vue路由
vue路由官方文档地址:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
接口地址参考:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API
1.
-
URL的hash也就是锚点(#), 本质上是改变window.location的href属性.
-
我们可以通过直接赋值location.hash来改变href, 但是页面不发生刷新
-
history接口是HTML5新增的, 它有五种模式改变URL而不刷新页面.
-
history.pushState(state, title[, url])
- 使用pushState()方法 可以控制浏览器自带的返回按钮,有时候我们想让用户点击浏览器返回按钮时,不返回,或执行其他操作,这时,就用到history.pushState()方法
两个方法的区别: pushState添加一个最新的历史记录。 replaceState则是把当前的页面的历史记录替换掉。他们最大的特点是添加或替换历史记录后,浏览器地址栏会变成你传的地址,而页面并不会重新载入或跳转。 例如,假设当前的页面地址是temp.com/A.html,且history中此时只有一条当前页面的记录。 当你执行history.pushState(null,null,"B.html")后,浏览器的地址栏会显示temp.com/B.html,但并不会跳转到B.html,甚至并不会去检查B.html存不存在,
只是加入一个最新的历史记录项。此时history中会有两个记录。假如你此时点击页面上的link跳转到另外一个页面后,点击浏览器的后退按钮,则url会变成temp.com/B.html,
如果此前的A.html的页面浏览器有缓存的话会显示A.html的内容,否则会发起请求temp.com/B.html。如果再次点后退,url会变成temp.com/A.html。 而如果执行history.replaceState(null,null,"B.html")的话,浏览器的地址栏也会显示temp.com/B.html,区别是history中只有当前B.html的记录,而A.html的
记录已被替换掉。 利用这些特性,可以用来修改当前页面的URL来达成某些目的,比如可以用来记住搜索条件。
- 在会话历史中向前移动一页。它与使用delta参数为1时调用 history.go(delta)的效果相同。
- window.history.forward();
-
-
history.forward() 则等价于 history.go(1)
2.vue路由
步骤一: 安装vue-router
npm install vue-router --save
步骤二: 在模块化工程中使用它(因为是一个插件, 所以可以通过Vue.use()来安装路由功能)
第一步:导入路由对象,并且调用 Vue.use(VueRouter)
第二步:创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
第三步:在Vue实例中挂载创建的路由实例
2.1.1创建路由组件
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是首页</h2>
<p>我是关于内容, 呵呵呵</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
message: '你好啊',
}
},
created() {
console.log('home created');
},
}
</script>
2.1.2index.js创建路由,并配置组件和路径的映射关系
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' // 1.通过Vue.use(插件), 安装插件 Vue.use(Router) // 2.配置路由和组件直接的应用关系 const routs = [ { path: '/', name: 'HelloWorld', component: HelloWorld } ] // 创建路由 const router = new VueRouter({ routs }) // 3.将router对象传入到Vue实例 export default router
2.1.3main.js挂载路由
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ el: '#app', router, render: h => h(App) })
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>我是主页面</h1>
<!--<router-link to="/HelloWorld" tag="button" replace >首页</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>-->
<button @click="homeClick">首页</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
userId:'zhangsan'
}
},
methods:{
homeClick(){
// 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router
// push => pushState
// this.$router.push('/HelloWorld')
this.$router.replace('/HelloWorld').catch(err=>err)
}
}
}
</script>
- 创建VueRouter对象,并指定路由参数
- routes:路由规则的数组,可以指定多个对象,每个对象是一条路由规则,包含以下属性:
- path:路由的路径
- component:组件名称
- <router-link>: 该标签是一个vue-router中已经内置的组件, 它会被渲染成一个<a>标签.
- <router-view>: 该标签会根据当前的路径, 动态渲染出不同的组件.
- 网页的其他内容, 比如顶部的标题/导航, 或者底部的一些版权信息等会和<router-view>处于同一个等级.
- 在路由切换时, 切换的是<router-view>挂载的组件, 其他内容不会发生改变.
2.2
在前面的<router-link>中, 我们只是使用了一个属性: to, 用于指定跳转的路径.<router-link>还有一些其他属性:
<router-link to='/home' tag='li'>
- tag: tag可以指定<router-link>之后渲染成什么组件, 比如上面的代码会被渲染成一个<li>元素, 而不是<a>
- replace: replace不会留下history记录, 所以指定replace的情况下, 后退键返回不能返回到上一个页面中
- active-class: 当<router-link>对应的路由匹配成功时, 会自动给当前元素设置一个router-link-active的class, 设置active-class可以修改默认的名称.
- 在进行高亮显示的导航菜单或者底部tabbar时, 会使用到该类.
- 但是通常不会修改类的属性, 会直接使用默认的router-link-active即可.
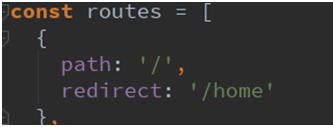
让路径默认跳到到指定页面, 并且<router-view>渲染首页组件,我们只需要配置多配置一个映射就可以了.
配置解析:
- 我们在routes中又配置了一个映射.
- path配置的是根路径: /
- redirect是重定向, 也就是我们将根路径重定向到/home的路径下, 这样就可以得到我们想要的结果了.
上边说过改变路径的方式有两种:
- URL的hash(浏览器的url会有一个#)
- HTML5的history
默认情况下, 路径的改变使用的URL的hash.
如果希望使用HTML5的history模式, 非常简单, 进行如下配置即可
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系 const router = new VueRouter({ routes, mode: 'history',//hash模式浏览器url会有#,所有改成history模式 linkActiveClass:"active"//设置选中的按钮的样式 })
代码示例:
index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from '../components/Home' import About from '../components/About' // 1.通过Vue.use(插件), 安装插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) //多次点击同一button出现问题的解决方案satrt const originalPush = VueRouter.prototype.push VueRouter.prototype.push = function push(location) { return originalPush.call(this, location).catch(err => err) } //多次点击同一button出现问题的解决方案end // 2.创建VueRouter对象 const routes = [ { path: '/', //name: 'HelloWorld', redirect:'/home' }, { path: '/home', //name: 'HelloWorld', component: Home }, { path: '/about', //name: 'HelloWorld', component: About } ] // 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系 const router = new VueRouter({ routes, mode: 'history',//hash模式浏览器url会有#,所有改成history模式 linkActiveClass:"active"//设置选中的按钮的样式 }) // 3.将router对象传入到Vue实例 export default router
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>我是主页面</h1>
<!-- <router-link to="/home" tag="button" replace active-class="active">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace active-class="active">关于</router-link>-->
<!-- <router-link to="/home" tag="button" replace >首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace >关于</router-link>-->
<button @click="homeClick">首页</button>
<button @click="aboutClick">关于</button>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
homeClick(){
// 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router
// push => pushState
// this.$router.push('/home')
//多次点击同一button出现问题的解决方案
this.$router.replace('/home').catch(err=>err)
},
aboutClick(){
// this.$router.push('/about')
//多次点击同一button出现问题的解决方案
this.$router.replace('/about').catch(err=>err)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{color:red;}
</style>
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是首页</h2>
<p>我是关于内容, 呵呵呵</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
About.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是关于</h2>
<p>我是关于内容, 呵呵呵</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "About"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, render: h => h(App) })
router.beforeEach方式。
如何改变网页的标题
- 网页标题是通过<title>来显示的, 但是SPA只有一个固定的HTML, 切换不同的页面时, 标题并不会改变.
- 但是我们可以通过JavaScript来修改<title>的内容.window.document.title = '新的标题'.
普通的修改方式:
- 我们比较容易想到的修改标题的位置是每一个路由对应的组件.vue文件中.
- 通过mounted声明周期函数, 执行对应的代码进行修改即可.
- 但是当页面比较多时, 这种方式不容易维护(因为需要在多个页面执行类似的代码).
- 有没有更好的办法呢? 使用导航守卫即可.
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from '../components/Home' import About from '../components/About' import User from '../components/User' const HomeNews = () => import('../components/HomeNews') const HomeMessage = () => import('../components/HomeMessage') const Profile = () => import('../components/Profile') // 1.通过Vue.use(插件), 安装插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) const originalPush = VueRouter.prototype.push VueRouter.prototype.push = function push(location) { return originalPush.call(this, location).catch(err => err) } // 2.创建VueRouter对象 const routes = [ { path: '/', //name: 'HelloWorld', redirect:'/home' }, { path: '/home', //name: 'HelloWorld', meta:{ title:'首页home' }, component: Home, children:[ /* { path:"", redirect:'news' },*/ { path:"news", component:HomeNews, // meta:{ // title:'新闻' // }, },{ path:"msg", component:HomeMessage, // meta:{ // title:'消息' // }, } ] }, { path: '/about', //name: 'HelloWorld', component: About, meta:{ title:'关于' }, }, { path: '/user/:userId', //name: 'HelloWorld', component: User, meta:{ title:'用户' }, }, { path:'/profile', component:Profile, meta:{ title:'我' }, } ] // 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系 const router = new VueRouter({ routes, mode: 'history',//hash模式浏览器url会有#,所有改成history模式 linkActiveClass:"active"//设置选中的按钮的样式 }) router.beforeEach((to, from, next)=> { document.title= to.meta.title //document.title= to.matched[0].meta.title next() }) // 3.将router对象传入到Vue实例 export default router
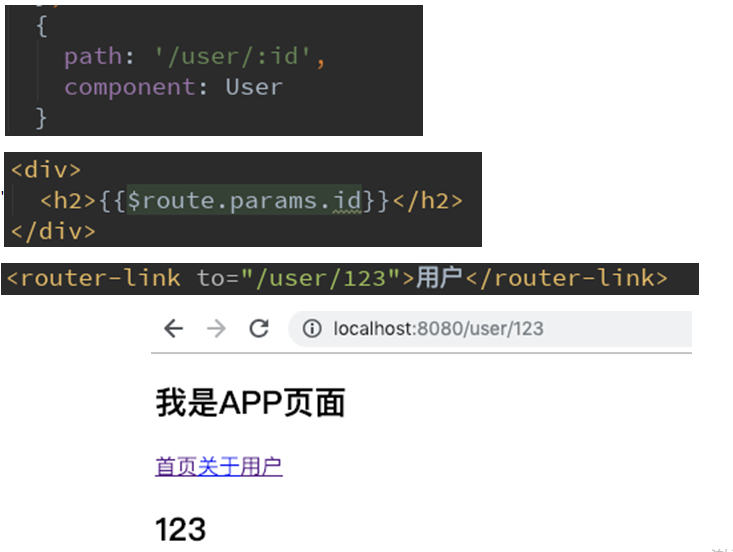
在某些情况下,一个页面的path路径可能是不确定的,比如我们进入用户界面时,希望是如下的路径:
- /user/aaaa或/user/bbbb
- 一个“路径参数”使用冒号 : 标记。当匹配到一个路由时,参数值会被设置到 this.$route.params,可以在每个组件内使用
除了有前面的/user之外,后面还跟上了用户的ID
这种path和Component的匹配关系,我们称之为动态路由(也是路由传递数据的一种方式)。
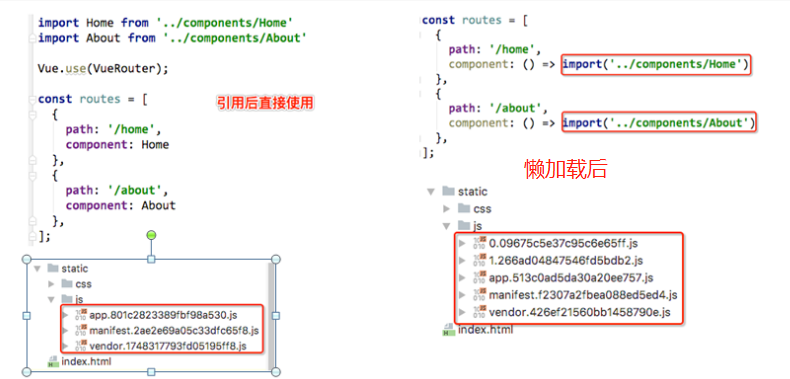
当打包构建应用时,Javascript 包会变得非常大,影响页面加载。
如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就更加高效了
存在问题:
首先, 路由中通常会定义很多不同的页面.
一般情况下, 这个页面最后被打包是放在一个js文件中.
但是, 页面这么多放在一个js文件中, 必然会造成这个页面非常的大.
如果我们一次性从服务器请求下来这个页面, 可能需要花费一定的时间, 甚至用户的电脑上还出现了短暂空白的情况.
如何避免这种情况呢? 使用路由懒加载就可以了.
懒加载作用:
路由懒加载的主要作用就是将路由对应的组件打包成一个个的js代码块.
只有在这个路由被访问到的时候, 才加载对应的组件
方式一: 结合Vue的异步组件和Webpack的代码分析.
const Home = resolve => { require.ensure(['../components/Home.vue'], () => { resolve(require('../components/Home.vue')) })};
方式二: AMD写法
const About = resolve => require(['../components/About.vue'], resolve);
方式三: 在ES6中, 我们可以有更加简单的写法来组织Vue异步组件和Webpack的代码分割.
const Home = () => import('../components/Home.vue')
const router = new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/user/:id', component: User, children: [ { // 当 /user/:id/profile 匹配成功, // UserProfile 会被渲染在 User 的 <router-view> 中 path: 'profile', component: UserProfile }, { // 当 /user/:id/posts 匹配成功 // UserPosts 会被渲染在 User 的 <router-view> 中 path: 'posts', component: UserPosts } ] } ] }
配置子路由默认页面
{ path: '',//注意和父路由配置默认路径不一样没有/ redirect:'/home' },
传递参数主要有两种类型: params和query
params的类型:
- 配置路由格式: /router/:id
- 传递的方式: 在path后面跟上对应的值
- 传递后形成的路径: /router/123, /router/abc
query的类型:
- 配置路由格式: /router, 也就是普通配置
- 传递的方式: 对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
- 传递后形成的路径: /router?id=123, /router?id=abc
- 取值方式:{{$route.query.name}}
query传递。
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>我是主页面</h1>
<!--<router-link :to="/profile" tag="button" replace >档案</router-link>-->
<!--<router-link :to="{path:'/profile',query:{name:'lufei'}}" tag="button" replace >档案</router-link>-->
<button @click="userClick">用户</button>
<button @click="profileClick">档案</button>
<keep-alive>
<router-view/>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
userId:'zhangsan'
}
},
methods:{
homeClick(){
// 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router
// push => pushState
// this.$router.push('/home')
this.$router.replace('/home').catch(err=>err)
},
aboutClick(){
// this.$router.push('/about')
this.$router.replace('/about').catch(err=>err)
},
userClick(){
this.$router.replace('/user/'+this.userId).catch(err=>err)
},
profileClick(){
this.$router.replace({
path:'/profile',
query:{name:"zhangsan"}
}).catch(err=>err)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{color:red;}
</style>
- 获取参数通过$route对象获取的.
- 在使用了 vue-router 的应用中,路由对象会被注入每个组件中,赋值为 this.$route ,并且当路由切换时,路由对象会被更新。
<template> <div>我是 档案 <h2>{{$route.query.name}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Profile" } </script> <style scoped> </style>
$route和$router的区别
- $router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法(VueRouter实例)
- $route为当前router跳转对象里面可以获取name、path、query、params等 (VueRouter里的每个path,处于活跃的,也就是点击的那个)
keep-alive 是 Vue 内置的一个组件,可以使被包含的组件保留状态,或避免重新渲染。activated和beforeRouteLeave和keep-alive一起使用才有效。
它们有两个非常重要的属性:
- include - 字符串或正则表达,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
- exclude - 字符串或正则表达式,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
router-view 也是一个组件,如果直接被包在 keep-alive 里面,所有路径匹配到的视图组件都会被缓存:
<div id="app" class='wrapper'>
<keep-alive>
<!-- 需要缓存的视图组件 -->
<router-view"></router-view>
</div>
通过activated和beforeRouteLeave和keep-alive一起使用来实现记录之前的路径。
<keep-alive exclude="Profile,User">
<router-view/>
</keep-alive>
export default { name: "Home", data() { return { message: '你好啊', path: '/home/news' } }, created() { console.log('home created'); }, destroyed() { console.log('home destroyed'); }, // 这两个函数, 只有该组件被保持了状态使用了keep-alive时, 才是有效的 activated() { this.$router.push(this.path); console.log('activated'); }, deactivated() { console.log('deactivated'); }, beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) { console.log(this.$route.path); this.path = this.$route.path; next() } }