PrincetonAlgorithm I - Assignment2 Deques and Randomized Queues
Programming Assignment2 - Deque and Randomized Queues Review
课程笔记
Subtext: Modular Programming
- Stacks and Queues are fundamental data types
- Value: collection of objects
- Basic Operation: insert, remove, iterate.
- Difference: which item do we move? -> Stack: LIFO(last in first out) Queue: FIFO(first in first out)
- Client, implementation, interface
- Client: program using operations defined in interface
- Implementation: actual code implementing operations
- Interface: description of data type, basic operations
Stack Programming API:
public class StackOfStrings
StackOfStrings() //create an empty stack
void push(String item) //insert a new string onto stack
String pop() //remove and return the string most recently added
boolean isEmpty() //is the stack empty?
linked-list implementation
//Attention: Stack have only one exit -> only one pointer is enough
/*Corner Cases:
client add a null item -> IllegalArgumentException
remove() from empty stack -> NoSuchElementException
*/
public class StackOfStrings {
private Node first;
private class Node {
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public StackOfStrings {
Node first = null;
}
public void push(String item) {
//Improve: add exception to deal with invalid operation
Node oldfirst = first;
first = new Node(); //Attention: must craete a new instance here
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
}
public String pop() {
String item = first.item;
first = first.next;
return item;
}
Proposition: Every operation takes constant time in the worst case. A stack with N items uses 40N bytes
Object overhead (16) + inner class extra overhead(8) + item reference (8) + next reference(8) = 40
array implementation
/*
Underflow: throw exception if pop from an empty stack
Overflow: use resizing array for array implementation
*/
public class FixedCapacityStackOfStrings {
private String[] s;
private int N = 0;
public FixedCapacityStackOfStrings (int capacity) {
s = new String[capacity];
}
public String pop() {
//Attention: declare null pointer to avoid loitering so garbage collector can reclaim memory
String item = s[--N];
s[N] = null;
return item;
}
public void push(String item) {
s[N++] = item;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
}
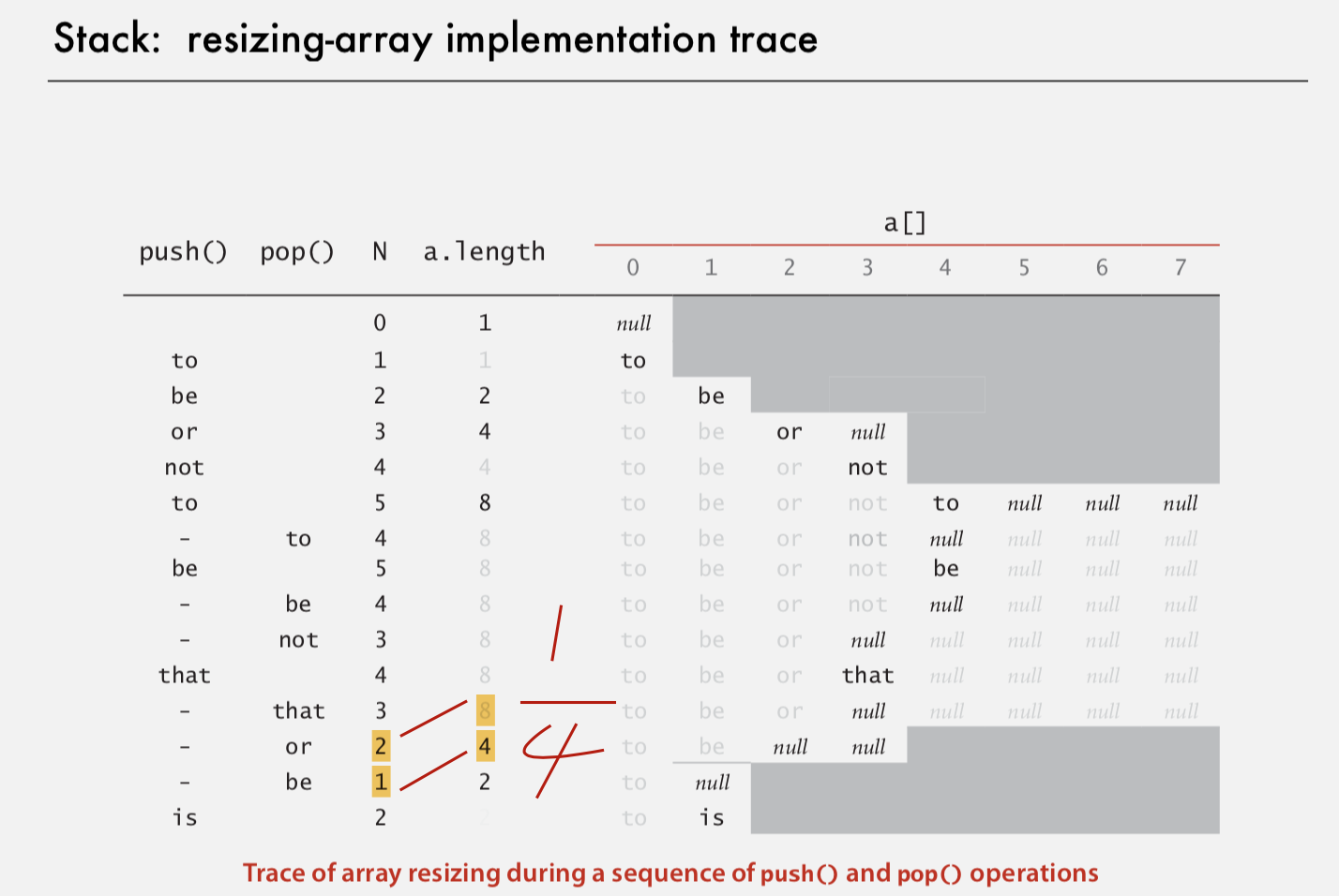
- Resizing array
- Problem: Require client to provide capacity does not implement API. Constructor should not have int input
- Question: How to grow and shrink array?
- Answer: grow: double shrink: quarter - > Why? ->
- double array for grow-> cost of is Linear N + (2 + 4 + 8 + .... + N) ~ 3N Geometric sequence: Sn = (a1 - an * q) / 1 - q
- quarter for shrink -> avoid thrashing push - pop - push - pop when sequence is full -> each operation takes time propotional to N
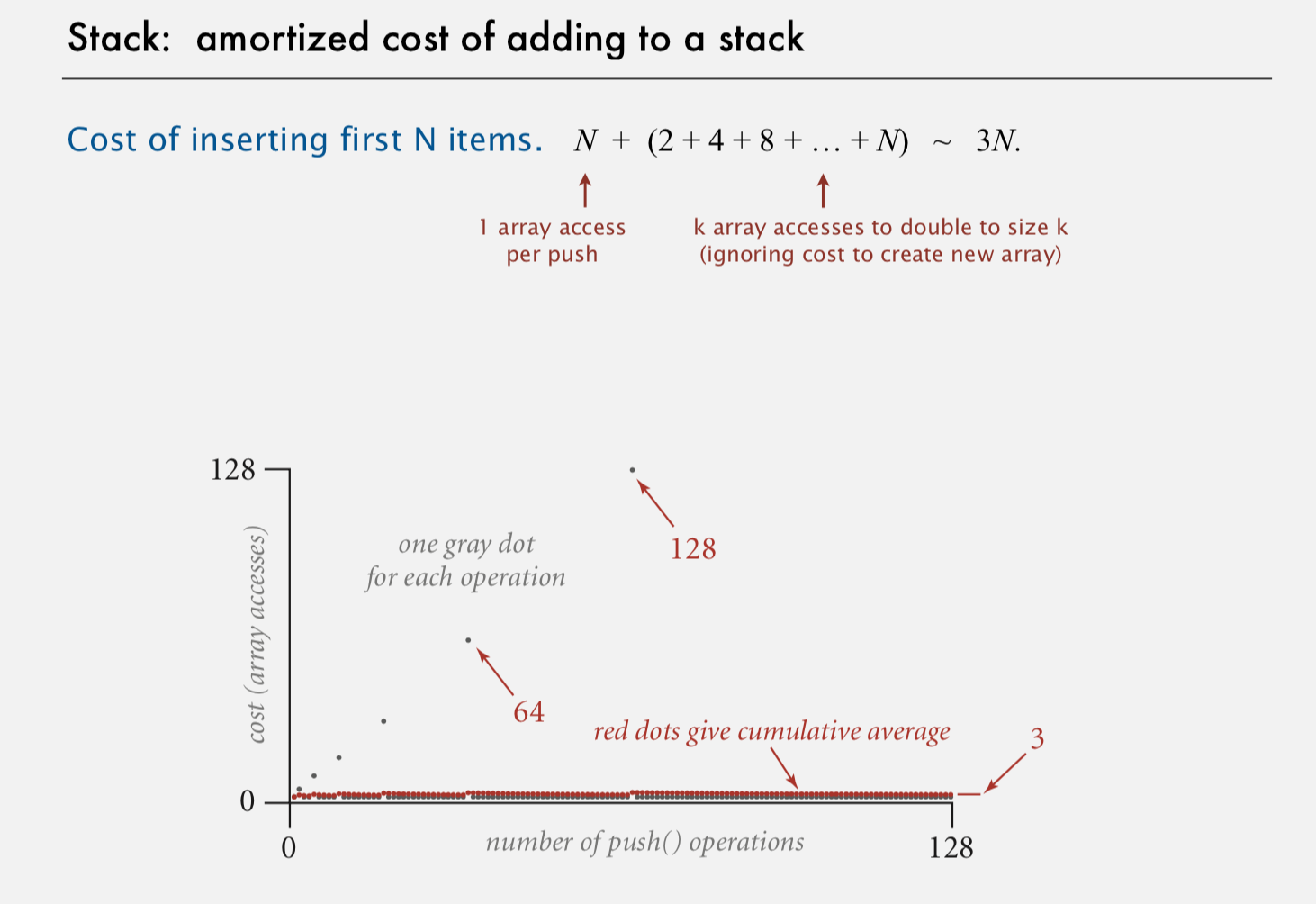
//Note: array is between 25% and 100% full
public class ResizingArrayStackOfStrings {
private String[] s;
public ResizaingArrayStackOfStrings() {
s = new String[1];
}
public void push(String item) {
if (N == s.length) resize (2 * s.length);
s[N++] = item;
}
private void resize(int capacity) {
//create a double size array, copy the element from the old String array, update the pointer
String[] copy = new String[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
copy[i] = s[i];
s = copy;
}
public String pop() {
String item = s[--N];
S[N] = null;
if (N > 0 && N = s.length/4) resize(s.length / 2);
return item;
}
}
- Queue Programming API
- QueueOfStrings()
- void enqueue(String item)
- String dequeue()
- boolean isEmpty()
Same API with stack, only name changed
*linked list implementation
/*Attention:
Queue has two exit, so it needs two pointers
*/
public class LinkedQueueOfStrings {
public LinkedQueueOfStrings() {
Node first, last;
int N = 0;
}
private class Node {
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
//enqueue elements added to the last of the queue
public void enqueue(String item) {
Node oldlast = last; // here last already points to an exist instance
//Create a totally new Node
last = new Node();
last.item = item;
last.next = null;
//linked back with the queue
if (isEmpty()) {
//there is only one element exist ->
first = last;
}
else {
oldlast.next = last;
}
}
public String dequeue() {
String item = first.item;
first = first.next;
if (isEmpty()) {
last = null;
}
return item;
}
}
- Generic data types: autoboxing and unboxing
- Autoboxing: Automatic cast between a primitive type and its wrapper
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>(); s.push(17); //s.push(Integer.valueOf(17)); int a = s.pop(); //int a = s.pop().intValue();
在写代码的过程当中,心里需要有转换角色的意识,当你在实现一个API的时候,需要考虑的是
* 实现某个方法所要使用的数据结构,
* 调用方法 or 自己写方法,
* API的性能要求 -> 使用哪种算法可以满足要求 查找,插入,删除 时间 + 空间
-
Iterators
- What is an Iterable?
- What is an Iterator?
public interface Iterator<Item> { boolean hasNext(); Item next(); }- Why make data structures Iterable ?
-
Java collections library
List Interface. java.util.List is API for an sequence of items- java.util.ArrayList uses resizing array -> only some operations are effieient
- java.util.LinkedList uses linked list -> only some operations are effieient
tip: 不清楚library的具体实现的时候,尽量避免调用相关的方法。可能效率会很低。
-
Arithmetic expression evaluation
( 1 + ( ( 2 + 3 ) * ( 4 * 5 ) ) )
Two-stack algorithm. 【E. W. Dijkstra】- value: push onto the value stack
- Operator: push onto the operator stack
- Left parenthesis: ignore
- Right parenthesis: pop operator and two values; push the result of applying that operator to those values onto the operand stack
总结:
Stack的链表实现
Stack的数组实现(resize array)
Queue的链表实现
Queue的数组实现(resize array)
对于双向队列的理解有误,导致错误实现。
双向对别不应当是两个队列的水平叠加,见figure 1
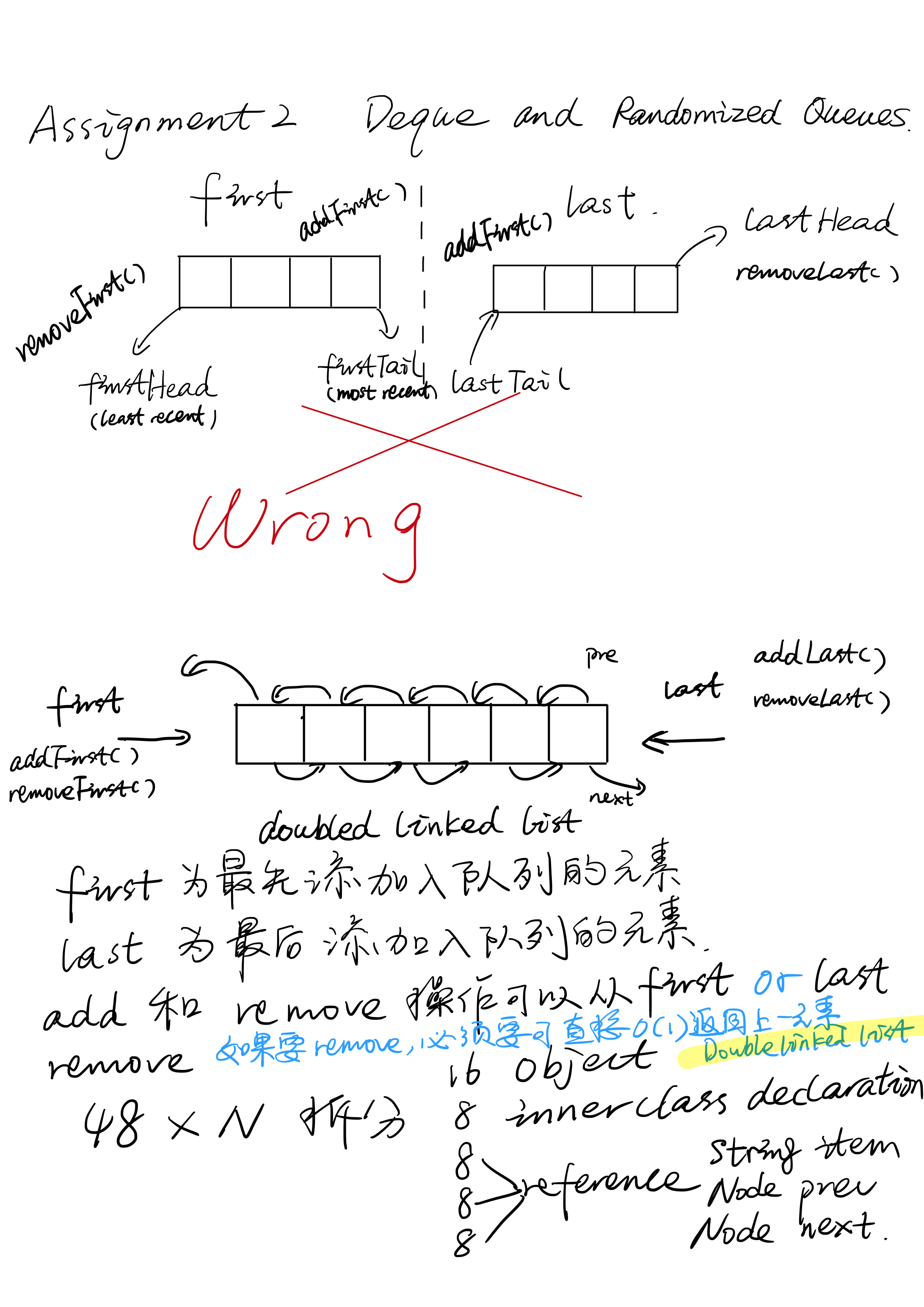
作业总结:
- 对于文件的读写基本操作命令不够熟悉
- 对于问题的定义 出现了没有搞清楚题目要求的现象,包括Deque的基本操作 以及Permutation 类当中,应当是读取全部数据,输出k个数据,而不是读取k个数据,输出全部数据的问题




