一、 实验目的
通过模拟进程的调度,进一步了解进程调度的具体过程。
二、 实验内容和要求
1.进程PCB的结构体定义
2.定义队列
3.输入进程序列
4.排序(按到位时间)
5.输出进程运行的结果
三、实验方法、步骤及结果测试
1.源程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define READY 1
#define RUN 2
#define BLOCK 3
typedef struct pcbNode{
int num;
struct pcbNode *next;
int cputime;
int state;}pcb;
pcb *head;
pcb *run;
pcb *CreatPCB(int n){
int i;
pcb *p,*q;
head=(pcb *)malloc(sizeof(pcb));
head->next=NULL;
p=head;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){q=(pcb *)malloc(sizeof(pcb));
q->num=i;
q->next=NULL;
q->cputime=rand()%100;q->state=READY;
p->next=q;p=q;
}
return head;
}
void DeletePCB(){
pcb *p;
if(head->next!=NULL){
p=head->next;
head->next=head->next->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Display(){
pcb *p;
p=head->next;
while(p){
printf(" %d",p->num);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void control(){
run=head->next;
run->state=RUN;{
while(run->cputime)run->cputime--;
printf("正在执行的进程编号是: %d\n",run->num);
run->state=RUN;
run=run->next;
DeletePCB();
printf("执行进程后就绪队列中的进程:");
Display();
printf("\n");
}
}
void main(void){
int n;
int flag=1;
printf("请输入要创建的进程数量:");
scanf("%d",&n);
head=CreatPCB(n);
printf("就绪队列里的进程有:");
Display();
printf("\n");
while(flag)/*由flag的值判断是否继续执行control()函数*/
{if(head->next)/*判断进程是否完成*/
control();
else flag=0;
}
printf("\n");
}
2.原理分析
主函数:实现对函数的运用
void main(void){
int n;
int flag=1;
printf("请输入要创建的进程数量:");
scanf("%d",&n);
head=CreatPCB(n);
printf("就绪队列里的进程有:");
Display();
printf("\n");
while(flag)/*由flag的值判断是否继续执行control()函数*/
{if(head->next)/*判断进程是否完成*/
control();
else flag=0;
}
printf("\n");
}
定义结构体:
typedef struct pcbNode{
int num;
struct pcbNode *next;
int cputime;
int state;}pcb;
pcb *head;
pcb *run;
pcb *CreatPCB(int n){
int i;
pcb *p,*q;
head=(pcb *)malloc(sizeof(pcb));
head->next=NULL;
p=head;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){q=(pcb *)malloc(sizeof(pcb));
q->num=i;
q->next=NULL;
q->cputime=rand()%100;q->state=READY;
p->next=q;p=q;
}
return head;
}
对结构体的调用:
void DeletePCB(){
pcb *p;
if(head->next!=NULL){
p=head->next;
head->next=head->next->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Display(){
pcb *p;
p=head->next;
while(p){
printf(" %d",p->num);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void control(){
run=head->next;
run->state=RUN;{
while(run->cputime)run->cputime--;
printf("正在执行的进程编号是: %d\n",run->num);
run->state=RUN;
run=run->next;
DeletePCB();
printf("执行进程后就绪队列中的进程:");
Display();
printf("\n");
}
}
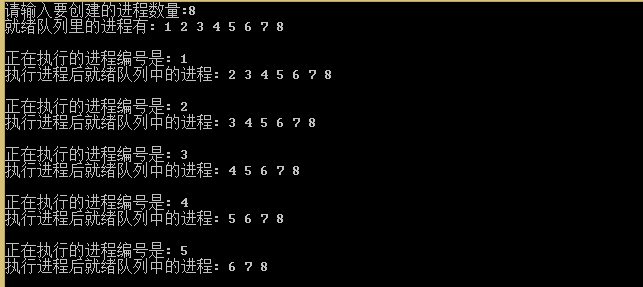
实验结果:

实验总结
遇到问题:
长时间没有用过C++,对C++的运用不太灵活,对结构体的定义,队列的应用不太熟悉。
解决方法:
多操作,多实验


