Python基础-v1
为什么要学Python?大一大二学了“线代、概率统计、高数”,如今临近大三暑假,想通过学习“深度学习”来复习巩固这些数学知识;然后就是每次开发小项目系统,很痛苦的就是数据来源问题,最有效的一个办法就是通过爬虫,而据我了解的一般都是通过Python爬取的;还有Python是“胶水语言”,跨平台,兼容性好,学的意义很大。
1 学习资源
2 环境配置
2.1 Anaconda环境配置
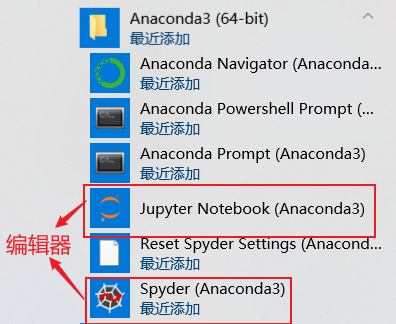
编辑器包括Spyder和Jupyter,我这里选择Jupyter
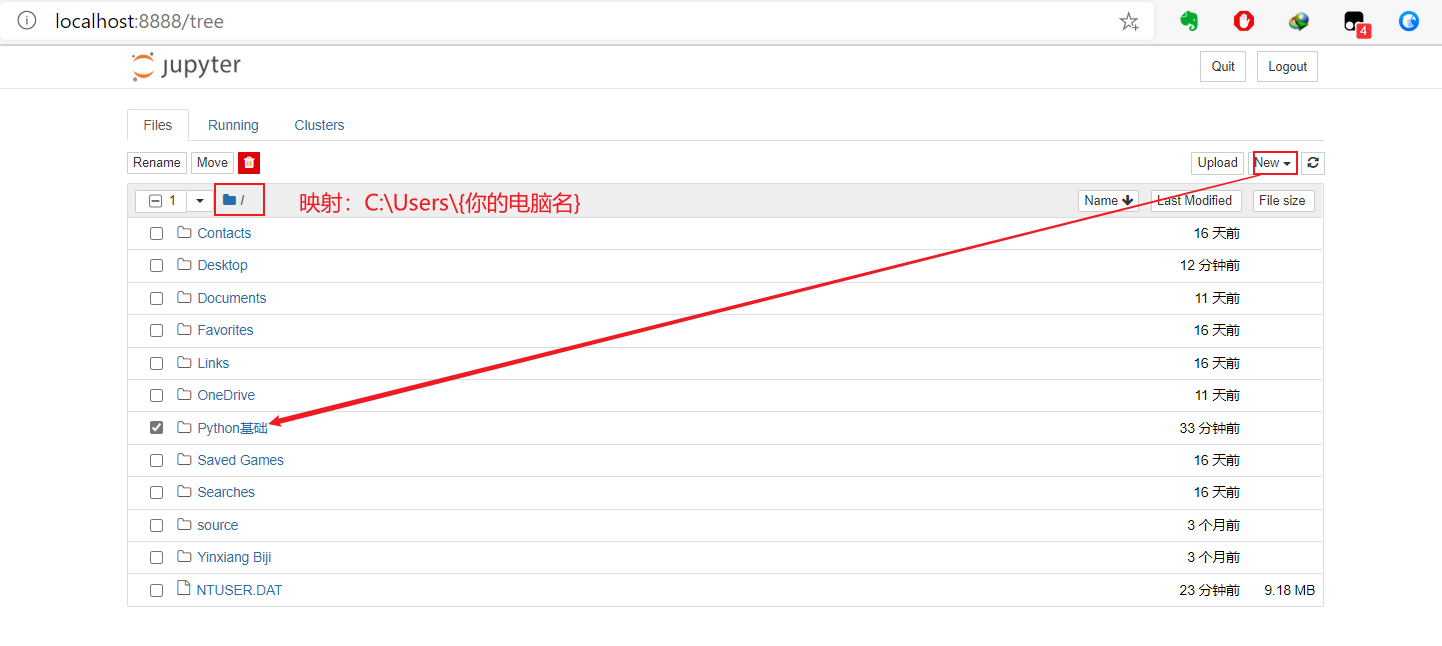
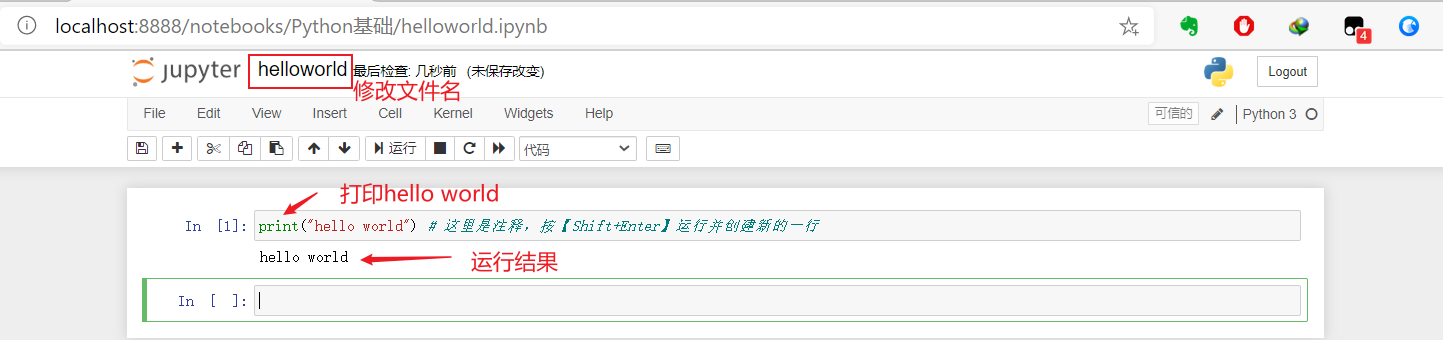
3 常量变量
变量
i = 666 # 将666赋值给变量
print(i) # 打印变量i
666
i = 888 # 将888重新赋值给变量
print(i) # 打印变量i
888
string = "abc" # 将abc赋值给变量,注意是双引号
print(string)
abc
string = 'abcd' # 将abcd重新赋值给变量,注意单引号
print(string)
abcd
del string # 删除变量string
string # 运行变量string
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-5-c0ce0be654d5> in <module>
1 del string # 删除变量string
----> 2 string # 运行变量string
NameError: name 'string' is not defined
变量运算--算数运算
a = 888
b = 3
a + b
891
a - b
885
a * b
2664
a / b
296.0
a % b # 取余
0
a // b # 取商
296
a ** b # 指数
700227072
常用运算函数
abs(-3) # 绝对值
3
round(5.6) # 四舍五入,不保留小数
6
round(5.646,1) # 四舍五入,保留1位小数
5.6
pow(9,2) # 平方
81
pow(9,1/2) # 开根号
3.0
sum([1,2,3,4,5,6]) # 对列表求和
21
比较运算
a > b
True
a < b
False
a == b
False
a != b
True
逻辑运算
a == 3 or b == 3 # 或
True
a == 3 and b ==3 # 与
False
not(a == 3 and b ==3) # 非
True
True == 1
True
True * 2
2
False == 0
True
False * 2
0
3.1 基本数据类型
数字
type(666) # int
int
type(6.66) # float
float
type("6.66") # string
str
type('6.66') # string
str
isinstance('6.66',float) # 判断浮点型
False
a = 6.66
isinstance(a,float) # 判断浮点型
True
666 == 666.00
True
字符串
单双引号问题
print("'hello world'") #双引号嵌套单引号
'hello world'
print('"hello world"') #单引号嵌套双引号
"hello world"
'' # 空字符串
''
len('') # 空字符串长度
0
len(' ') # 非空字符串长度
1
常用转义符
print("hello\tworld") #\t 制表符,4个空格,键盘【tab】键
hello world
print("hello\nworld") #\n 换行符
hello
world
print("\\t") # 打印 \t
\t
常用字符串操作
str1 = "HELLO"
str2 = "world"
print(str1.lower()) # 转小写
print(str2.upper()) # 转大写
hello
WORLD
str1 = "hello"
str2 = "world"
print(str1 + "\t" + str2) # 拼接
hello world
",".join(str1) # 插入
'h,e,l,l,o'
str3 = str1 + "\t" + str2
str3.split("\t") # 分隔,输出“列表(list)”
['hello', 'world']
str1[0] # 第一个字符
'h'
str1[-1] # 倒数第一个字符
'o'
str1[0] = 'b' # 不可修改,报错
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-22-069543d164da> in <module>
----> 1 str1[0] = 'b' # 不可修改,报错
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
str1[1:] # 切片,输出第二个到最后
'ello'
str1[0:4:2] # 起始位置,结束位置,间隔(步长)
'hl'
字符串操作进阶
提取字符串中的数字、字母、大小写字母
方法1:for循环
- str.isdigit() 判断数字
- str.islower() 判断小写
- str.isupper() 判断大写
str1 = "AAaaa22"
number = ""
lower = ""
upper = ""
for i in str1:
if i.isdigit():
number += i
elif i.islower():
lower += i
elif i.isupper():
upper += i
print(number + '\n'
+ lower + '\n'
+ upper)
22
aaa
AA
方法2:正则表达式
\d 匹配任意数字,等价于[0-9]
[0-9] 匹配数字
\D 匹配任意非数字
[a-z] 匹配小写
[A-Z] 匹配大写
[a-zA-Z0-9] 匹配数字和字母
import re #加载正则表达式re模块
str1 = 'AAaaa22@qq.com'
print(''.join(re.findall(r'[A-Za-z]',str1))) # 提取字母
print(''.join(re.findall(r'[0-9]',str1))) # 提取数字
print(re.sub("\D","",str1)) # 提取数字,将非数字替换为空字符
AAaaaqqcom
22
22
数字类型转换
float(6) # int→float
6.0
int(6.66) # float→int
6
float("6.66") # str→float
6.66
int("6.66") # str→int,失败
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-15-55f008fa896e> in <module>
----> 1 int("6.66") # str→int,失败
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '6.66'
3.2 容器
列表(list)
- 列表是有序集合:可以通过index或者key访问
- 购物车(注意与数组的差别,数组只能一种类型): 整型、浮点行、字符串、列表、字典、元组
- 支持操作:插入、添加、删除、修改、排序、反转
- 无序集合:只能遍历访问
创建列表
list1 = [] # 空列表
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)] # 整型、浮点型、字符串、列表、字典、元组
list(range(1,11)) # 自动生成1-10列表
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
添加元素
- 拼接
- 复制(自身拼接)
- list.extend(列表/元组)
- list.append(元素)
- list.insert(索引,元素)
# 添加元素
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.append([4,5,6])
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9), [4, 5, 6]]
# 添加元素--不推荐
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1[len(list1):len(list1)] = [[4,5,6]]
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9), [4, 5, 6]]
# 批量添加元素
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.extend([4,5,6]) # 会展开,遍历元素插入
list1.extend(('A',9)) # 会展开,遍历元素插入
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9), 4, 5, 6, 'A', 9]
# 批量添加元素(拼接)
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1 += [4,5,6]
list1 += ('A',9)
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9), 4, 5, 6, 'A', 9]
# 复制(自身拼接)
list1 = [6] * 3
print(list1)
[6, 6, 6]
# 拼接
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list2 = [4,5,6]
print(list1 + list2)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9), 4, 5, 6]
# 指定位置插入
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.insert(3,[7,8,9])
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [4, 5, 6], [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9)]
# 指定位置插入--不推荐
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1[3:3] = [[7,8,9]]
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', [7, 8, 9], [4, 5, 6], {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9)]
查询
# 列表长度
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
len(list1) # 长度
6
1 in [1,2,3] # 判断元素是否在列表内
True
# 元素索引
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.index([4,5,6]) # 索引
3
# 统计元素
list1 = [1,2,3,6,6,6]
list1.count(6)
3
# 获取最值--确保列表内元素是相同类型(数组)
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
max(list1) # 最大值
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-38-e286fb0cfffb> in <module>
1 list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
----> 2 max(list1) # 最大值
TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'float'
# 获取最值--列表作为元素
list1 = [[4,5,6,7],[5,3,8,2],[6,6,6]] # 只比较第一个数
print(max(list1)) # 最大值
print(min(list1)) # 最小值
[6, 6, 6]
[4, 5, 6, 7]
删除
- list.pop(索引)
- list.remove(元素)
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.pop(3)
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9)]
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.remove([4,5,6])
print(list1)
[1, 2.0, '3', {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, ('A', 9)]
排序
# 排序前提:确保数据类型相同
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.sort(reverse=True)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-9-50eede7c89b5> in <module>
1 list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
----> 2 list1.sort(reverse=True)
TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'dict' and 'tuple'
list1 = [5,2,6,8,6.8,6,1]
list1.sort() # 升序
print(list1)
list1.sort(reverse = True) #降序
print(list1)
[1, 2, 5, 6, 6, 6.8, 8]
[8, 6.8, 6, 6, 5, 2, 1]
其他操作
- 反向
- 切片(跟字符串一样)
# 反向
list1 = [1,2.0,'3',[4,5,6],{"a":7,"b":8},('A',9)]
list1.reverse()
print(list1)
[('A', 9), {'a': 7, 'b': 8}, [4, 5, 6], '3', 2.0, 1]
元组(tuple)
元素不可修改(只读)
tuple1 = () # 创建空元组
type(tuple1)
tuple
tuple1 = (1,) # 必需有逗号
type(tuple1)
tuple
集合(set)
无重复元素
- 添加
- set.add(元素)
- set.update(容器)
- 删除
- set.remove(元素)
- 运算
- 并集 |
- 交集 &
- 差集 -
- 交集的补集 ^
set1 = set() # 创建空集合
type(set1)
set
set1 = {1}
type(set1)
set
set1 = {1,1,2,3,4} # 去重操作
print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 4}
# 添加元素
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
set1.add(5)
print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# 添加集合
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
tuple1 = (5,)
set1.update(tuple1)
print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# 删除元素
set1 = {1,2,3,4,5}
set1.remove(5)
print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 4}
# 并集
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
set2 = {1,5,6}
set3 = set1 | set2
print(set3)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
# 差集
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
set2 = {1,5,6}
set3 = set1 - set2
print(set3)
{2, 3, 4}
# 交集
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
set2 = {1,5,6}
set3 = set1 & set2
print(set3)
{1}
# 交集的补集
set1 = {1,2,3,4}
set2 = {1,2,5,6}
set3 = set1 ^ set2
print(set3)
{3, 4, 5, 6}
字典(dict)
key-value(键值对),json
# 创建空字典
dict1 = {}
type(dict1)
dict
# 用列表创建字典
name = ["张三","李四"]
phone = ["16666666666","18888888888"]
dict1 = dict(zip(name,phone))
print(dict1)
{'张三': '16666666666', '李四': '18888888888'}
4 流程控制
4.1 顺序结构
程序从上到下按顺序执行语句
分支结构
# 求a,b,c的最大值
a = 8
b = 9
c = 6
if a>b and a>c:
print(a)
elif b>a and b>c:
print(b)
else:
print(c)
9
# 求a,b,c的最大值(嵌套)
a = 8
b = 9
c = 6
if a>b:
if a>c:
print(a)
else:
print(c)
elif b>c:
print(b)
else:
print(c)
9
4.2 循环结构
while循环
# 求和(前100)
num = 1
sum = 0
while num<=100:
sum += num
num += 1
print(sum)
5050
for循环
# 求和(前100)
sum = 0
for i in range(1,101):
sum += i
print(sum)
5050
# 奇数和(前100)
sum = 0
for i in range(1,101,2):
sum += i
print(sum)
2500
5 函数与类
函数(function)
包装,封装成一个个黑盒子(会用就行),不关注如何执行,只关注输入、输出
def(define缩写) 函数名(参数):
语句1
语句2
return 返回值
# 封装“打招呼”函数
def sayHi(name,sex):
if(sex == '男'):
print("{0}{1},您好!".format(name,"先生"))
else:
print(f"{name}女士,您好!")
return None #可以省略
name = input("请输入您的名字:")
sex = input("请输入您的性别:")
sayHi(name,sex)
请输入您的名字:刘小贝
请输入您的性别:女
刘小贝女士,您好!
类(Class)
- 封装性,可以把
数据和函数打包在一起- 抽象性,类(class)是抽象的,可以理解为模板,用的时候必需实例化为一个个对象(Instance)
- 继承性,子类继承父类的所有
数据和函数
# 定义类
class Student(object):
# 封装数据--属性成员,第一个参数self是指自身
def __init__(self,name,sex):
self.name = name
self.sex = sex
# 封装函数--方法成员,第一个参数self是指自身
def Eat(self):
print(f"{self.name}在直播吃粑粑。。。")
def Sleep(self):
print(f"{self.name}睡的像猪一样!!!")
def Social(self):
if self.sex=='男':
print(f"{self.name}在泡妹纸~~~")
else:
print(f"{self.name}在泡马子~~~")
# 实例化对象
XiaoBei = Student("刘小贝","男")
XiaoBei.Eat()
XiaoBei.Sleep()
XiaoBei.Social()
刘小贝在直播吃粑粑。。。
刘小贝睡的像猪一样!!!
刘小贝在泡妹纸~~~
6 文件读写
6.1 内置读写
# 声明变量
title = ''
time = ''
author = ''
poem = []
def SaveFile(fileName,writedContext):
poemFile = open(fileName,'w')
poemFile.writelines(writedContext)
poemFile.close()
# 打开文件(读),跟本程序文件相同文件夹
f = open("诗词.txt",encoding="UTF-8")
# 读取文件
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
# 获取文件名
if('\t' in line):
if '-' in line:
temp = line.strip('-\t\n')
templist = temp.split(':')
time = '['+templist[0]+']'
author = templist[1]
else:
title = '《'+line.strip()+'》'
fileName = title + time + author + '.txt'
# 分隔诗词
if(line[:6] != '======'):
poem.append(line)
else:
SaveFile(fileName,poem)
poem = []
SaveFile(fileName,poem)
f.close()
6.2 Pandas读写
import pandas as pd # 导入模块并命名为pd
df = pd.read_csv('个人信息表.csv')
df.to_csv("个人信息表_副本.csv",index=False)
7 数据处理Numpy
import numpy as np
vector = np.array([1,2,3,4]) # 向量
matrix = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]) # 矩阵
print(vector)
print(matrix)
[1 2 3 4]
[[ 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8]
[ 9 10 11 12]]
zerosVector = np.zeros([3,4],np.int)
print(zerosVector)
[[0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0]]
onesVector = np.ones([3,4],np.float)
print(onesVector)
[[1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]]
# 形状
a = np.array([0,10,20,30]).reshape(4,1)
print(a)
[[ 0]
[10]
[20]
[30]]
# 转置
b = a.T
print(b)
[[ 0 10 20 30]]
# 元素和
b = a.sum()
print(b)
60
# 点乘
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
b = np.array([5,6,7,8]).reshape(4,1)
print(np.dot(a,b))
[70]
# 广播机制(拉伸)--针对维度不一致问题
a = np.array([0,10,20,30]).reshape(4,1)
b = np.array([0,1,2]).reshape(1,3)
c = a + b
print(c)
[[ 0 1 2]
[10 11 12]
[20 21 22]
[30 31 32]]
API查询
8 二维绘图Matplotlib
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1,2,3,4])
plt.show()
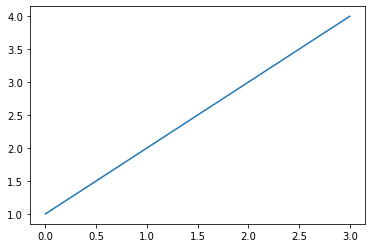
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[1,4,9,16],"r--")
plt.show()
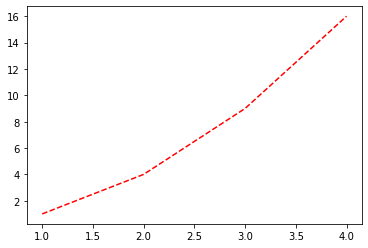
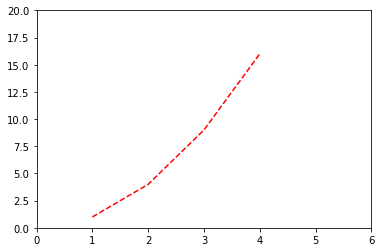
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[1,4,9,16],"r--")
plt.axis([0,6,0,20]) # xMin,xMax,yMin,yMax
plt.show()
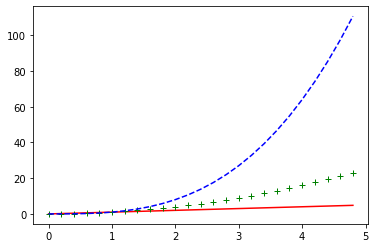
import numpy as np
t =np.arange(0.0,5.0,0.2)
lines = plt.plot(t,t,'r',t,t**2,'g+',t,t**3,'b--')
plt.show()
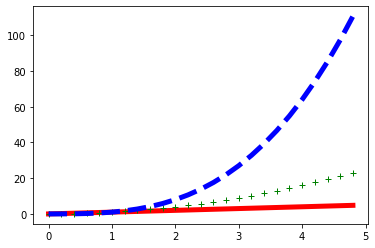
lines = plt.plot(t,t,'r',t,t**2,'g+',t,t**3,'b--')
plt.setp(lines,linewidth = 5.0)
plt.show()
API查询
9 数据处理Pandas
9.2 Pandas-数据结构
- 一维数据:序列(Series)
- 二维数据:数据框(DataFrame)
- 三维数据:面板(MultiIndex/Panel(后面版本可能放弃))
从数据结构角度,一般实现“增删改查”操作,官方接口提供了如下操作:
9.2.1 Series
pandas.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None, name=None, copy=False, fastpath=False)
1. 创建
# 通过列表
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([1,3,'555',np.nan,'6.66',8.8],index=list('abcdef'),name='value')
s1
a 1
b 3
c 555
d NaN
e 6.66
f 8.8
Name: value, dtype: object
# 通过字典
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
d = {'b': 1, 'a': 0, 'c': 2}
s2 = pd.Series(d,name='value')
s2
b 1
a 0
c 2
Name: value, dtype: int64
2. 查找
获取元素
s1.get('c')
s1[['a','c','d']]
s1[[1,2,4]]
索引、列名、值
# 索引
s1.index
# 列名
s1.name
# 值
type(s1.values) #返回ndarray类型
type(s1.items())#返回tuples类型
条件查询
# 查找空值数据
s1[s1.isna()]
# 条件查找
d = {'b': 1, 'a': 0, 'c': 2}
s2 = pd.Series(d,name='value')
s2[s2.values>0]
切片
# 切片
s1['b':'e']
# 切片-前5行
s1.head()
# 切片-后3行
s1.tail(3)
3. 修改
排序
# 索引排序
s2.sort_index()
# 值排序,要求类型相同
s2.sort_values()
运算
# 算术运算
s1*2
# 统计运算
s2.sum()
类型转换、输出
# 类型转换
s1 = s1.astype("float64")
# 导出到csv
s1.to_csv(".\data\\666.csv")
# 导出到json
s1.to_json(".\data\\666.json")
9.2.2 创建数据框(dataframe)
DataFrame([data, index, columns, dtype, copy])
1. 创建
# 通过Series
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
d = {'col1': pd.Series([1., 2., 3.], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),\
'col2': pd.Series([1., 2., 3., 4.], index=list('abcd'))}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(d)
df1
| col1 | col2 | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| b | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| c | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| d | NaN | 4.0 |
# 通过列表
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
dates = pd.date_range('20200801',periods=5)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5,3),index=dates,columns=list('ABC'))
df2
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-08-01 | 0.929269 | 0.054059 | -0.799349 |
| 2020-08-02 | 1.116938 | -1.851482 | 0.533290 |
| 2020-08-03 | 0.304800 | 1.123371 | 0.044546 |
| 2020-08-04 | -2.935934 | 0.733118 | 1.029774 |
| 2020-08-05 | 0.043839 | -1.736654 | -0.178451 |
# 通过字典
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'col1':[1,3],'col2':[2,4]},index=list('ab'))
df3
| col1 | col2 | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | 2 |
| b | 3 | 4 |
2. 查询
获取单元
# 直接索引(先列后行)--不推荐
df2['col2']['b']
# 名字索引(先行后列)
df2.loc['b','col2']
4.0
# 数字索引
df2.iloc[1,1]
df2.loc['b']
获取行
df2.loc['b']
df2.iloc[1]
获取列
df2['col2']
a 8.88
b 4
Name: col2, dtype: object
df2.col2
a 8.88
b 4
Name: col2, dtype: object
行列集合、列类型
# index
df2.index
# columns
df2.columns
# type
df2.dtypes
条件查询
# 条件查询--不推荐
df3[df3['col2'].values>2]
# 条件查询--推荐
df3.query("col2 > 2")
# 条件查询
df3['col2'].isin([2])
3. 修改
赋值
# 单元赋值
df1.loc['d','one']=666
df1
| one | two | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 2 | 1.0 |
| b | 2 | 2.0 |
| c | 2 | 3.0 |
| d | 666 | 4.0 |
# 列赋值
df1.one=2
df1
| one | two | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 2 | 1.0 |
| b | 2 | 2.0 |
| c | 2 | 3.0 |
| d | 2 | 4.0 |
# 行赋值
df1.loc['d']=888
df1
| one | two | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 2 | 1.0 |
| b | 2 | 2.0 |
| c | 2 | 3.0 |
| d | 888 | 888.0 |
排序
# 值排序
df2=df2.sort_values('B',ascending=False) #降序
df2
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-08-03 | 0.304800 | 1.123371 | 0.044546 |
| 2020-08-04 | -2.935934 | 0.733118 | 1.029774 |
| 2020-08-01 | 0.929269 | 0.054059 | -0.799349 |
| 2020-08-05 | 0.043839 | -1.736654 | -0.178451 |
| 2020-08-02 | 1.116938 | -1.851482 | 0.533290 |
# 索引排序
df2=df2.sort_index()
df2
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-08-01 | 0.929269 | 0.054059 | -0.799349 |
| 2020-08-02 | 1.116938 | -1.851482 | 0.533290 |
| 2020-08-03 | 0.304800 | 1.123371 | 0.044546 |
| 2020-08-04 | -2.935934 | 0.733118 | 1.029774 |
| 2020-08-05 | 0.043839 | -1.736654 | -0.178451 |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号