母函数 <普通母函数(HDU - 1028 ) && 指数型母函数(hdu1521)>
给出我初学时看的文章:母函数(对于初学者的最容易理解的)
普通母函数--------->HDU - 1028
例题:若有1克、2克、3克、4克的砝码各一 枚,能称出哪几种重量?各有几种可能方案?
如何解决这个问题呢?考虑构造母函数。
如果用x的指数表示称出的重量,则:
1个1克的砝码可以用函数1+x表示,
1个2克的砝码可以用函数1+x2表示,(x2表示x的2次方)
1个3克的砝码可以用函数1+x3表示,
1个4克的砝码可以用函数1+x4表示,
(1+x)(1+x2)(1+x3)(1+x4)
=(1+x+x2+x3)(1+x3+x4+x7)
=1+x+x2+2x3+2x4+2x5+2x6+2x7+x8+x9+x10 (2x3表示用1、2、3、4砝码组成3的方式有2种,同样2x4表示用1、2、3、4砝码组成4的方式有2种)
从上面的函数知道:可称出从1克到10克,系数便是方案数。
例如右端有2x5 项,即称出5克的方案有2:5=3+2=4+1;同样,6=1+2+3=4+2;10=1+2+3+4。
故称出6克的方案有2,称出10克的方案有1
如果一种砝码有多个,那么母函数怎么构造?
这样一来,一个括号内有多少个x,那么就表示有多少个砝码,如果有3个值为1的砝码,那么就是(1+x+x2+x3),其中,xk中的k就表示用k个值为1的组成,他的系数为1,也就是说用只用值为1的要配出3出来只有一种方法。
按照上面的方法,3个值为2的砝码那就是(1 + x2 + x4 + x6),x6相当于(x2)3,就是说3 个值为2的构成6。同理如果有3个值为3的砝码,那就是(1+x3+x6+x9)
代码:

1 //母函数板子题 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<vector> 5 #include<string.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 using namespace std; 9 typedef long long ll; 10 const int maxn=125; 11 int c1[maxn],c2[maxn]; 12 int main() 13 { 14 int n; 15 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 16 { 17 for(int i=0;i<=n;++i) //给c1数组初赋值为1,就是操作的第一个括号 18 c1[i]=1,c2[i]=0; 19 for(int i=2;i<=n;++i) //操作第i个括号 20 { 21 for(int j=0;j<=n;++j) //对指数j进行枚举 22 { 23 for(int k=0;k+j<=n;k+=i) //这个k枚举的是i可以组成的数 24 { 25 c2[j+k]+=c1[j]; //记录系数 26 } 27 } 28 for(int j=0;j<=n;++j) 29 { 30 c1[j]=c2[j]; 31 c2[j]=0; 32 } 33 } 34 printf("%d\n",c1[n]); 35 } 36 return 0; 37 }
这里再给出普通母函数的一道变形题:The Balance HDU - 1709
题意:
给你一些砝码和一个天平,你要找出来在范围[1,S]中,哪些质量你称不出来并输出。。这个S是所有砝码质量之和
样例解析:
输入
3 9 2 1
Sample Output
2 4 5
有三个质量为9,2,1的砝码,在范围[1,12]中有4,5两个质量称不出来。。。
可能有人很疑惑6,7,8怎么称出来的,,如果9这个砝码在一个盘,1,2砝码在另一个盘就可以了。。。
代码较原代码有就只有一点改变:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<string.h> 5 #include<stdio.h> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 using namespace std; 9 typedef long long ll; 10 const int maxn=105; 11 int c1[maxn*maxn],c2[maxn*maxn],v[maxn]; 12 int main() 13 { 14 int n; 15 queue<int>r; 16 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 17 { 18 int sum=0; 19 memset(c1,0,sizeof(c1)); 20 memset(c2,0,sizeof(c2)); 21 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) 22 { 23 scanf("%d",&v[i]); 24 sum+=v[i]; 25 } 26 c1[0]=1; 27 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) 28 { 29 for(int j=0;j<=sum;++j) 30 { 31 for(int k=0;k+j<=sum && k<=v[i];k+=v[i]) 32 { 33 if(j>k) c2[j-k]+=c1[j]; 34 else c2[k-j]+=c1[j]; 35 c2[k+j]+=c1[j]; 36 } 37 } 38 for(int j=0;j<=sum;++j) 39 c1[j]=c2[j];//,c2[j]=0; 40 } 41 for(int i=1;i<=sum;++i) 42 { 43 if(!c1[i]) 44 r.push(i); 45 } 46 printf("%d\n",r.size()); 47 int flag=0; 48 while(!r.empty()) 49 { 50 if(!flag) 51 printf("%d",r.front()),flag=1; 52 else printf(" %d",r.front()); 53 r.pop(); 54 } 55 if(flag) 56 printf("\n"); 57 } 58 return 0; 59 }
代码中c1[i]仍然代表能构成i质量的方法数,因为本题不涉及方法数,也就无关大小了。。。
指数型母函数--------->HDU - 1521
题目:
Input每组输入数据有两行,第一行是二个数n,m(1<=m,n<=10),表示物品数,第二行有n个数,分别表示这n件物品的数量。Output对应每组数据输出排列数。(任何运算不会超出2^31的范围)Sample Input
2 2 1 1
Sample Output
2
指数型母函数:(用来求解多重集的排列问题)
n个元素,其中a1,a2,····,an互不相同,进行全排列,可得n!个不同的排列。
若其中某一元素ai重复了ni次,全排列出来必有重复元素,其中真正不同的排列数应为 (n!/ni!),重复度为ni!
同理a1重复了n1次,a2重复了n2次,····,ak重复了nk次,n1+n2+····+nk=n。对于这样的n个元素进行全排列,可得不同排列的个数实际上是(n!/(n1!*n2!...nk!)).若只对其中的r个元素进行排列呢,那就用到了指数型母函数。


仔细看指数型母函数和普通母函数的构造函数之间的差别就是指数型多了一个分母,其他的还是没有变化。具体见代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<string.h> 5 #include<stdio.h> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 using namespace std; 9 typedef long long ll; 10 const int maxn=105; 11 double c1[maxn*maxn],c2[maxn*maxn],v[maxn]; 12 double jiecheng(int n) 13 { 14 double ans=1.0; 15 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) 16 ans*=i; 17 return ans; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 int n,m; 22 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) 23 { 24 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) 25 scanf("%lf",&v[i]); 26 memset(c1,0,sizeof(c1)); 27 memset(c2,0,sizeof(c2)); 28 c1[0]=1.0; 29 double ans=1.0; 30 for(int i=1; i<=v[0]; ++i) 31 { 32 ans*=(double)i; 33 c1[i]=1.0/ans; 34 } 35 for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) 36 { 37 for(int j=0; j<=m; ++j) 38 { 39 ans=1.0; 40 for(int k=0; k<=v[i] && j+k<=m; ++k) 41 { 42 if(k==0) 43 c2[j+k]+=c1[j]; 44 else ans*=(double)k,c2[j+k]+=c1[j]/ans; 45 } 46 } 47 for(int j=0; j<=m; ++j) 48 c1[j]=c2[j],c2[j]=0; 49 } 50 printf("%.0lf\n",c1[m]*jiecheng(m)); 51 } 52 return 0; 53 }
指数型母函数变形-------->POJ3734
题意:
一段长度为nn nn的序列,你有红黄蓝绿四种颜色的砖块,一块砖长度为11 11,问你铺砖的方案数,其中红黄颜色之和必须为偶数。
题解:
泰勒展开式:
chx = (e^x+e^(-x))/2 = 1 + x^2/2! + x^4/4! + x^6/6! + ... ...
shx = (e^x-e^(-x))/2 = x + x^3/3! + x^5/5! + x^7/7! + ... ...
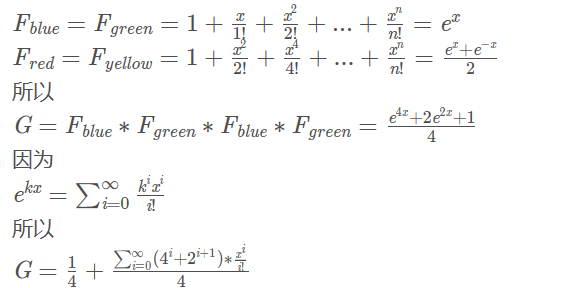
因为我们最后求的是对n个方块的填充方式,那么肯定答案就是x的n次方的系数,即4n-1+2n-1
代码:

1 /* 2 指数型生成函数: 3 4 泰勒展开式: 5 chx = (e^x+e^(-x))/2 = 1 + x^2/2! + x^4/4! + x^6/6! + ... ... 6 shx = (e^x-e^(-x))/2 = x + x^3/3! + x^5/5! + x^7/7! + ... ... 7 8 参看链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43464645/article/details/95488472 9 矩阵快速幂做法:https://www.cnblogs.com/bhlsheji/p/4049394.html 10 11 */ 12 #include<iostream> 13 #include<queue> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<string.h> 16 #include<stdio.h> 17 #include<queue> 18 #include<math.h> 19 #include<algorithm> 20 using namespace std; 21 typedef long long ll; 22 const int maxn=105; 23 const ll mod = 10000 + 7;//19260817 24 const double pi = acos(-1.0); 25 ll n, res; 26 ll pow(ll a, ll n) 27 { 28 ll ans = 1; 29 while(n) 30 { 31 if(n & 1) ans = ans * a % mod; 32 a = a * a % mod; 33 n >>= 1; 34 } 35 return ans; 36 } 37 int main() 38 { 39 int T; 40 scanf("%d", &T); 41 while(T--) 42 { 43 scanf("%lld", &n); 44 printf("%lld\n", (1ll * pow(4, n - 1) % mod + pow(2, n - 1) % mod) % mod); 45 } 46 return 0; 47 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号