二叉树入门到进阶——c语言刷题合集
二叉树概念
二叉树的遍历方式
DFS(前序 中序 后序遍历)
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
递归解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
#define MAX_NUM 100
void PreTra(int *arr, int *returnSize, struct TreeNode *node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
arr[(*returnSize)++] = node->val;
PreTra(arr, returnSize, node->left);
PreTra(arr, returnSize, node->right);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = 0;
int *res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NUM);
PreTra(res, returnSize, root);
return res;
}
迭代解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
#define MAX_NUM 100
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
int top = 0;
struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NUM];
stack[top++] = root;
struct TreeNode* node;
int *res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NUM);
*returnSize = 0;
while (top != 0) {
node = stack[--top];
if (node == NULL) {
break;
}
res[(*returnSize)++] = node->val;
if (node->right != NULL) {
stack[top++] = node->right;
}
if (node->left != NULL) {
stack[top++] = node->left;
}
}
return res;
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
层序遍历--队列的作用
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
#define MAX_LEN 2000
int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes)
{
*returnSize = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
int **res = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * MAX_LEN);
*returnColumnSizes = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_LEN);
struct TreeNode *node = root;
struct TreeNode *list[MAX_LEN];
int head, tail;
head = 0, tail = 0;
list[tail++] = node; // 第一次入队
int lastTail, index;
while (head != tail) {
lastTail = tail;
// 申请内存
res[(*returnSize)] = malloc(sizeof(int) * (tail - head));
(*returnColumnSizes)[(*returnSize)] = tail - head;
index = 0;
while (head < lastTail) {
// 出队
node = list[head++];
res[(*returnSize)][index++] = node->val;
if (node->left != NULL) {
list[tail++] = node->left;
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
list[tail++] = node->right;
}
}
(*returnSize)++;
}
return res;
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
二叉搜索树
概念:
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
98. 验证二叉搜索树
graph graphname {
a -- b -- c;
b -- d;
}
-
思路1:利用中序遍历,将二叉树转换为数组,然后判断数组是否有序
-
思路2:直接在递归过程中,有两个指针模拟左(pre)->中(cur)->右,左->中(pre)->右(cur)
- 陷阱:不能单纯的比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点就完事了,要比较的是左子树所有节点小于中间节点,右子树所有节点大于中间节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isOk(struct TreeNode *cur, struct TreeNode **pre)
{
if (cur == NULL) return true; // 先沉底
bool left = isOk(cur->left, pre);
if (*pre != NULL && (*pre)->val >= cur->val) {
return false;
}
// if (*pre != NULL) printf("cur=%d, pre=%d\n", cur->val, (*pre)->val);
*pre = cur;
bool right = isOk(cur->right, pre);
return left && right;
}
bool isValidBST(struct TreeNode* root)
{
struct TreeNode *pre = NULL;
return isOk(root, &pre);
}
- 思路3:迭代法,用栈模拟递归压栈和弹栈的过程
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
#define MAX_NUM 10000
bool isValidBST(struct TreeNode* root)
{
int top = 0;
struct TreeNode *stack[MAX_NUM];
struct TreeNode *cur = root;
struct TreeNode *pre = NULL;
// 用栈模拟 递归压栈和弹栈的过程
while (cur != NULL || top != 0) {
if (cur != NULL) {
stack[top++] = cur;
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = stack[--top];
if (pre != NULL && pre->val >= cur->val) return false;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
return true;
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* searchBST(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
if (root->val == val) {
return root;
} else if (root->val > val) {
return searchBST(root->left, val);
} else {
return searchBST(root->right, val);
}
return NULL;
}
- 迭代法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* searchBST(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
while (root != NULL) {
if (root->val == val) {
return root;
} else if (root->val > val) {
root = root->left;
} else {
root = root->right;
}
}
return NULL;
}
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
- 中序遍历1次搞定,不适用额外的空间:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int g_preVal, g_count, g_maxCount;
int g_resSize;
int *g_res;
void Update(int curVal)
{
if (curVal == g_preVal) {
g_count++;
} else {
g_preVal = curVal;
g_count = 1;
}
if (g_count == g_maxCount) {
g_res[g_resSize++] = curVal;
}
if (g_count > g_maxCount) {
g_maxCount = g_count;
g_resSize = 0;
g_res[g_resSize++] = curVal;
}
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void MidTravle(struct TreeNode *node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
MidTravle(node->left);
Update(node->val);
MidTravle(node->right);
}
int* findMode(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
g_count = 0, g_maxCount = 0, g_resSize = 0;
g_preVal = root->val;
g_res = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10001);
MidTravle(root);
*returnSize = g_resSize;
return g_res;
}
- 使用hash表记录出现次数,使用了额外空间,并且还需要排序
struct HashTable {
int num;
int count;
UT_hash_handle hh;
};
struct HashTable *g_hash;
int g_count = 0;
struct HashTable *FindeNode(int num)
{
struct HashTable *tmp = NULL;
HASH_FIND_INT(g_hash, &num, tmp);
return tmp;
}
void AddNode(int num)
{
struct HashTable *tmp = FindeNode(num);
if (tmp == NULL) {
g_count++;
tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
tmp->num = num;
tmp->count = 1;
HASH_ADD_INT(g_hash, num, tmp);
} else {
tmp->count++;
}
}
void Func(struct TreeNode *node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
AddNode(node->val);
Func(node->left);
Func(node->right);
}
int HashSort(struct HashTable *a, struct HashTable *b)
{
return b->count - a->count;
}
int* findMode(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
// 1、遍历整棵树
// 2、记录每个数字出现的次数
// 3、返回出现次数最高的数
g_hash = NULL;
Func(root);
HASH_SORT(g_hash, HashSort);
int n = g_hash->count;
int *res = malloc(sizeof(int) * g_count);
*returnSize = 0;
struct HashTable *cur, *tmp;
HASH_ITER(hh, g_hash, cur, tmp) {
if (cur->count == n) {
res[(*returnSize)++] = cur->num;
}
HASH_DEL(g_hash, cur);
free(cur);
}
return res;
}
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode *Func(int *arr, int len)
{
if (len == 0) return;
int mid = len / 2;
struct TreeNode *node = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = arr[mid];
node->left = Func(arr, mid);
node->right = Func(arr + mid + 1, len - mid - 1);
return node;
}
struct TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
if (numsSize == 0) return NULL;
struct TreeNode *root = Func(nums, numsSize);
return root;
}
二叉树剪枝
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 涉及到树结构的调整,较为复杂
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* deleteNode(struct TreeNode* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
if (root->val == key) {
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
free(root);
return NULL;
}
if (root->left != NULL && root->right == NULL) {
struct TreeNode *node = root->left;
free(root);
return node;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) {
struct TreeNode *node = root->right;
free(root);
return node;
}
// 左右孩子都非空
struct TreeNode *left = root->left; // 左
struct TreeNode *right = root->right; // 左
struct TreeNode *node = right; // 左
free(root);
while (right->left != NULL) {
right = right->left;
}
// 挂上
right->left = left;
return node;
}
if (root->val > key) {
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
}
if (root->val < key) {
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
}
return root;
}
回溯思想
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/*
* 1.前序遍历
* 2.左子树和右子树每颗树都完整的遍历1遍
* 3.回溯,利用左子树和右子树的返回值,来判断最近公共祖先
*/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if (root == p || root == q || root == NULL) return root;
struct TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
struct TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left != NULL && right != NULL) return root;
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return right;
return left;
}
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if (root == NULL || root == q || root == p) return root;
int val = root->val;
if (p->val < val && q->val < val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
} else if (p->val > val && q->val >val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
} else {
return root;
}
}
二叉树中的插入操作
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 递归解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* insertIntoBST(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
if (root == NULL) {
struct TreeNode *node = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = val;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
root = node;
return root;
}
if (root->val > val) {
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
}
if (root->val < val) {
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
}
return root;
}
- 迭代解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* insertIntoBST(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
struct TreeNode *node = root;
struct TreeNode *add = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
add->val = val;
add->left = NULL;
add->right = NULL;
if (node == NULL) return add;
while (node != NULL) {
if (node->val > val && node->left == NULL) {
node->left = add;
break;
}
if (node->val < val && node->right == NULL) {
node->right = add;
break;
}
if (node->left != NULL && val < node->val) {
node = node->left;
}
if (node->right != NULL && val > node->val) {
node = node->right;
}
}
return root;
}
构建二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int inorderSize)
{
if (preorderSize == 0) return NULL;
int leftSize, rightSize;
struct TreeNode *node = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = preorder[0];
for (int i = 0; i < inorderSize; i++) {
if (node->val == inorder[i]) {
leftSize = i;
break;
}
}
rightSize = inorderSize - leftSize - 1;
node->left = buildTree(preorder + 1, leftSize, inorder, leftSize);
node->right = buildTree(preorder + 1 + leftSize, rightSize, inorder + leftSize + 1, rightSize);
return node;
}
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode *Func(int *arr, int len)
{
if (len == 0) return;
int mid = len / 2;
struct TreeNode *node = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = arr[mid];
node->left = Func(arr, mid);
node->right = Func(arr + mid + 1, len - mid - 1);
return node;
}
struct TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
if (numsSize == 0) return NULL;
struct TreeNode *root = Func(nums, numsSize);
return root;
}
完全二叉树
- 参考数据结构堆
- 完全二叉树定义:
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
验证完全二叉树
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
剑指 Offer II 043. 往完全二叉树添加节点
二叉树的后继节点
- 举个例子

- x有右树的时候:后继节点为其右树最左边的节点
- x没有右树的时候:往其左树找,当找到节点为其父节点的左孩子时,则这个父节点为x的后继节点
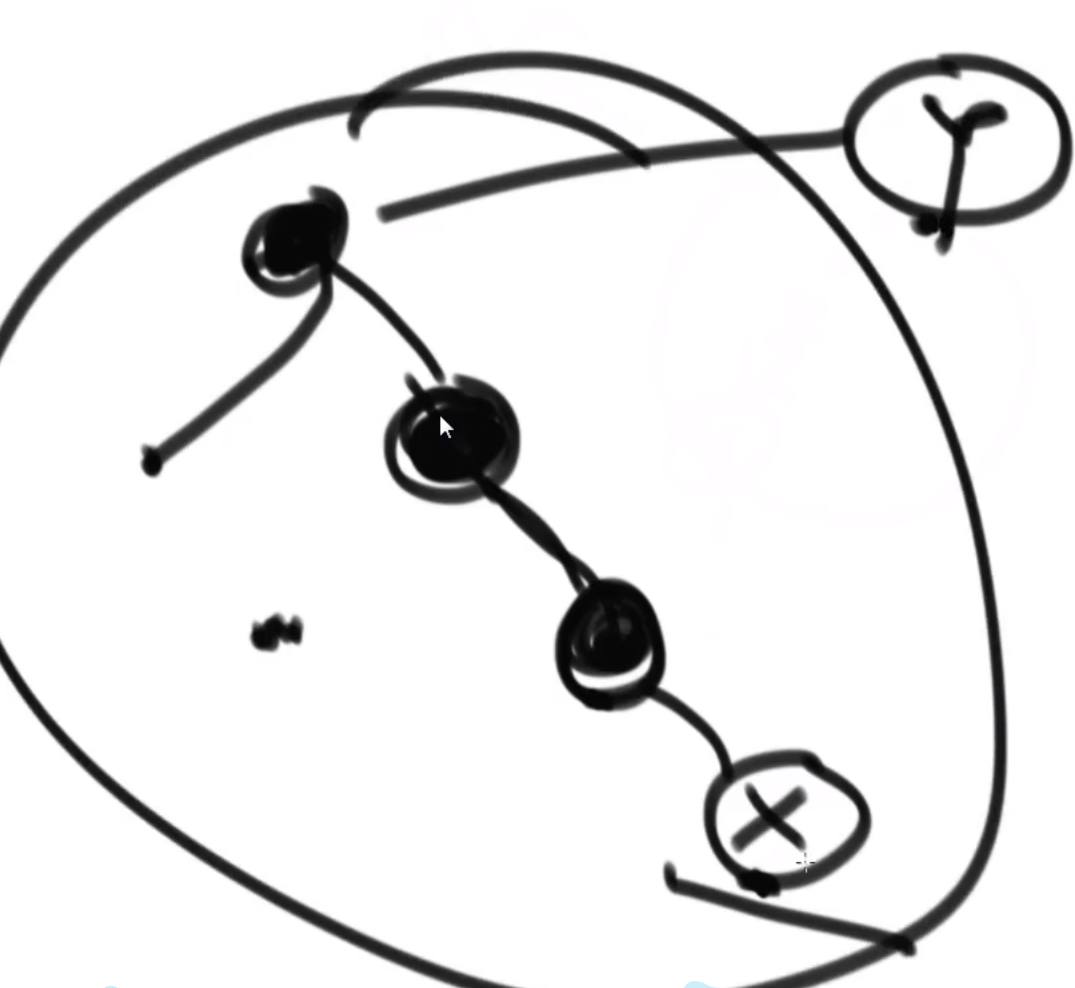
- 后继节点定义:中序遍历中,节点node的后一个节点叫做node的后继节点
- 前驱节点定义:中序遍历中,节点node的前一个节点叫做node的前驱节点
285. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继(Plus)

#define MAX_LEN 10000
struct TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p)
{
int top = 0;
struct TreeNode *stack[MAX_LEN];
struct TreeNode *pre = NULL;
struct TreeNode *cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || top != 0) {
if (cur != NULL) {
stack[top++] = cur;
cur = cur->left;
} else {
cur = stack[--top];
// printf("%d\n", cur->val);
if (pre == p) {
return cur;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
return NULL;
}
510. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继 II(Plus)
/*
// Definition for a Node.
struct Node {
int val;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
struct Node* parent;
};
*/
struct Node* ProcRight(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
if (node->left == NULL) {
return node;
}
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
struct Node* ProcNoRight(struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *p = NULL;
while (node != NULL) {
p = node->parent;
if (p != NULL && p->left == node) {
return p;
}
node = p;
}
// 囊括了node为整棵二叉树最底层最右侧节点的情况,返回NULL
return node;
}
struct Node* inorderSuccessor(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return node;
}
// 根据中序遍历,找node的后继节点有2种情况
// 1. node有右子树,则后继节点为右子树最左的节点
// 2. node无右子树,则向上找父节点,当这个父节点是再上一层节点p的左节点时,这个p为后继节点
// 1
if (node->right != NULL) {
return ProcRight(node->right);
}
// 2
return ProcNoRight(node);
}
2二叉树的序列化与反序列化
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
标签:
纯c刷leetcode记录






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)