MongoDB学习笔记
MongoEngine 基本命令
‘$set’: replace the value of a field with the specified value 更新新的value
假设我们有一个 products collection, 其中的字段如下
{
_id: 100,
sku: "abc123",
quantity: 250,
instock: true,
reorder: false,
details: { model: "14Q2", make: "xyz" },
tags: [ "apparel", "clothing" ],
ratings: [ { by: "ijk", rating: 4 } ]
}
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set:
{
quantity: 500,
details: { model: "14Q3", make: "xyz" },
tags: [ "coats", "outerwear", "clothing" ]
}
}
)
需要使用.进行修饰的
- 设定内嵌文档的字段
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set: { "details.make": "zzz" } }
)
- 设定数组内部元素的字段
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set:
{
"tags.1": "rain gear",
"ratings.0.rating": 2
}
}
)
'$and': 逻辑与符号
- 用法:
{ $and : [ {<expression1>}, {<expression2>}, ... {<expressionN>}]}
$or: 逻辑或符号
- 用法:
{ $or : [ {<expression1>}, {<expression2>}, ... {<expressionN>}]}
多重判断的写法
db.inventory.find( {
$and : [chaxun
{ $or : [ { price : 0.99 }, { price : 1.99 } ] },
{ $or : [ { sale : true }, { qty : { $lt : 20 } } ] }
]
} )
CRUD 命令
Create:
Retrieve:
Update: Supplier.update({'id': mer_supplier.id}, {'$set': {'bound_status': mer_supplier.bound_status}})
Delete:
正则表达式
直接给出字符, 就是精确匹配,
\d 匹配数字
\w 匹配一个字母或数字
\s 匹配空格
00\d 匹配 007
. 可以匹配任意字符
* 表示任意个字符(0个或0个以上)
+ 表示至少一个字符
? 表示0个或1个字符
{n} 表示n个字符
{n, m} 表示n-m个字符
| 表示或关系
[] 表示范围 [0-9] 数字0-9, [0-9a-z]数字0到9以及字母a到字母z都可以匹配
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/001374738125095c955c1e6d8bb493182103fac9270762a000/001386832260566c26442c671fa489ebc6fe85badda25cd000
{"$regex":r"[0-9a-z]{24}"}
"_id":
"text":
"entities": {
"user_mentions": [
{
"screen_name": : "",
...
}
],
"urls": [],
"hashtags": []
},
"user“: {
"friends_count" : 544,
"screen_name": "",
"follwers_count" : 100,
...
},
MongoDB Aggregation
$group :
Example: Who Tweeted Most?
Answer:
* Group tweets by user
* Count each user's tweets
* Sort into descending order
* Select user at top
def most_tweets():
result = db.tweets.aggregate([
{ "$group" : {"_id" : "$user.screen_name",
"count" : { "$sum" : 1 } } } , # 合并所有_id 名字为 user.screen_name的字段,并在每次遇到同样字段的时候加一
{ "sort" : { "count" : -1 } } ] )
return result
\(project*: shape documents you receive as input into what you need for the next stage
*\)match: filter the document, 选出想要的document
* Example Question: Who has the highest followers to friends ratio?
def highest_ratio():
result = db.tweets.aggregate([
{ "$match" : { "user.friends_count" : {"$gt" : 0},
"user.followers_count" : {"$gt" : 0 } } },
{ "$project" : { "ratio" : { "$divide" : ["$user.followers_count", "$user.friends_count"]},
"screen_name" : "$user.screen_name"} },
{ "$sort" : { "ratio" : -1 } },
{ "$limit" : 1 } ])
return result
\(skip*: 直接跳过某些document,
*\)limit: 和skip作用相反, 直接划定向下继续传入的文档数量
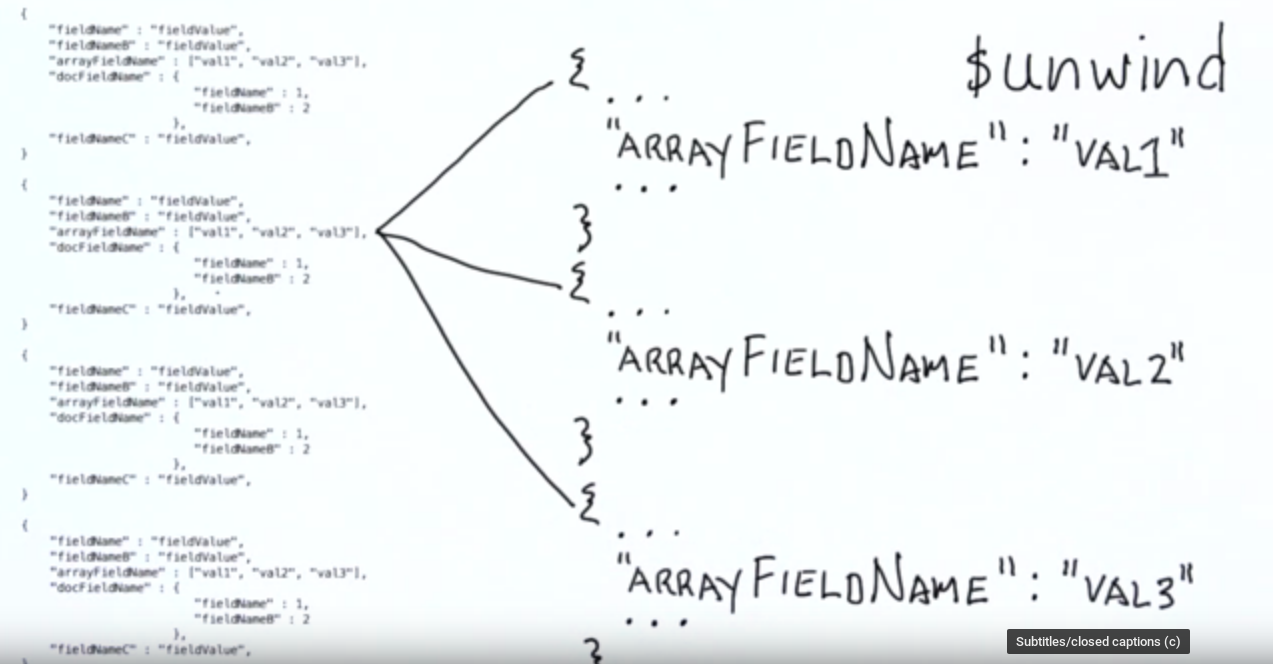
$unwind: 把数组的元素抽离出来, 方便根据数组元素的来进行聚合等进一步操作
Example Question: Who included the most user mentions?
def user_mentions():
result = db.tweets.aggregate([
{ "$unwind" : "$entities.user_mentions" },
{ "$group" : { "_id" : "$user.screen_name",
"count" : { "$sum" : 1 } } },
{ "$sort" : { "count" : -1 } },
{ "$limit" : 1 } ] )
return result
所有的query 语句都是在server side执行, 只有最后的结果会通过网络传输返回
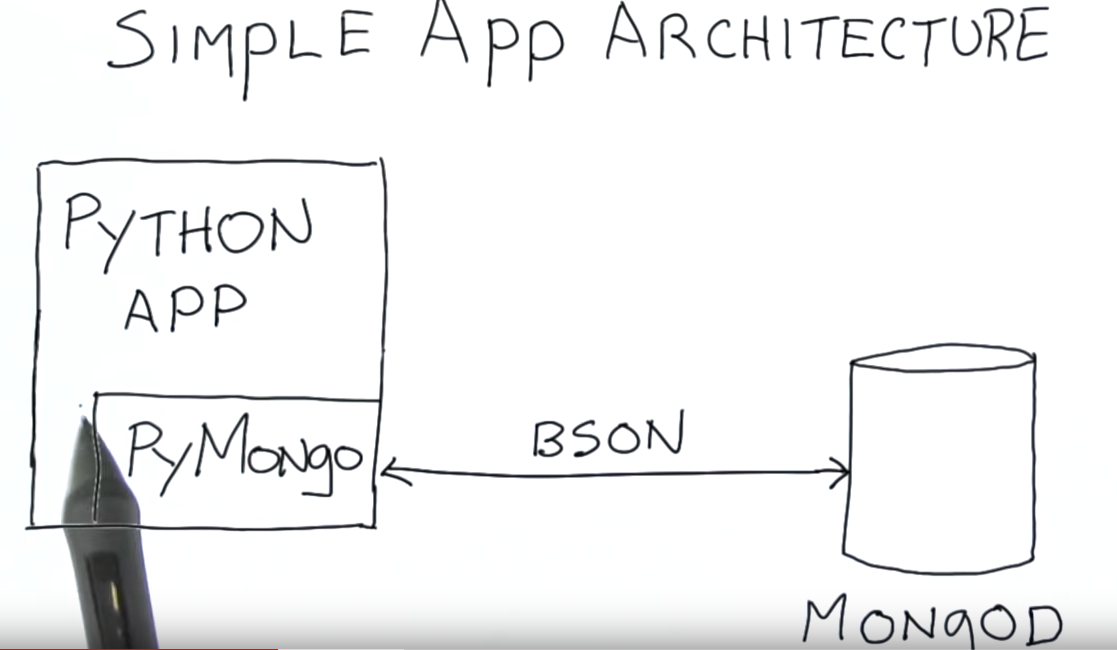
BSON: binary encode of JSON
Python Application Pymongo -> MongoDB
使用Pymongo来进行数据的存取和操作




