有部分小伙伴反馈说前面基于注解的Spring中大量使用注解,由于对Java的注解不熟悉,有点难受。建议总结一篇的Java注解的基础知识,那么,它来了!
本文内容
- 什么是注解?
- 如何定义注解
- 如何使用注解
- 如何获取注解信息
- Spring 中对注解做了什么增强?
什么是注解?
什么是代码中写的注释?那是给开发者看的,但是编译之后的字节码文件中是没有注释信息的,也就是说注释对于java编译器和JVM来说是没有意义的,看不到!
类比注释是给人看的,注解则是给java编译器和JVM看的一些标识,编译器和虚拟机在运行的过程中可以获取注解信息来做一些处理。
如何定义注解
注解定义的语法如下:
public @interface 注解类名{
参数类型 参数名称1() [default 参数默认值];
参数类型 参数名称2() [default 参数默认值];
}
参数名称可以没有,也可以定义多个,定义细节如下:
- 参数类型只能是基本类型、String、Class、枚举类型、注解类型以及对应的一维数组
- 如果注解参数只有1个,建议定义名称为value,方便使用时缺省参数名
- default 可以指定默认值,如果没有默认值使用注解时必须给定参数值
定义注解时候需要考虑2个主要问题:
- 注解可以使用在哪里也就是使用范围?
- 注解保留到什么阶段,源码阶段,还是运行阶段?
java提供了一部分的元注解来解决上面的问题。
@Target指定注解的使用范围
来看下源码,主要是指定了可以应用注释类型的元素种类的数组参数。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
// 返回可以应用注释类型的元素种类的数组
ElementType[] value();
}
/*注解的使用范围*/
public enum ElementType {
/*类、接口、枚举、注解上面*/
TYPE,
/*字段上*/
FIELD,
/*方法上*/
METHOD,
/*方法的参数上*/
PARAMETER,
/*构造函数上*/
CONSTRUCTOR,
/*本地变量上*/
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/*注解上*/
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/*包上*/
PACKAGE,
/*类型参数上 1.8之后*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/*类型名称上 1.8之后*/
TYPE_USE
}
@Retention指定注解的保留策略
指示要保留带注释类型的注释多长时间。如果注释类型声明中不存在保留注释,则保留策略默认为 RetentionPolicy.CLASS
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
RetentionPolicy value();
}
public enum RetentionPolicy {
// 源码阶段,注解被编译器丢弃。
SOURCE,
// 注释将由编译器记录在类文件中,但不需要在运行时由 VM 保留。这是默认行为。
CLASS,
// 注释将由编译器记录在类文件中,并在运行时由 VM 保留,因此可以反射性地读取它们。
RUNTIME
}
综合上面2个注解,自定义一个保留到运行期的仅用在方法上的注解如下。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface DemoAnnotation {
String name() default "";
Class targetClazz();
}
如何使用注解
使用语法
@注解类(参数1=值1,参数2=值2,参数3=值3,参数n=值n)
目标对象
使用前一节的注解来个简单的案例
public class MyBean {
@DemoAnnotation(name = "xxx", targetClazz = MyBean.class)
public void m() {
}
}
来一个综合案例,注解位置包括类上、方法上、构造函数上、方法参数上、字段上、本地变量上、泛型类型参数和类型名称上。
/**
* 综合案例
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 13:31
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE)
public class UseStrongAnnotation<@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类型参数上T0", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER) T0,
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类型名称上T1", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) T1> {
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在字段上", elementType = ElementType.FIELD)
private String field;
@StrongAnnotation(value = "构造方法上", elementType = ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
public UseStrongAnnotation(@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在方法参数上", elementType = ElementType.PARAMETER) String field) {
this.field = field;
}
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在普通方法上", elementType = ElementType.METHOD)
public void m(@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法参数上", elementType = ElementType.PARAMETER) String name) {
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在本地变量上", elementType = ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)
String prefix = "hello ";
System.out.println(prefix + name);
}
public <@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法的类型参数T2上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER) T2> void m1() {
}
public <@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法的类型名称T3上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) T3> void m2() {
}
private Map<@StrongAnnotation(value = "Map后面的尖括号也是类型名称", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) String ,
@StrongAnnotation(value = "Map后面的尖括号也是类型名称", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER)Object> map;
}
如何获取注解信息
java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement接口表示当前在此 VM 中运行的程序的注解元素。 该接口允许以反射方式读取注解。 此接口中方法返回的所有注解都是不可变的和可序列化的。 该接口的方法返回的数组可以被调用者修改,而不影响返回给其他调用者的数组。其获取注解的主要方法如下,见名知意。
主要的实现类或接口图如下
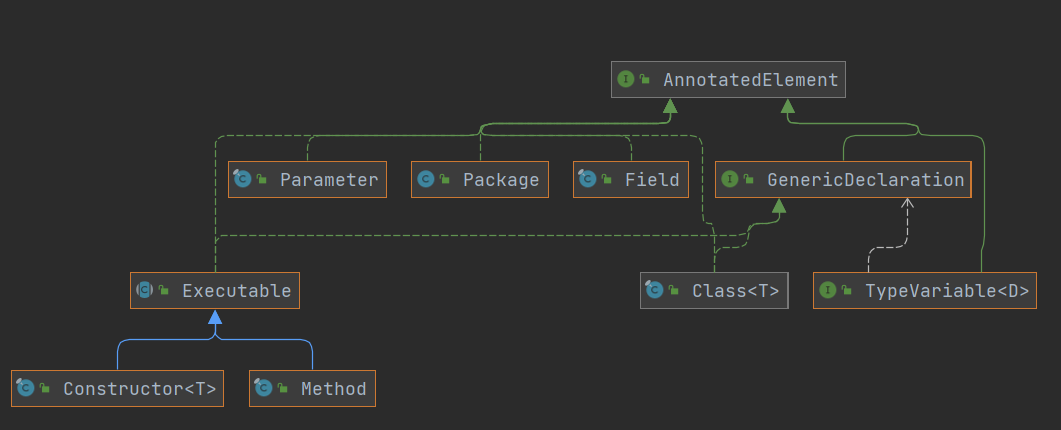
对应的实现的含义也很明确:
- Package:用来表示包的信息
- Class:用来表示类的信息
- Constructor:用来表示构造方法信息
- Field:用来表示类中属性信息
- Method:用来表示方法信息
- Parameter:用来表示方法参数信息
- TypeVariable:用来表示类型变量信息,如:类上定义的泛型类型变量,方法上面定义的泛型类型变量
综合案例
来一个综合案例来解析上一节的注解使用UseStrongAnnotation。测试用例和结果如下,建议多实战敲敲代码。
package com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17;
import com.sun.xml.internal.bind.v2.model.core.ID;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 13:52
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class UseStrongAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void test_annotated_class() {
System.out.println("解析类上注解:");
Arrays.stream(UseStrongAnnotation.class.getAnnotations())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 解析类上注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类上, elementType=TYPE)
@Test
public void test_annotated_class_type_parameter() {
TypeVariable<Class<UseStrongAnnotation>>[] typeParameters = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getTypeParameters();
for (TypeVariable<Class<UseStrongAnnotation>> typeParameter : typeParameters) {
System.out.println(typeParameter.getName() + " 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:");
Annotation[] annotations = typeParameter.getAnnotations();
Arrays.stream(annotations).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
// T0 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型参数上T0, elementType=TYPE_PARAMETER)
// T1 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型名称上T1, elementType=TYPE_USE)
@Test
public void test_annotated_field() throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field field = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredField("field");
Arrays.stream(field.getAnnotations()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在字段上, elementType=FIELD)
@Test
public void test_annotated_constructor() {
Constructor<?> constructor = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
for (Annotation annotation : constructor.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=构造方法上, elementType=CONSTRUCTO
@Test
public void test_annotated_normal_method() throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredMethod("m", String.class);
System.out.println("方法注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : method.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
System.out.println("方法参数注解:");
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (Parameter parameter : parameters) {
System.out.println(parameter.getName() + " 参数注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : parameter.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
// 方法注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在普通方法上, elementType=METHOD)
// 方法参数注解:
// name 参数注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=方法参数上, elementType=PARAMETER)
@Test
public void test_annotated_map_type() throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field field = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredField("map");
// 返回一个 Type 对象,该对象表示此 Field 对象表示的字段的声明类型。
// 如果 Type 是参数化类型,则返回的 Type 对象必须准确反映源代码中使用的实际类型参数。
Type genericType = field.getGenericType();
// 获取返回表示此类型的实际类型参数的 Type 对象数组
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericType).getActualTypeArguments();
// 返回一个 AnnotatedType 对象,该对象表示使用一个类型来指定此 Field 表示的字段的声明类型。
AnnotatedType annotatedType = field.getAnnotatedType();
// 获取此参数化类型的可能带注释的实际类型参数数组
AnnotatedType[] annotatedActualTypeArguments =
((AnnotatedParameterizedType) annotatedType).getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments();
int index = 0;
for (AnnotatedType annotatedActualTypeArgument : annotatedActualTypeArguments) {
Type actualTypeArgument = actualTypeArguments[index++];
System.out.println(annotatedActualTypeArgument.getType());
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument.getTypeName() + " 类型上的注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : annotatedActualTypeArgument.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
// T0 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型参数上T0, elementType=TYPE_PARAMETER)
// T1 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型名称上T1, elementType=TYPE_USE)
}
@Inherited实现子类继承父类的注解
@Inherited指示注解类型是自动继承的。注意针对的父类的注解,接口是无效的
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Inherited {
}
来看一个案例,父类和接口上都有可继承的注解,观察下子类的上的注解情况。
/**
* 测试父类注解的继承
* 注意:是类,不是接口,接口无效
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 17:15
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class TestInherited {
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface Annotation1{}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface Annotation2{}
@Annotation1
interface Interface1{}
@Annotation2
static class SupperClass{}
// 继承 SupperClass 实现 Interface1,观察其注解继承情况
static class SubClass extends SupperClass implements Interface1{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Annotation annotation : SubClass.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// 输出
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestInherited$Annotation2()
// 只继承了父类注解 无法继承接口上的注解
}
@Repeatable重复注解
常规情况下同一个目标上是无法使用同一个注解多个重复标记的。如果自定义注解需要实现可重复注解,则在定义的时候可以使用 @Repeatable来声明的注解类型是可重复的。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Repeatable {
// 指定容器注解类型
Class<? extends Annotation> value();
}
模拟 @ComponentScan @ComponentScans来提供一个案例。
/**
* 测试 @Repeatable 注解重复使用
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 17:30
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class TestRepeatable {
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
@interface ComponentScan{}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface ComponentScans{
// 注意: 必须定义value参数,其类型是子重复注解的数组类型
ComponentScan[] value();
}
// 重复注解方式1
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan
static class MyComponent{}
// 重复注解方式2
@ComponentScans({@ComponentScan, @ComponentScan})
static class MyComponentB{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Annotation annotation : MyComponent.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
for (Annotation annotation : MyComponentB.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// 输出
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScans(value=[@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17
// .TestRepeatable$ComponentScan(), @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScan()])
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScans(value=[@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17
// .TestRepeatable$ComponentScan(), @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScan()])
}
Spring 中@AliasFor对注解的增强
注解的定义参数是不能继承,如注解A上面有注解B,但是实际在使用B注解在目标类C的过程中想要设置A的参数是做不到的。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnnotationA {
String name() default "";
int value() default -1;
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@AnnotationA
public @interface AnnotationB {
String name() default "";
int value() default 1;
String aliasForName() default "";
}
@AnnotationB(name = "xxx", value = 1) // 无法设置AnnotiaonA的参数值
public class ClassC {
}
Spring 中 提供了@AliasFor 元注解,用于声明注解属性的别名,主要的使用场景:
- 注解中的显式别名:在单个注解中, @AliasFor可以在一对属性上声明,以表明它们是彼此可互换的别名
- 元注解中属性的显式别名:如果@AliasFor的annotation属性设置为与声明它的注解不同的注解,则该attribute被解释为元注解中属性的别名(即显式元注解属性覆盖)。 这可以精确控制注解层次结构中覆盖的属性。
- 注解中的隐式别名:如果注解中的一个或多个属性被声明为相同元注解属性的属性覆盖(直接或传递),则这些属性将被视为彼此的一组隐式别名,从而导致类似于注解中显式别名的行为。
源码简单过一下
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
// 声明别名属性的注解类型。默认为 Annotation,这意味着别名属性在与此属性相同的注解中声明。
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}
综合案例
来使用@AliasFor 改造下 AnnotationB。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@AnnotationA
public @interface AnnotationB {
// 注解AnnotationB内部显式别名
@AliasFor(value = "aliasForName")
String name() default "";
int value() default 1;
// 注解AnnotationB内部显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationB.class, attribute = "name")
String aliasForName() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性name显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "name")
String aliasForAnnotationAName() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性name显式别名2
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "name")
String aliasForAnnotationAName2() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性value显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "value")
int aliasForAnnotationAValue() default -1;
}
使用AnnotationB 注解,注意:互为别名的属性设置时只能设置其中一个,否则设置多个会报错。
@AnnotationB(value = 100,
name = "xx",
aliasForAnnotationAName = "a1",
aliasForAnnotationAValue = -100
)
public class ClassC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//spring提供一个查找注解的工具类AnnotatedElementUtils
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(ClassC2.class, AnnotationB.class));
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(ClassC2.class, AnnotationA.class));
}
}
输出结果显示AnnotationB 通过别名设置AnnotationA中属性成功。
@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.AnnotationB(aliasForAnnotationAName=a1, aliasForAnnotationAName2=a1, aliasForAnnotationAValue=-100, aliasForName=xx, name=xx, value=100)
@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.AnnotationA(name=a1, value=-100)
总结
本文详解了注解的概念,如何定义注解、使用注解、获取注解;并介绍了元注解@Target、@Retention、@Inherited、@Repeatable 的使用;重点讲解了Spring 中 @AliasFor 注解来为元注解属性设置别名的增强处理。
本篇源码地址: https://github.com/kongxubihai/pdf-spring-series/tree/main/spring-series-ioc/src/main/java/com/crab/spring/ioc/demo17
知识分享,转载请注明出处。学无先后,达者为先!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义