平面或空间中任意点的旋转
平面或空间中任意点的旋转
自己琢磨出来的。若有错误请指出。谢谢!
1. 旋转2D
假设平面上有一个点,旋转任意角度,求旋转后的点。
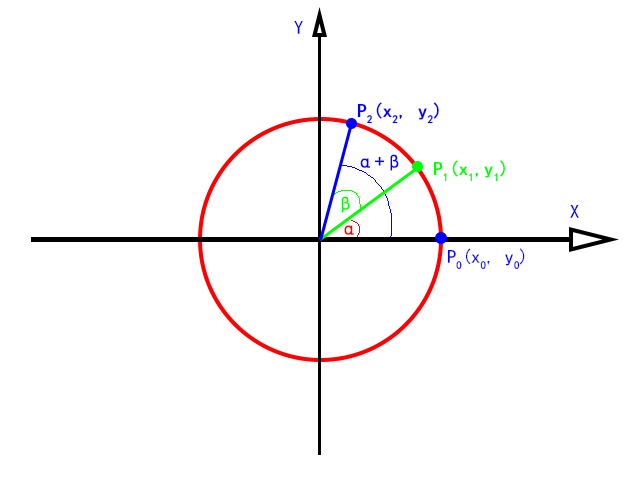
设平面坐标系上有一个半径为的圆,圆心位于原点。圆与轴正坐标的交点为。
将点旋转任意角度弧度得任意点,那么点的坐标该怎么通过计算获得?
现在将另一任意点相对于点旋转任意角度,那么点的坐标该怎么通过计算获得?
使用三角函数的和角公式把点的坐标公式展开得:
把得坐标带入上面的坐标展开式,则有:
总结:对于平面上任意点,旋转任意角度后,得到的点为:
三角函数和差公式
2. 旋转3D
假设平面上有一个点,绕轴、轴和轴相对于原点旋转任意角度、和,求旋转后的点。
按照类似于2D的情况来考虑此问题。该问题可以分解为分别在平面,平面和平面内相对于原点旋转。那么,有以下结论:
在平面内绕轴相对于原点旋转角度旋转:
在平面内绕轴相对于原点旋转角度旋转:
在平面内绕轴相对于原点旋转角度旋转:
注:绕轴旋转,理解为点在平面内的投影,并绕原点旋转。其余的情况类似。
3. 代码
这里使用Python语言来编写上面两种旋转的代码,如下:
import math
def rotate_2d(x: int | float,
y: int | float,
rad: int | float) -> (float, float):
"""
Rotate a point around orientation at any given radian.
:param x: X scale of point.
:param y: Y scale of point.
:param rad: Radian value to be rotated.
:return: A new point has been rotated by rad radian.
:raise: None.
"""
rad = float(rad)
r_x: float = (x * math.cos(rad)) - (y * math.sin(rad))
r_y: float = (y * math.cos(rad)) + (x * math.sin(rad))
return r_x, r_y
def rotate_3d(x: int | float,
y: int | float,
z: int | float,
ax: float,
ay: float,
az: float) -> (float, float, float):
"""
Rotate a point in 3d space around orientation at any given radian.
:param x: X scale of point.
:param y: Y scale of point.
:param z: Z scale of point.
:param ax: Radian value to be rotated around orientation x.
:param ay: Radian value to be rotated around orientation y.
:param az: Radian value to be rotated around orientation z.
:return: A new point has been rotated by rad radian.
:raise: None.
"""
ax = float(ax)
ay = float(ay)
az = float(az)
# rotate around axis x
r_x = x
r_y = y * math.cos(ax) - z * math.sin(ax)
r_z = z * math.cos(ax) + y * math.sin(ax)
x, y, z = r_x, r_y, r_z
# rotate around axis y
r_y = y
r_x = x * math.cos(ay) - z * math.sin(ay)
r_z = z * math.cos(ay) + x * math.sin(ay)
x, y, z = r_x, r_y, r_z
# rotate around axis z
r_z = z
r_x = x * math.cos(az) - y * math.sin(az)
r_y = y * math.cos(az) + x * math.sin(az)
return r_x, r_y, r_z
def radian(degree: int | float):
"""
Convert radian value in to radian value.
:param degree: Degree value to be converted.
:return: Radian value.
:raise: None.
"""
return degree * math.pi / 180.0
if __name__ == "__main__":
def main():
x = 1.0
y = 0.0
for i in range(360+1):
p = rotate_2d(x, y, radian(i))
print("{:>3d} degree, ".format(i), '(x: {:+.3f}, y:{:+.3f})'.format(*p))
return
main()
参考资料:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现