Spring:IOC
IOC容器
IOC思想
IOC:Inversion of Control,翻译过来是反转控制。
①获取资源的传统方式
自己做饭:买菜、洗菜、择菜、改刀、炒菜,全过程参与,费时费力,必须清楚了解资源创建整个过程中的全部细节且熟练掌握。
在应用程序中的组件需要获取资源时,传统的方式是组件主动的从容器中获取所需要的资源,在这样的
模式下开发人员往往需要知道在具体容器中特定资源的获取方式,增加了学习成本,同时降低了开发效率。
②反转控制方式获取资源
点外卖:下单、等、吃,省时省力,不必关心资源创建过程的所有细节。
反转控制的思想完全颠覆了应用程序组件获取资源的传统方式:反转了资源的获取方向——改由容器主动的将资源推送给需要的组件,开发人员不需要知道容器是如何创建资源对象的,只需要提供接收资源的方式即可,极大的降低了学习成本,提高了开发的效率。这种行为也称为查找的被动形式。
③DI
DI:Dependency Injection,翻译过来是依赖注入。
DI 是 IOC 的另一种表述方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如:setter 方法)接受来自于容器
的资源注入。相对于IOC而言,这种表述更直接。
所以结论是:IOC 就是一种反转控制的思想, 而 DI 是对 IOC 的一种具体实现。
IOC容器在Spring中的实现
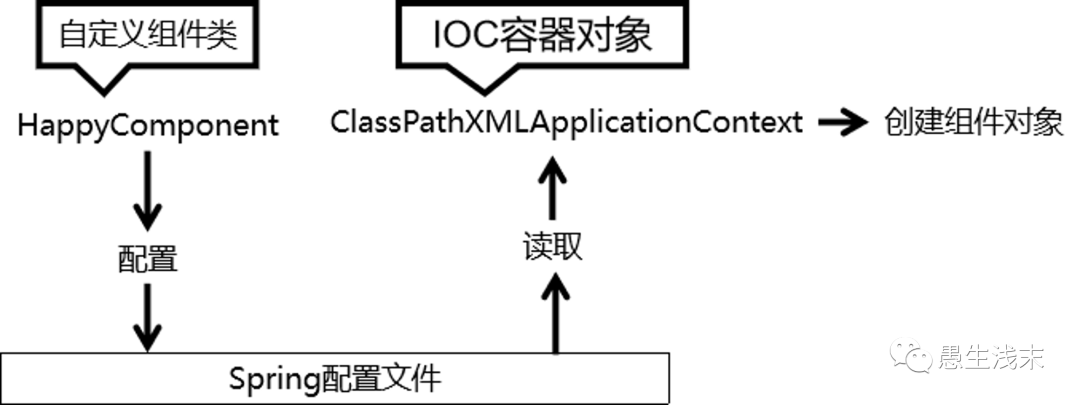
Spring 的 IOC 容器就是 IOC 思想的一个落地的产品实现。IOC 容器中管理的组件也叫做 bean。在创建bean 之前,首先需要创建 IOC 容器。Spring 提供了 IOC 容器的两种实现方式:
①BeanFactory
这是 IOC 容器的基本实现,是 Spring 内部使用的接口。面向 Spring 本身,不提供给开发人员使用。
②ApplicationContext
BeanFactory 的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向 Spring 的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用
ApplicationContext 而不是底层的 BeanFactory。
③ApplicationContext的主要实现类
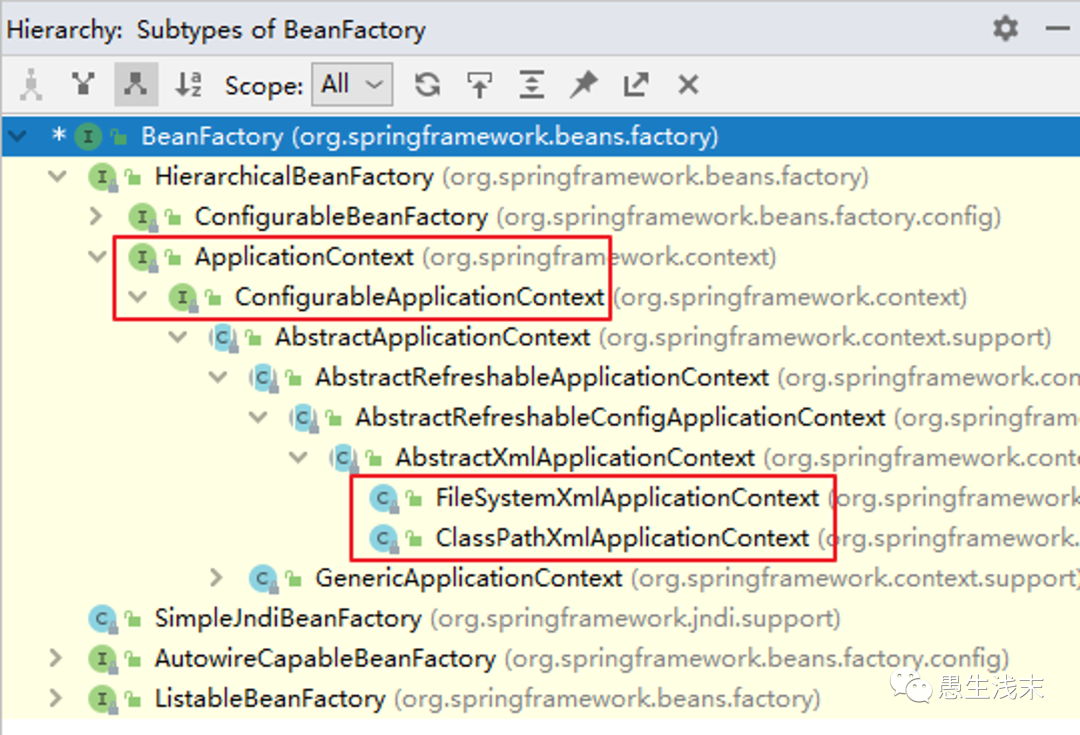
| 类型名 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| ClassPathXmlApplicationContext | 通过读取类路径下的 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象 |
| FileSystemXmlApplicationContext | 通过文件系统路径读取 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象 |
| ConfigurableApplicationContext | ApplicationContext 的子接口,包含一些扩展方法refresh() 和 close() ,让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、关闭和刷新上下文的能力。 |
| WebApplicationContext | 专门为 Web 应用准备,基于 Web 环境创建 IOC 容器对象,并将对象引入存入 ServletContext 域中。 |
基于XML管理bean
入门案例
- 创建Maven Module
- 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 基于Maven依赖传递性,导入spring-context依赖即可导入当前所需所有jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 创建类HelloSpring
public class HelloSpring {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("helloSpring");
}
}
- 创建Spring的配置文件
- 在Spring的配置文件中配置bean
<!--
配置HelloSpring所对应的bean,即将HelloSpring的对象交给Spring的IOC容器管理
通过bean标签配置IOC容器所管理的bean
属性:
id:设置bean的唯一标识
class:设置bean所对应类型的全类名
-->
<bean id="helloSpring" class="com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring"></bean>
- 创建测试类测试
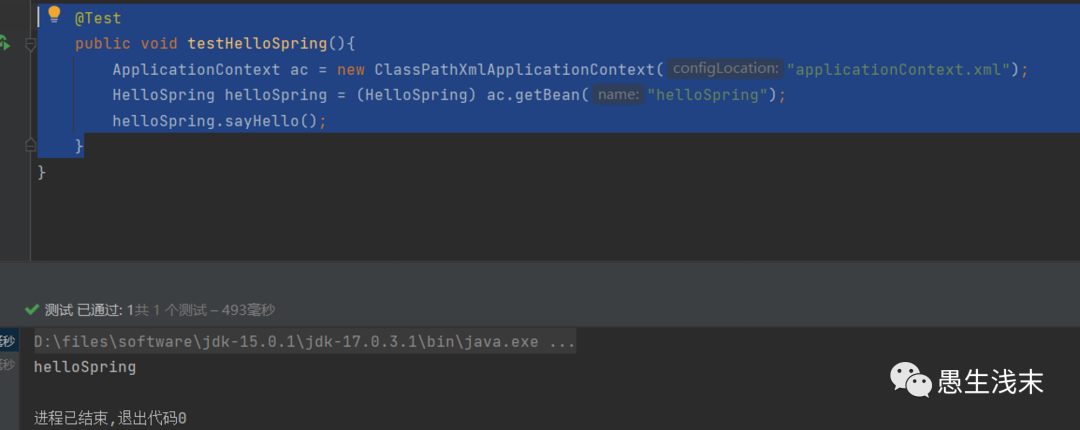
@Test
public void testHelloSpring(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloSpring helloSpring = (HelloSpring) ac.getBean("helloSpring");
helloSpring.sayHello();
}
测试结果:
-
思路
-
注意
Spring 底层默认通过反射技术调用组件类的无参构造器来创建组件对象,这一点需要注意。如果在需要无参构造器时,没有无参构造器,则会抛出下面的异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name'helloSpring' defined in class path resource [applicationContext.xml]: Instantiation of beanfailed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failedto instantiate [com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring]: No default constructor found; nestedexception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring.
()
获取bean
方式一:根据id获取
由于 id 属性指定了 bean 的唯一标识,所以根据 bean 标签的 id 属性可以精确获取到一个组件对象。
上个实验中我们使用的就是这种方式。
方式二:根据类型获取
@Test
public void testHelloSpring(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloSpring bean = ac.getBean(HelloSpring.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
方式三:根据id和类型
@Test
public void testHelloSpring(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloSpring bean = ac.getBean("helloSpring",HelloSpring.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
注意
当根据类型获取bean时,要求IOC容器中指定类型的bean有且只能有一个
当IOC容器中一共配置了两个:
<bean id="helloSpringOne" class="com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring"></bean>
<bean id="helloSpringTwo" class="com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring"></bean>
根据类型获取时会抛出异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean
of type 'com.kailong.bean.HelloSpring' available: expected single matching bean but
found 2: helloSpringOne,helloSpringTwo
扩展
-
如果组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型也可以获取bean,但前提是bean唯一
-
如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了 bean,根据接口类型不可以获取 bean,因为bean不唯一
结论
根据类型来获取bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:『对象 instanceof 指定的类型』的返回结果,只要返回的是true就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。
公众号本文地址:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Wgrz5X-uTAZnITRy-jF1bA
欢迎关注公众号:愚生浅末。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号