操作系统学习笔记
Udacity Introduction to Operating System
Introduction
What is operating system?
OS Elements
OS Design Principles
OS Services
Different OS design
- Modular OS
- Monolithic OS
- Microkernel
Linux and Mac OS Architectures
Processes and Process Management
What is a process?
Process == state of a program when executing loaded in memory
If the same program is launched more than once, multiple processes will be created
page table, do the mapping of the virtual address to the physical address
What does a process look like?
Data and text: 静态信息
page table
stack: 记录位置信息
heap
Process Control Block
process state
process number
registers
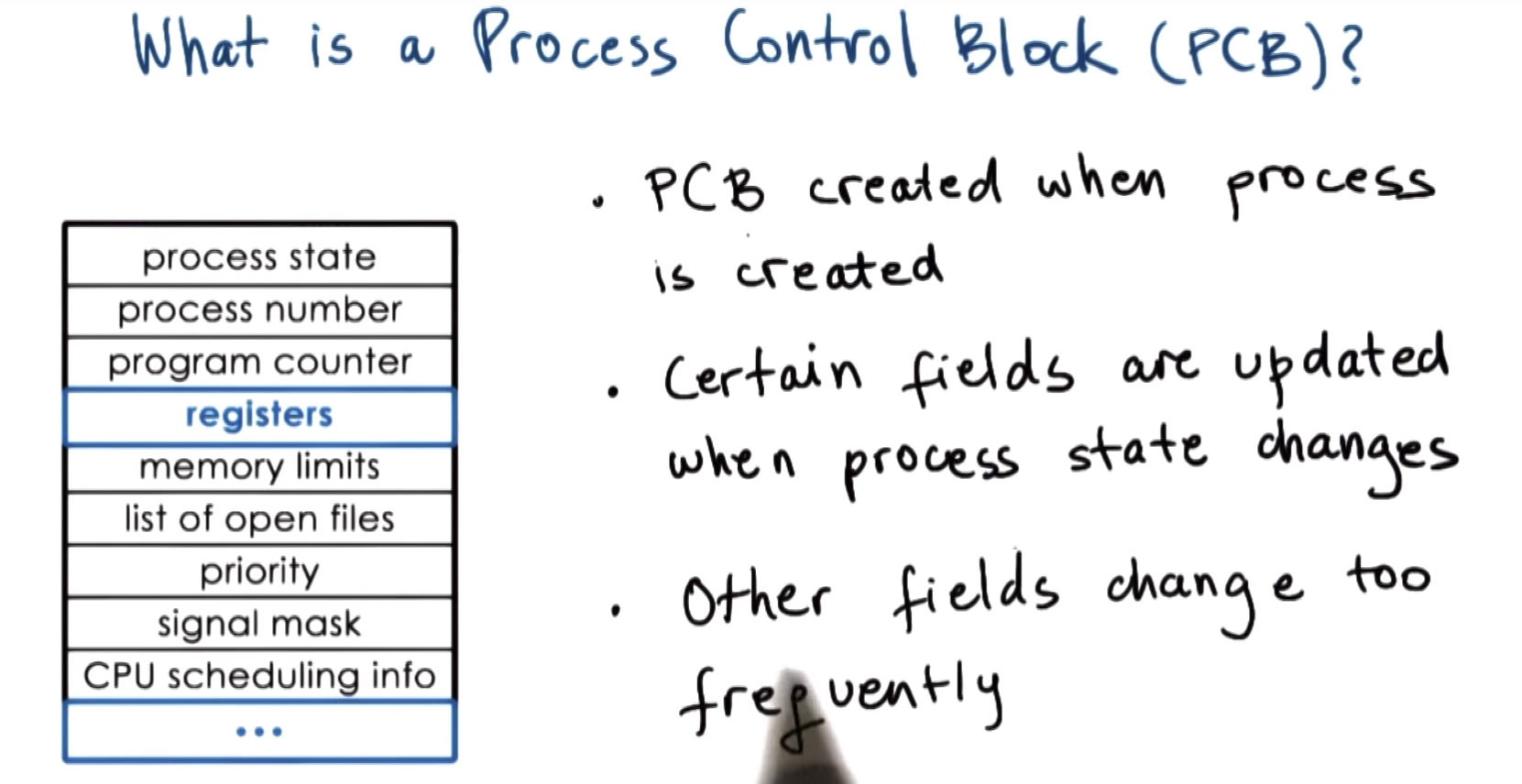
How is PCB used?
What is a Context Switch?
进程切换花销很大
direct cost: number of cycles for loading instructions
indirect cost: cold cache/ hot cache
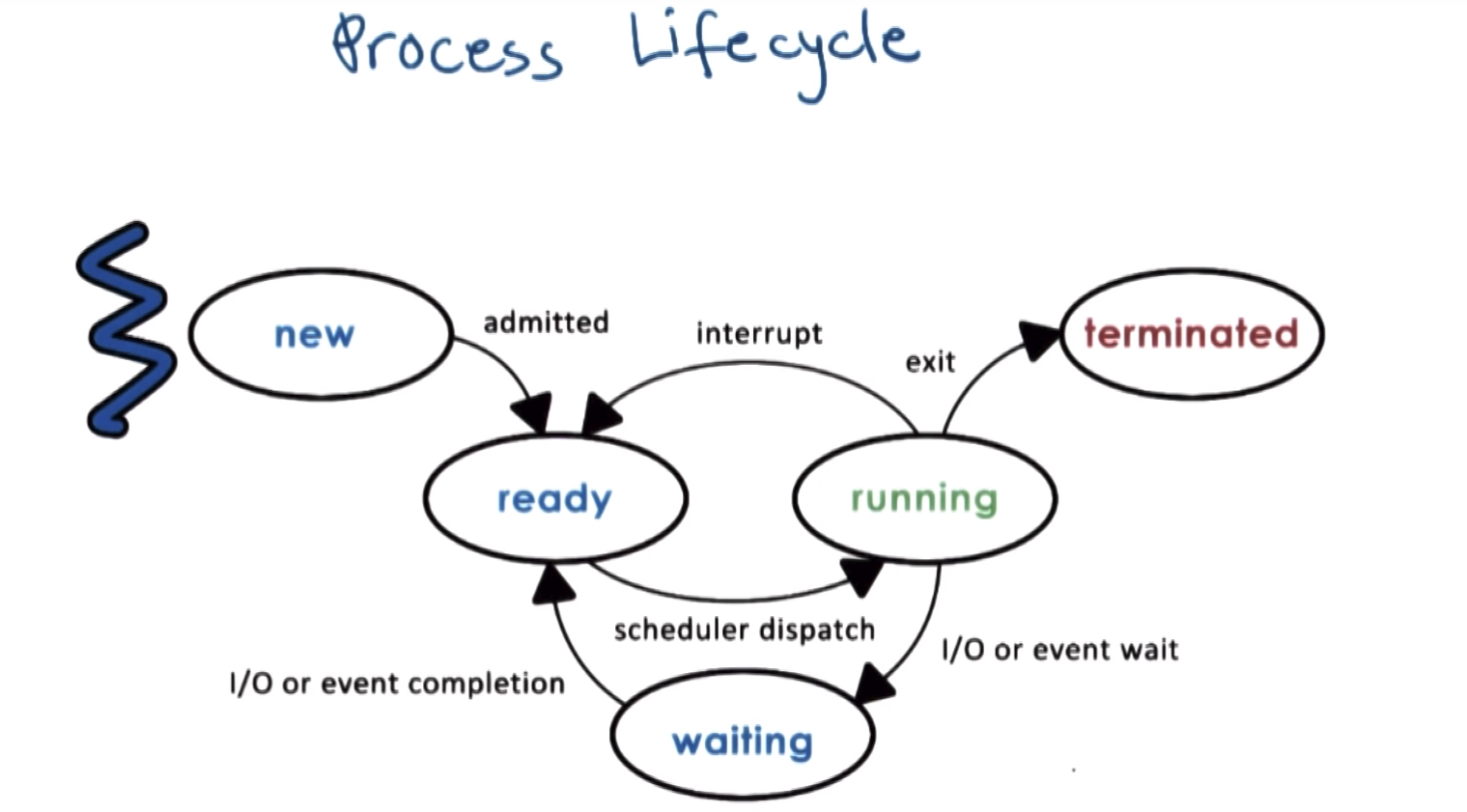
Process Lifecycle
- running:
- idle:
creation: fork (copy the parent PCB into new child PCB) and exec(replace child image with new one)
Threads and Concurrency
Process vs. Thread
the address space
code, data, files and its own thread
进程是不会有共同的address mapping的
不同的线程会有自己私有的程序计数器, 栈, 栈指针
thread would share all of the virtual to physical address mappings
可以访问地址空间的不同部分
- Benefits of Multithreading
并发执行: 将任务分解来加速
specialization: hot cache
高效: lower mm requirement & cheaper IPC
single CPU
multiple CPU
简单的比较:
- if (t_idle) > 2 * (t_ctx_switch)
- t_ctx_switch threads < t_ctx_switch processes

Basic Thread Mechanisms
thread data structure:
mechanisms to create and manage threads
mechanisms to safely coordinate among threads running concurrently
可以读取同样的地址, 会导致inconsistency
面试题整理
- 进程与线程的区别?
- 答
进程和线程都是一个时间段的描述, 是CPU工作时间段的描述
CPU太快,
得到CPU的时候,相关的资源必须已经就位, 除CPU之外的构成了程序的执行环境, 也就是我们所说的程序上下文。
轮流执行CPU的方法: 先加载程序A的上下文,然后开始执行A,保存程序A的上下文,调入下一个要执行的程序B的程序上下文,然后开始执行B,保存程序B的上下文
进程就是包括了上下文切换的程序执行时间总和 = CPU 加载上下文 + CPU执行 + CPU保存上下文
线程就是贡献了进程的上下文环境的更细小的CPU时间段




