data tmp;
tmp.num = a->num;
tmp.cnt = a->cnt;
(*a).num = (*b).num;
(*a).cnt = (*b).cnt;
(*b).num = tmp.num;
(*b).cnt = tmp.cnt;
}
int TopCnt(Heap *heap)
{
return heap->data[0].cnt;
}
/* 上浮:添加到堆的指定位置(一般是尾巴),然后按照小根堆依次上浮上来 */
void Swim(Heap *heap, int index)
{
while (index >= 0 && heap->data[GetParent(index)].cnt < heap->data[index].cnt) {
Swap(&heap->data[GetParent(index)], &heap->data[index]);
index = GetParent(index);
}
}
/* 下沉:从堆的指定位置(一般是顶部),开始下沉 */
void Sink(Heap *heap, int index)
{
int left, right;
int reChild;
while (index < heap->capacity) {
left = GetLeftChid(index);
if (left >= heap->capacity) {
break;
}
right = GetRightChild(index);
if (right < heap->capacity) {
reChild = heap->data[left].cnt < heap->data[right].cnt ? left : right;
} else {
reChild = left;
}
if (heap->data[reChild].cnt < heap->data[index].cnt) {
Swap(&heap->data[reChild], &heap->data[index]);
} else {
break;
}
index = reChild;
}
}
void HeapAdd(Heap *heap, int num, int cnt)
{
if (heap->heapSize >= heap->capacity) { // 如果堆没有满则无脑添加
heap->data[heap->heapSize].num = num;
heap->data[heap->heapSize].cnt = cnt;
(heap->heapSize)++;
Swim(heap, heap->heapSize - 1);
} else if (TopCnt(heap) < cnt) { // 如果堆满了,则要在堆顶元素频次小于待添加元素频次,才添加
heap->data[0].num = num;
heap->data[0].cnt = cnt;
Sink(heap, 0);
}
}
int* topKFrequent(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize)
{
// 1. 遍历数组,将每个数出现的频次存到hash表中
g_hash = NULL;
HashTable *cur = NULL;
HashTable *tmp = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
HASH_FIND_INT(g_hash, &nums[i], cur);
if (cur == NULL) {
cur = malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
cur->key = nums[i];
cur->val = 1;
HASH_ADD_INT(g_hash, key, cur);
} else {
++(cur->val);
}
}
// 2. 遍历hash表,开始往小根堆里push或pop节点
Heap *heap = malloc(sizeof(Heap));
heap->data = malloc(sizeof(Data) * k);
heap->heapSize = 0;
heap->capacity = k;
HASH_ITER(hh, g_hash, cur, tmp) {
HeapAdd(heap, cur->key, cur->val);
HASH_DEL(g_hash, cur);
}
// 3. 取出小根堆的结果存到结果数组中
*returnSize = k;
int *res = malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
res[i] = heap->data[i].num;
}
return res;
}
标签:
数据结构与算法






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)