拓扑排序
引入
把完成一件事情或一个项目当成一个工程来对待,又将其分为若干个“活动”的子工程。例如:“炒一盘肉”这个工程,可以按照先后步骤画出以下这么一张图。
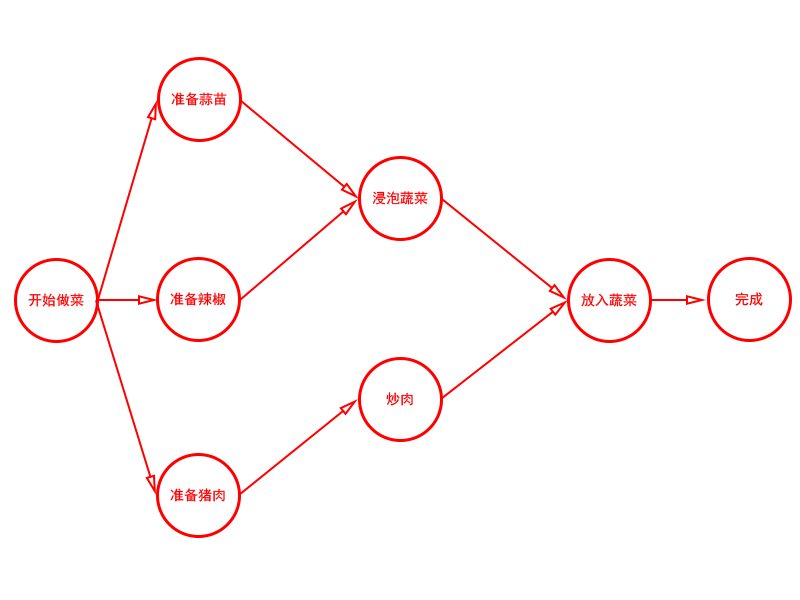
把上面这张图看成是一个表示工程的有向图,用顶点(Vertex)表示活动(Activity),用弧(Edge)表示活动(Activity)之间的优先关系,称这样的图为顶点表示活动的网(Activity On Vertex Network),即AOV网。
AOV网中弧(Edge)表示活动(Activity)之间有制约关系。另外AOV网中不能存在回路,即A这个活动的开始条件是以A这个活动的结束为先决条件的。
定义
设G=(V, E)是具有n个顶点的有向图,V中顶点序列v1、v2、……、vn满足:若从顶点vi到vj有一条路径,则vi必在顶点vj之前。则这样的顶点序列为拓扑序列。(图G的拓扑序列可以不止一个)
即:
①有向图G=(V, E)中,有顶点V={v1, v2, … , vn}(前提)
②v1、v2、……、vn以某种顺序构成顶点序列S,从中任取两个相异顶点vi,vj。(前提)
③若vi到vj有路径,且vi在vj之前。(条件)
④则顶点序列S为一个拓扑序列。(结论)
核心思想
拓扑排序解决的是“一个工程能否按顺序进行”的问题。其算法过程如下:
①用邻接表来表示有向图G。计数器counter置0。
②将图G中所有入度为0的顶点入栈S。
③若栈S不为空,则从栈中弹出一个顶点vtop。
④将顶点vtop的出边弧头顶点vadj的入度减1。
⑤如果vadj的入度为0了,则将vadj入栈S。
⑥计数器counter++。
⑦跳至步骤③。
⑧如果计数器counter与图G的顶点数相等,则完成拓扑排序,否则图G中有环,不能进行拓扑排序。
问题:尝试对上面的图进行拓扑排序?
推演
使用邻接表来表示上面的图,如下:
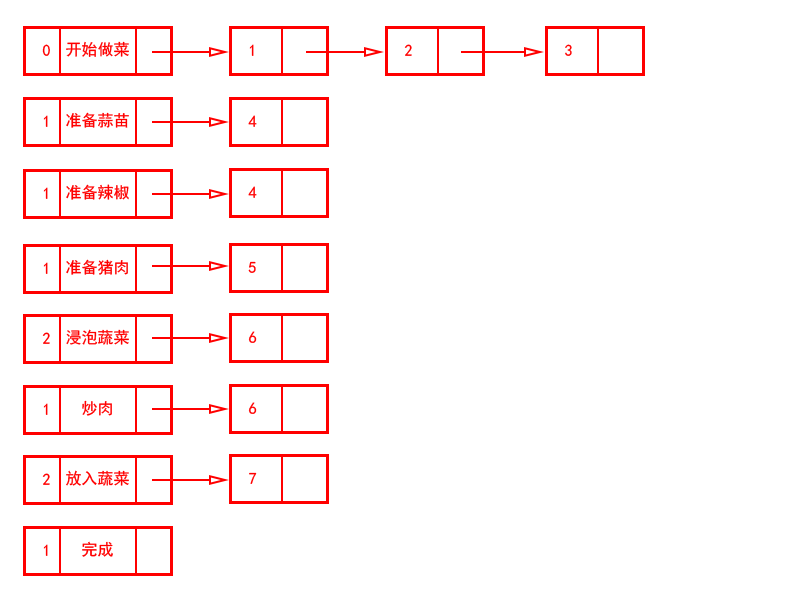
基于前面的核心思想对排序过程进行推演如下:
初始所有入度为0的顶点:栈顶->[开始做菜]
第0次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[开始做菜]
开始做菜出栈:栈顶->[]
准备蒜苗入度:1-1=0。
准备蒜苗入栈。栈:栈顶->[准备蒜苗]
准备辣椒入度:1-1=0。
准备辣椒入栈。栈:栈顶->[准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
准备猪肉入度:1-1=0。
准备猪肉入栈。栈:栈顶->[准备猪肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
第0次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[准备猪肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
第1次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[准备猪肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
准备猪肉出栈:栈顶->[准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
炒肉入度:1-1=0。
炒肉入栈。栈:栈顶->[炒肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
第1次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[炒肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
第2次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[炒肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
炒肉出栈:栈顶->[准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
放入蔬菜入度:2-1=1。
第2次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
第3次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[准备辣椒,准备蒜苗]
准备辣椒出栈:栈顶->[准备蒜苗]
浸泡蔬菜入度:2-1=1。
第3次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[准备蒜苗]
第4次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[准备蒜苗]
准备蒜苗出栈:栈顶->[]
浸泡蔬菜入度:1-1=0。
浸泡蔬菜入栈。栈:栈顶->[浸泡蔬菜]
第4次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[浸泡蔬菜]
第5次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[浸泡蔬菜]
浸泡蔬菜出栈:栈顶->[]
放入蔬菜入度:1-1=0。
放入蔬菜入栈。栈:栈顶->[放入蔬菜]
第5次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[放入蔬菜]
第6次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[放入蔬菜]
放入蔬菜出栈:栈顶->[]
完成入度:1-1=0。
完成入栈。栈:栈顶->[完成]
第6次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[完成]
第7次循环开始时栈:栈顶->[完成]
完成出栈:栈顶->[]
第7次循环结束时栈:栈顶->[]
开始做菜,准备猪肉,炒肉,准备辣椒,准备蒜苗,浸泡蔬菜,放入蔬菜,完成
代码
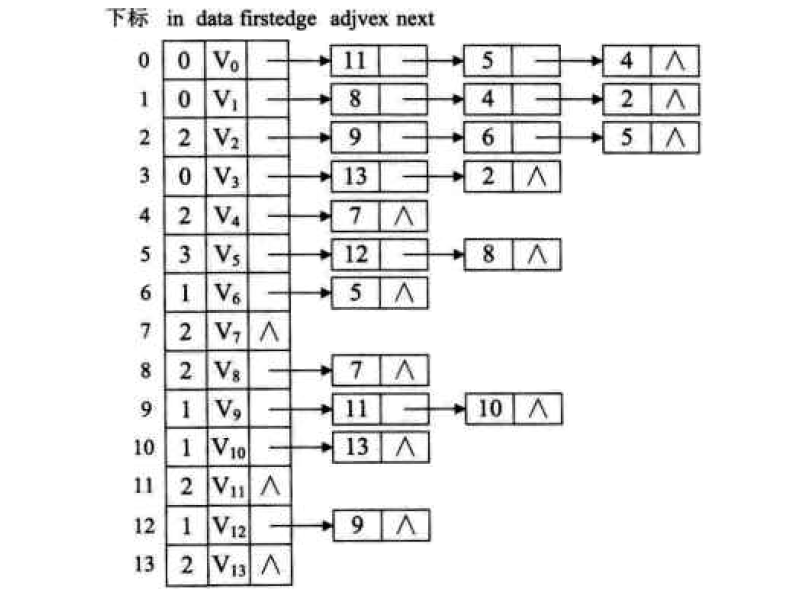
用邻接矩阵来表示图G。如前面的图。以及大话数据结构上的图,如下图:
C#代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace TopologicalSort
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TopologicalSort(new Vertex[] {
new Vertex(0,"0",new int[]{11, 5, 4 }),
new Vertex(0,"1",new int[]{8, 4, 2 }),
new Vertex(2,"2", new int[]{9, 6, 5 }),
new Vertex(0,"3",new int[]{13,2 }),
new Vertex(2,"4",new int[]{7 }),
new Vertex(3,"5",new int[]{12,8 }),
new Vertex(1,"6",new int[]{ 5}),
new Vertex(2,"7",new int[]{ }),
new Vertex(2,"8",new int[]{7 }),
new Vertex(1,"9",new int[]{ 11,10}),
new Vertex(1,"10",new int[]{13 }),
new Vertex(2,"11",new int[]{ }),
new Vertex(1,"12",new int[]{ 9}),
new Vertex(2,"13",new int[]{ }),
});
TopologicalSortWithDebug(new Vertex[] {
new Vertex(0,"开始做菜",new int[]{1, 2, 3}),
//new Vertex(2,"准备蒜苗",new int[]{4,1}), // 让图中存在环
new Vertex(1,"准备蒜苗",new int[]{4}),
new Vertex(1,"准备辣椒", new int[]{4}),
new Vertex(1,"准备猪肉",new int[]{5}),
new Vertex(2,"浸泡蔬菜",new int[]{6}),
new Vertex(1,"炒肉",new int[]{6}),
new Vertex(2,"放入蔬菜",new int[]{7}),
new Vertex(1,"完成",new int[]{ })
});
}
public static void TopologicalSort(Vertex[] graph)
{
List<string> result = new List<string>();
// 1.用于判断最终图中是否还有入度为0的顶点。若没有则拓扑排序成功。否则没有。
int counter = 0;
// 缓存入度为0的顶点。
Stack<Vertex> s = new Stack<Vertex>();
// 2.将所有入度为0的顶点入栈。
for (int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
{
Vertex v = graph[i];
if (v.InDegree == 0)
{
s.Push(v);
}
}
// 3.若栈S不为空,
while (s.Count != 0)
{
// 则从栈中弹出一个顶点Vtop。
Vertex top = s.Pop();
// 4.将顶点Vtop的出边弧头
for (var e = top.Edge; e != null; e = e.Next)
{
// 弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
int n = e.Vertex;
Vertex adj = graph[n];
// 顶点Vadj的入度减1。
adj.InDegree--;
// 5.如果Vadj的入度为0,
if (adj.InDegree == 0)
{
// 则将Vadj入栈S。
s.Push(adj);
}
}
result.Add(top.Data);
// 6.计数器递增。
counter++;
// 7.跳至步骤3。
}
if (counter != graph.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine($"错误:图G中顶点数:{graph.Length},还剩{graph.Length - counter}个顶点入度非0。");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", result.ToArray()));
}
}
public static void TopologicalSortWithDebug(Vertex[] graph)
{
List<string> result = new List<string>();
// 1.用于判断最终图中是否还有入度为0的顶点。若没有则拓扑排序成功。否则没有。
int counter = 0;
// 缓存入度为0的顶点。
Stack<Vertex> s = new Stack<Vertex>();
// 2.将所有入度为0的顶点入栈。
for (int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
{
Vertex v = graph[i];
if (v.InDegree == 0)
{
s.Push(v);
}
}
Console.WriteLine($"初始所有入度为0的顶点:{PrintStackVertex(s)}");
// 3.若栈S不为空,
while (s.Count != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"第{counter}次循环开始时栈:{PrintStackVertex(s)}");
// 则从栈中弹出一个顶点Vtop。
Vertex top = s.Pop();
Console.WriteLine($"{top.Data}出栈:{PrintStackVertex(s)}");
// 4.将顶点Vtop的出边弧头
for (var e = top.Edge; e != null; e = e.Next)
{
// 弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
int n = e.Vertex;
Vertex adj = graph[n];
// 顶点Vadj的入度减1。
//adj.InDegree--;
Console.WriteLine($"{adj.Data}入度:{adj.InDegree}-1={--adj.InDegree}。");
// 5.如果Vadj的入度为0,
if (adj.InDegree == 0)
{
// 则将Vadj入栈S。
s.Push(adj);
Console.WriteLine($"{adj.Data}入栈。栈:{PrintStackVertex(s)}");
}
}
result.Add(top.Data);
Console.WriteLine($"第{counter}次循环结束时栈:{PrintStackVertex(s)}");
// 6.计数器递增。
counter++;
// 7.跳至步骤3。
Console.WriteLine();
}
if (counter != graph.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine($"错误:图G中顶点数:{graph.Length},还剩{graph.Length - counter}个顶点入度非0。");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", result.ToArray()));
}
}
public static string PrintStackVertex(Stack<Vertex> s)
{
string[] datas = s.ToArray().Select(e => e.Data).ToArray();
return $"栈顶->[{string.Join(',', datas)}]";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 图G的顶点。用邻接表来表示顶点的出边。
/// </summary>
public class Vertex
{
/// <summary>
/// 入度。
/// </summary>
public int InDegree { get; set; } = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 存储的数据。
/// </summary>
public string Data { get; set; } = "";
/// <summary>
/// 出边。
/// </summary>
public Edge Edge { get; set; } = null;
public Vertex(int inDegree, string data, int[] vertexIndexes)
{
this.InDegree = inDegree;
this.Data = data;
Edge e = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexIndexes.Length; i++)
{
if (e == null)
{
e = new Edge(vertexIndexes[i], null);
this.Edge = e;
}
else
{
e.Next = new Edge(vertexIndexes[i], null);
e = e.Next;
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 图G的边。以邻接表表示顶点的出边。
/// </summary>
public class Edge
{
/// <summary>
/// 边的弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
/// </summary>
public int Vertex { get; set; } = -1;
/// <summary>
/// 边的弧尾顶点的下一条出边。
/// </summary>
public Edge Next { get; set; } = null;
public Edge(int vertex = -1, Edge edge = null)
{
this.Vertex = vertex;
this.Next = edge;
}
}
}
TypeScript代码
/**
* 图G的顶点。用邻接表来表示顶点的出边。
*/
class Vertex {
// 入度。
InDegree: number = 0;
// 存储的数据。
Data: string = "";
// 首条出边。
Edge: Edge = null;
/**
* 创建邻接表的一行。
* @param inDegree 顶点的入度。
* @param data 顶点存储的数据。
* @param vertexIndexes 顶点的出边(弧)的弧头。
*/
constructor(inDegree: number, data: string, vertexIndexes: number[]) {
this.InDegree = inDegree;
this.Data = data;
let e: Edge = null;
for (let i = 0; i < vertexIndexes.length; i++) {
if (e === null) {
e = new Edge(vertexIndexes[i], null);
this.Edge = e;
}
else {
e.Next = new Edge(vertexIndexes[i], null);
e = e.Next;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 图G的边。以邻接表表示顶点的出边。
*/
class Edge {
// 边的弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
Vertex: number = -1;
// 边的弧尾顶点的下一条出边。
Next: Edge = null;
/**
* 创建邻接表中的一条边/弧。
* @param vertex 邻接表中,该边的弧尾顶点的在顶点数组中的下标。
* @param next 邻接表中,该边的弧尾顶点的下一条出边。
*/
constructor(vertex: number, next: Edge) {
this.Vertex = vertex;
this.Next = next;
}
}
/**
* 对图G进行拓扑排序。图G中若无环,则可进行拓扑排序,否则会输出错误信息。
* @param graph 图G。
*/
function topologicalSort(graph: Vertex[]) {
let result: string[] = [];
// 1.用于判断最终图中是否还有入度为0的顶点。若没有则拓扑排序成功。否则没有。
let counter: number = 0;
// 缓存入度为0的顶点。
let s: Vertex[] = [];
// 2.将所有入度为0的顶点入栈。
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
let v: Vertex = graph[i];
if (v.InDegree === 0) {
s.push(v);
}
}
// 3.若栈S不为空,
while (s.length != 0) {
// 则从栈中弹出一个顶点Vtop。
let top: Vertex = s.pop();
// 4.将顶点Vtop的出边弧头
for (let e: Edge = top.Edge; e !== null; e = e.Next) {
// 弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
let n: number = e.Vertex;
let adj: Vertex = graph[n];
// 顶点Vadj的入度减1。
adj.InDegree--;
// 5.如果Vadj的入度为0,
if (adj.InDegree == 0) {
// 则将Vadj入栈S。
s.push(adj);
}
}
result.push(top.Data);
// 6.计数器递增。
counter++;
// 7.跳至步骤3。
}
if (counter != graph.length) {
console.log(`错误:图G中顶点数:${graph.length},还剩${graph.length - counter}个顶点入度非0。`);
}
else {
console.log(result.join(","));
}
}
/**
* 对图G进行拓扑排序。图G中若无环,则可进行拓扑排序,否则会输出错误信息。
* @param graph 图G。
*/
function topologicalSortWithDebug(graph: Vertex[]) {
let result: string[] = [];
// 1.用于判断最终图中是否还有入度为0的顶点。若没有则拓扑排序成功。否则没有。
let counter: number = 0;
// 缓存入度为0的顶点。
let s: Vertex[] = [];
// 2.将所有入度为0的顶点入栈。
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
let v: Vertex = graph[i];
if (v.InDegree === 0) {
s.push(v);
}
}
console.log(`初始所有入度为0的顶点:${PrintStackVertex(s)}`);
// 3.若栈S不为空,
while (s.length != 0) {
console.log(`第${counter}次循环开始时栈:${PrintStackVertex(s)}`);
// 则从栈中弹出一个顶点Vtop。
let top: Vertex = s.pop();
console.log(`${top.Data}出栈:${PrintStackVertex(s)}`);
// 4.将顶点Vtop的出边弧头
for (let e: Edge = top.Edge; e !== null; e = e.Next) {
// 弧头顶点在顶点数组中的索引。
let n: number = e.Vertex;
let adj: Vertex = graph[n];
// 顶点Vadj的入度减1。
//adj.InDegree--;
console.log(`${adj.Data}入度:${adj.InDegree}-1=${--adj.InDegree}。`);
// 5.如果Vadj的入度为0,
if (adj.InDegree == 0) {
// 则将Vadj入栈S。
s.push(adj);
console.log(`${adj.Data}入栈。栈:${PrintStackVertex(s)}`);
}
}
result.push(top.Data);
console.log(`第${counter}次循环结束时栈:${PrintStackVertex(s)}`);
// 6.计数器递增。
counter++;
// 7.跳至步骤3。
}
if (counter != graph.length) {
console.log(`错误:图G中顶点数:${graph.length},还剩${graph.length - counter}个顶点入度非0。`);
}
else {
console.log(result.join(","));
}
}
function PrintStackVertex(s: Vertex[]): string {
let result: string[] = [];
s.forEach(e=>result.push(e.Data));
return `栈顶->[${result.join(",")}]`;
}
function main() {
// let vs: Vertex[] = [
// new Vertex(0, "0", [11, 5, 4]),
// new Vertex(0, "1", [8, 4, 2]),
// new Vertex(2, "2", [9, 6, 5]),
// new Vertex(0, "3", [13, 2]),
// new Vertex(2, "4", [7]),
// new Vertex(3, "5", [12, 8]),
// new Vertex(1, "6", [5]),
// new Vertex(2, "7", []),
// new Vertex(2, "8", [7]),
// new Vertex(1, "9", [11, 10]),
// new Vertex(1, "10", [13]),
// new Vertex(2, "11", []),
// new Vertex(1, "12", [9]),
// new Vertex(2, "13", [])
// ];
// topologicalSort(vs);
let vertexes: Vertex[] = [
new Vertex(0, "开始做菜", [1, 2, 3]),
//new Vertex(2, "准备蒜苗", new int[]{4, 1}), // 让图中存在环
new Vertex(1, "准备蒜苗", [4]),
new Vertex(1, "准备辣椒", [4]),
new Vertex(1, "准备猪肉", [5]),
new Vertex(2, "浸泡蔬菜", [6]),
new Vertex(1, "炒肉", [6]),
new Vertex(2, "放入蔬菜", [7]),
new Vertex(1, "完成", [])
];
//topologicalSort(vertexes);
topologicalSortWithDebug(vertexes);
}
main();
参考资料
《大话数据结构》 - 程杰 著 - 清华大学出版社 第270页




