FFMPEG音视频同步-音视频实时采集编码封装
系统环境:
系统版本:lubuntu 16.04
Ffmpge版本:ffmpeg version N-93527-g1125277
摄像头:1.3M HD WebCan
虚拟机:Oracle VM VirtualBox 5.2.22
指令查看设备 ffmpeg -devices
本章文档基于《ffmpeg-摄像头采集编码封装》和《ffmpeg-音频实时采集编码封装》。在同一进程中,判断其产生的time=pts*time_base,根据其视频的帧率,以及音频产生的采样率等,来比较当前帧时间time,来写入音视频。
1.简介
FFmpeg中有一个和多媒体设备交互的类库:Libavdevice。使用这个库可以读取电脑(或者其他设备上)的多媒体设备的数据,或者输出数据到指定的多媒体设备上。
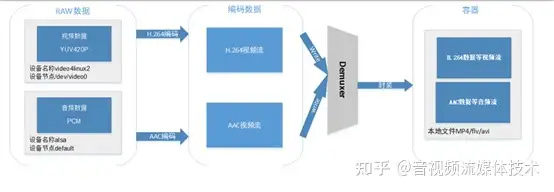
1.1数据流程图
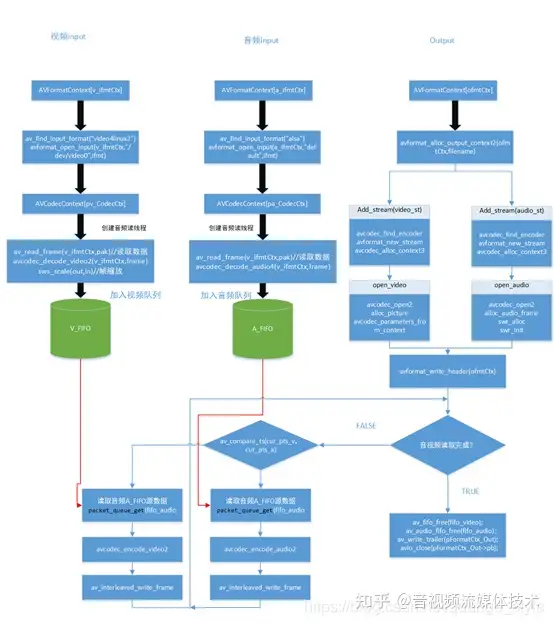
1.2 代码流程图
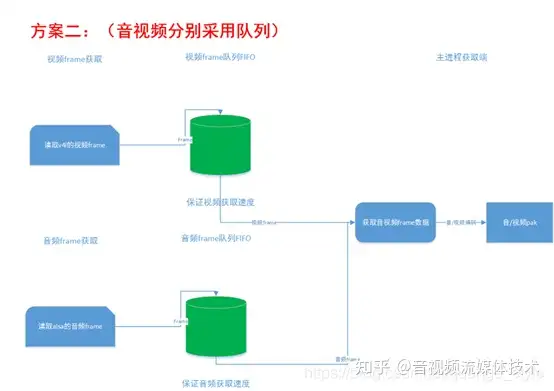
1.3 队列传输流程图
2.源码
最简单的基于Libavdevice的音频采集口数据读取一帧帧pcm数据,经过音频重采样获取目标AAC的音频源数据参数,同时基于Libavdevice的视频采集口,获取yuv420数据,再经过编码,封装等,保存成FLV文件。
程序主要是参考/doc/example/muxing.c源码的音视频同步方法。
2.1音频初始化
1. int open_audio_capture()
2. {
3.
4. printf("open_audio_capture\n");
5.
6. //********add alsa read***********//
7. AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx;
8. AVCodec *pCodec;
9. AVFormatContext *a_ifmtCtx;
10. int i,ret;
11. //Register Device
12. avdevice_register_all();
13.
14. a_ifmtCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
15.
16.
17. //Linux
18. AVInputFormat *ifmt=av_find_input_format("alsa");
19. if(avformat_open_input(&a_ifmtCtx,"default",ifmt,NULL)!=0){
20. printf("Couldn't open input stream.default\n");
21. return -1;
22. }
23.
24.
25. if(avformat_find_stream_info(a_ifmtCtx,NULL)<0)
26. {
27. printf("Couldn't find stream information.\n");
28. return -1;
29. }
30.
31. int audioindex=-1;
32. for(i=0; i<a_ifmtCtx->nb_streams; i++)
33. if(a_ifmtCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO)
34. {
35. audioindex=i;
36. break;
37. }
38. if(audioindex==-1)
39. {
40. printf("Couldn't find a video stream.\n");
41. return -1;
42. }
43.
44. pCodecCtx=a_ifmtCtx->streams[audioindex]->codec;
45. pCodec=avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
46. if(pCodec==NULL)
47. {
48. printf("Codec not found.\n");
49. return -1;
50. }
51. if(avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec,NULL)<0)
52. {
53. printf("Could not open codec.\n");
54. return -1;
55. }
56.
57. AVPacket *in_packet=(AVPacket *)av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));
58.
59. AVFrame *pAudioFrame=av_frame_alloc();
60. if(NULL==pAudioFrame)
61. {
62. printf("could not alloc pAudioFrame\n");
63. return -1;
64. }
65.
66. //audio output paramter //resample
67. uint64_t out_channel_layout = AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
68. int out_sample_fmt = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16;
69. int out_nb_samples =1024; //pCodecCtx->frame_size;
70. int out_sample_rate = 48000;
71. int out_nb_channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(out_channel_layout);
72. int out_buffer_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, out_nb_channels, out_nb_samples, out_sample_fmt, 1);
73. uint8_t *dst_buffer=NULL;
74. dst_buffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE);
75. int64_t in_channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(pCodecCtx->channels);
76.
77.
78. printf("audio sample_fmt=%d size=%d channel=%d sample_rate=%d in_channel_layout=%s\n",
79. pCodecCtx->sample_fmt, pCodecCtx->frame_size,
80. pCodecCtx->channels,pCodecCtx->sample_rate,av_ts2str(in_channel_layout));
81.
82. struct SwrContext *audio_convert_ctx = NULL;
83. audio_convert_ctx = swr_alloc();
84. if (audio_convert_ctx == NULL)
85. {
86. printf("Could not allocate SwrContext\n");
87. return -1;
88. }
89.
90. /* set options */
91. av_opt_set_int (audio_convert_ctx, "in_channel_count", pCodecCtx->channels, 0);
92. av_opt_set_int (audio_convert_ctx, "in_sample_rate", pCodecCtx->sample_rate, 0);
93. av_opt_set_sample_fmt(audio_convert_ctx, "in_sample_fmt", pCodecCtx->sample_fmt, 0);
94. av_opt_set_int (audio_convert_ctx, "out_channel_count", out_nb_channels, 0);
95. av_opt_set_int (audio_convert_ctx, "out_sample_rate", out_sample_rate, 0);
96. av_opt_set_sample_fmt(audio_convert_ctx, "out_sample_fmt", out_sample_fmt, 0);
97.
98. /* initialize the resampling context */
99. if ((ret = swr_init(audio_convert_ctx)) < 0) {
100. fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize the resampling context\n");
101. exit(1);
102. }
103.
104.
105. alsa_input.in_packet=in_packet;
106. alsa_input.pCodecCtx=pCodecCtx;
107. alsa_input.pCodec=pCodec;
108. alsa_input.a_ifmtCtx=a_ifmtCtx;
109. alsa_input.audioindex=audioindex;
110. alsa_input.pAudioFrame=pAudioFrame;
111. alsa_input.audio_convert_ctx=audio_convert_ctx;
112. alsa_input.dst_buffer=dst_buffer;
113. alsa_input.out_buffer_size=out_buffer_size;
114. alsa_input.bCap=1;
115.
116. //******************************//
117. } 2.2 视频初始化
1. int open_video_capture()
2. {
3. int i,ret;
4. printf("open_video_capture\n");
5.
6. //********add camera read***********//
7. AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx;
8. AVCodec *pCodec;
9. AVFormatContext *v_ifmtCtx;
10.
11. //Register Device
12. avdevice_register_all();
13.
14. v_ifmtCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
15.
16.
17. //Linux
18. AVInputFormat *ifmt=av_find_input_format("video4linux2");
19. if(avformat_open_input(&v_ifmtCtx,"/dev/video0",ifmt,NULL)!=0){
20. printf("Couldn't open input stream./dev/video0\n");
21. return -1;
22. }
23.
24.
25. if(avformat_find_stream_info(v_ifmtCtx,NULL)<0)
26. {
27. printf("Couldn't find stream information.\n");
28. return -1;
29. }
30.
31. int videoindex=-1;
32. for(i=0; i<v_ifmtCtx->nb_streams; i++)
33. if(v_ifmtCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
34. {
35. videoindex=i;
36. break;
37. }
38. if(videoindex==-1)
39. {
40. printf("Couldn't find a video stream.\n");
41. return -1;
42. }
43.
44. pCodecCtx=v_ifmtCtx->streams[videoindex]->codec;
45. pCodec=avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
46. if(pCodec==NULL)
47. {
48. printf("Codec not found.\n");
49. return -1;
50. }
51. if(avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec,NULL)<0)
52. {
53. printf("Could not open codec.\n");
54. return -1;
55. }
56.
57. AVFrame *pFrame,*pFrameYUV;
58. pFrame=av_frame_alloc();
59. pFrameYUV=av_frame_alloc();
60. unsigned char *out_buffer=(unsigned char *)av_malloc(avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height));
61. avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameYUV, out_buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
62.
63. printf("camera width=%d height=%d \n",pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
64.
65.
66. struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx;
67. img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL);
68. AVPacket *in_packet=(AVPacket *)av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));
69.
70.
71. video_input.img_convert_ctx=img_convert_ctx;
72. video_input.in_packet=in_packet;
73.
74. video_input.pCodecCtx=pCodecCtx;
75. video_input.pCodec=pCodec;
76. video_input.v_ifmtCtx=v_ifmtCtx;
77. video_input.videoindex=videoindex;
78. video_input.pFrame=pFrame;
79. video_input.pFrameYUV=pFrameYUV;
80. video_input.bCap=1;
81.
82. //******************************//
83. } 2.3输出初始化
1. int open_output( const char *filename,AVDictionary *opt)
2. {
3.
4. printf("open_output\n");
5. static OutputStream video_st = { 0 }, audio_st = { 0 };
6.
7. AVOutputFormat *fmt;
8. AVFormatContext *oc;
9. AVCodec *audio_codec, *video_codec;
10. int ret;
11. int have_video = 0, have_audio = 0;
12. int encode_video = 0, encode_audio = 0;
13.
14.
15. /* allocate the output media context */
16. avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, NULL, filename);
17. if (!oc) {
18. printf("Could not deduce output format from file extension: using MPEG.\n");
19. avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, "mpeg", filename);
20. }
21. if (!oc)
22. return 1;
23.
24. fmt = oc->oformat;
25.
26. /* Add the audio and video streams using the default format codecs
27. * and initialize the codecs. */
28. if (fmt->video_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE) {
29. add_stream(&video_st, oc, &video_codec, fmt->video_codec);
30. have_video = 1;
31. encode_video = 1;
32. }
33. if (fmt->audio_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE) {
34. add_stream(&audio_st, oc, &audio_codec, AV_CODEC_ID_AAC);//fmt->audio_codec);
35. have_audio = 1;
36. encode_audio = 1;
37. }
38.
39. /* Now that all the parameters are set, we can open the audio and
40. * video codecs and allocate the necessary encode buffers. */
41. if (have_video)
42. open_video(oc, video_codec, &video_st, opt);
43.
44. if (have_audio)
45. open_audio(oc, audio_codec, &audio_st, opt);
46.
47. av_dump_format(oc, 0, filename, 1);
48.
49. /* open the output file, if needed */
50. if (!(fmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) {
51. ret = avio_open(&oc->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);
52. if (ret < 0) {
53. fprintf(stderr, "Could not open '%s': %s\n", filename,
54. av_err2str(ret));
55. return 1;
56. }
57. }
58.
59. /* Write the stream header, if any. */
60. ret = avformat_write_header(oc, &opt);
61. if (ret < 0) {
62. fprintf(stderr, "Error occurred when opening output file: %s\n",
63. av_err2str(ret));
64. return 1;
65. }
66.
67.
68. output_dev.encode_audio=encode_audio;
69. output_dev.encode_video=encode_video;
70. output_dev.oc=oc;
71. output_dev.have_audio=have_audio;
72. output_dev.have_video=have_video;
73. output_dev.video_st=&video_st;
74. output_dev.audio_st=&audio_st;
75.
76. } 2.4音频采集线程
1. int audioThreadProc(void *arg)
2. {
3. int got_pic;
4. while(alsa_input.bCap)
5. {
6.
7. //printf("audioThreadProc running\n");
8.
9. AVPacket *pkt=get_audio_pkt(output_dev.audio_st,&alsa_input);
10. if(pkt==NULL) //从alsa中获取pkt音频源数据包
11. {
12. alsa_input.bCap =0;
13.
14. }
15. else
16. {
17. packet_queue_put(&output_dev.audioq,pkt,output_dev.audio_st->next_pts); //将获取的数据包发送到传输队列当中
18. }
19.
20.
21. }
22.
23. printf("videoThreadProc exit\n");
24. usleep(1000000);
25. return 0;
26.
27. } 2.5视频采集线程
1. int videoThreadProc(void *arg)
2. {
3. int got_pic;
4. while(video_input.bCap)
5. {
6.
7.
8. AVPacket * pkt=get_video_pkt(output_dev.video_st,&video_input);
9. //从V4L中获取视频源数据包pkt
10. if(pkt==NULL)
11. {
12. //packet_queue_put_nullpacket(&output_dev.videoq,0);
13. video_input.bCap =0;
14.
15. }
16. else
17. {
18. packet_queue_put(&output_dev.videoq,pkt,output_dev.video_st->next_pts); //将获取到的数据包发送到视频传输队列中
19. }
20.
21.
22.
23. }
24.
25. printf("videoThreadProc exit\n");
26. usleep(1000000);
27. return 0;
28.
29. } 2.6主进程
1. while (output_dev.encode_video || output_dev.encode_audio) { //判断进程是否退出
2. if (output_dev.encode_video &&
3. (!output_dev.encode_audio || av_compare_ts(frame_pts, output_dev.video_st->enc->time_base,
4. frame_audio_pts, output_dev.audio_st->enc->time_base) <= 0)) //比较音频视频产生是的pts* time_base大小,以音频pts*times_base为基准,若视频的pts*time_base小于音频,则写入视频帧,否则写入音频帧
5. {
6. if(packet_queue_get(&output_dev.videoq,&pkt,0,&frame_pts)<0) //获取队列中的视频pkt
7. {
8. printf("packet_queue_get Error.\n");
9. break;
10. }
11.
12. if(flush_pkt.data== pkt.data)
13. {
14. printf("get pkt flush_pkt\n");
15. continue;
16. }
17.
18.
19. vframe=get_video_pkt2Frame(output_dev.video_st,&video_input,&pkt,&got_pic,frame_pts); //解码pkt 成frame
20. if(!got_pic)
21. {
22. av_free_packet(&pkt);
23. printf("get_video_pkt2Frame error\n");
24. usleep(10000);
25. continue;
26. }
27. av_free_packet(&pkt);
28.
29. WRITE_FRAME:
30. output_dev.encode_video = !write_video_frame1(output_dev.oc, output_dev.video_st,vframe); //编码frame成pkt,并且写入封装
31. //usleep(300000);
32. }
33. else//audio
34. {if(packet_queue_get(&output_dev.audioq,&audio_pkt,0,&frame_audio_pts)<0) //获取队列中的音频pkt
35.
36. {
37. printf("packet_queue_get Error.\n");
38. break;
39. }
40.
41. if(flush_pkt.data== audio_pkt.data)
42. {
43. printf("get pkt flush_pkt\n");
44. continue;
45. }
46. //av_free_packet(&audio_pkt);
47.
48. #if 1
49.
50.
51. aframe=get_audio_pkt2Frame(output_dev.audio_st,&alsa_input,&audio_pkt,&got_pcm,frame_audio_pts); //解码pkt 成frame
52. if(!got_pcm)
53. {
54. av_free_packet(&audio_pkt);
55. printf("get_video_pkt2Frame error\n");
56. usleep(10000);
57. continue;
58. }
59. av_free_packet(&audio_pkt);
60.
61. WRITE_AUDIO_FRAME:
62. output_dev.encode_audio = !write_audio_frame1(output_dev.oc, output_dev.audio_st,aframe); //编码frame成pkt,并且写入封装
63.
64. //usleep(300000);
65. #endif
66. }
67.
68.
69.
70.
71. } 3.验证
3.1编译
1. #!/bin/sh
2. CC=gcc
3. SRCS=$(wildcard *.c */*.c)
4. OBJS=$(patsubst %.c, %.o, $(SRCS))
5. FLAG=-g
6. #LIB=-lavutil -lavformat -lavcodec -lavutil -lswscale -lswresample -lSDL2
7.
8.
9.
10. LIB=-lSDL2 -lSDLmain -I/usr/include/SDL -D_GNU_SOURCE=1 -D_REENTRANT -L/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu -lSDL -I./\
11. -I/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/include -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -L/usr/local/lib -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -lavcodec -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -pthread -lm -lz -lfdk-aac -lm -lmp3lame -lm -lopus -lm -lvorbis -lm -logg -lvorbisenc -lvorbis -lm -logg -lx264 -lpthread -lm -ldl -lx265 -lstdc++ -lm -lrt -ldl -lnuma -lswresample -lm -lavutil -pthread -lm -lXv -lX11 -lXext \
12. -I/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/include -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -L/usr/local/lib -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -lavdevice -lm -lxcb -lXau -lXdmcp -lxcb-shape -lxcb -lXau -lXdmcp -lxcb-xfixes -lxcb-render -lxcb-shape -lxcb -lXau -lXdmcp -lasound -lm -ldl -lpthread -lrt -lSDL2 -Wl,--no-undefined -lm -ldl -lasound -lm -ldl -lpthread -lpulse-simple -lpulse -lsndio -lX11 -lXext -lXcursor -lXinerama -lXi -lXrandr -lXss -lXxf86vm -lwayland-egl -lwayland-client -lwayland-cursor -lxkbcommon -lpthread -lrt -lsndio -lXv -lX11 -lXext -lavfilter -pthread -lm -lfreetype -lz -lpng12 -lz -lm -lswscale -lm -lpostproc -lm -lavformat -lm -lz -lavcodec -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -pthread -lm -lz -lfdk-aac -lm -lmp3lame -lm -lopus -lm -lvorbis -lm -logg -lvorbisenc -lvorbis -lm -logg -lx264 -lpthread -lm -ldl -lx265 -lstdc++ -lm -lrt -ldl -lnuma -lswresample -lm -lavutil -pthread -lm -lXv -lX11 -lXext \
13. -I/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/include -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -L/usr/local/lib -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -lavformat -lm -lz -lavcodec -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -pthread -lm -lz -lfdk-aac -lm -lmp3lame -lm -lopus -lm -lvorbis -lm -logg -lvorbisenc -lvorbis -lm -logg -lx264 -lpthread -lm -ldl -lx265 -lstdc++ -lm -lrt -ldl -lnuma -lswresample -lm -lavutil -pthread -lm -lXv -lX11 -lXext \
14. -I/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/include -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -L/usr/local/lib -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -lavformat -lm -lz -lavcodec -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -lvpx -lm -lpthread -pthread -lm -lz -lfdk-aac -lm -lmp3lame -lm -lopus -lm -lvorbis -lm -logg -lvorbisenc -lvorbis -lm -logg -lx264 -lpthread -lm -ldl -lx265 -lstdc++ -lm -lrt -ldl -lnuma -lswresample -lm -lavutil -pthread -lm -lXv -lX11 -lXext \
15. -I/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/include -L/home/quange/ffmpeg_build/lib -lswscale -lm -lavutil -pthread -lm -lXv -lX11 -lXext \
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21. NAME=$(wildcard *.c)
22. TARGET=av_record
23.
24. $(TARGET):$(OBJS)
25.
26. $(CC) $(FLAG) -o $@ $^ $(LIB)
27.
28.
29. %.o:%.c
30. $(CC) $(FLAG) -c -o $@ $^ $(LIB)
31.
32.
33.
34. clean:
35. rm -rf $(TARGET) $(OBJS)3.2结果
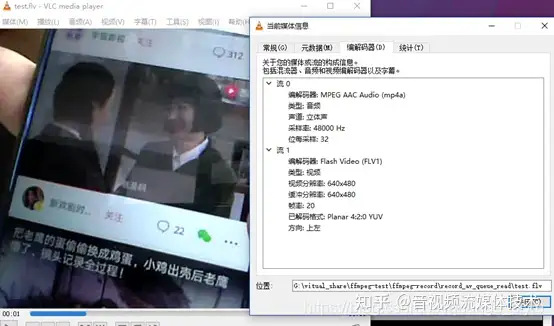
使用VLC打开test.flv,可以看到录制的实时音视频,音视频延时维持在200ms以内,更精确的有待测试优化
3.3存在的问题
无
3.6 思考
1、问:为啥不讲音视频数据的采集,编码,封装放在同一个进程里?
答:
1)、由于音视频的编码耗时比较久(特别是视频),所有操作都放在同一个进程里面,会影响到数据的采集,造成音频,视频数据采集丢失。
2)、由于音视频在写入封装时,需要比较音频与视频的pts*time_base,若视频的实时时间小于音频,则获取音频写入封装频,否则获取视频写入封装;这样的判断方法,或影响到音频和视频的采集,造成大部分数据丢失。
2、关于设备前端采集数据速度思考:
一开始,我是将前端数据采集,获取视频帧frame,视频帧编码成pkt等三个步骤放在采集线程里,然后再发送数据到队列,主进程再获取队列中的pkt,直接写入封装。但是,考虑到视频编码耗时较久,会影响到数据采集,所以还是直接单线程运行获取数据,最大限度保证数据的采集。
3、关于不同封装,编码数据的pts问题
这方面的相关在《ffmpeg-摄像头采集编码封装》中有详细的讲解。总的来说pts*time_base的值在flv,mp4,ts等容器中,值都是一样的。不同的表现在编码生成的pts与编码器时基(1/frame_rate),流时基有关。
4、关于摄像头实时采集帧率与编码器设定的帧率关系?
在本例中,摄像头采集的帧率为20帧,而由于将编码器时基设为(1/25),就会录制下来的视频要比实际上跑的快(ps:10s的视频从采集手机屏幕5s开始,播放结束后,显示20s)。主要是因为录制下来每帧间隔为(1/25),而实际摄像头是(1/20)。同样一秒的数据,写到封装里只有0.8s的数据。所以10s录制的视频,显示的是15s的时间。这问题,编码器时基改为实际帧率即可。
指令ffmpeg -f video4linux2 -s 640*480 -i /dev/video0 -f flv test.flv可以显示实时帧率
4.附件
无
5.参考资料
[1] ffmpeg之PCM转AAC
【FFmpeg(2016)】PCM编码AAC_pkt.data 就是pcm吗_mengzhengjie的博客-CSDN博客
[2]官方Encode pcm file to aac
[FFmpeg-user] Encode pcm file to aac
[3]PCM编码AAC,参考其普通PCM格式与AAC转格式差异 【FFmpeg(2016)】PCM编码AAC_pkt.data 就是pcm吗_mengzhengjie的博客-CSDN博客




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了