Java 基础 (IO转换流)
-
转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换
-
Java API提供了两个转换流:
InputStreamReader : 将 InputStream 转换为 Reader
OutputStreamWriter : 将 Writer 转换为 OutputStream -
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
-
很多时候我们使用转换流来处理文件乱码问题。实现编码和解码的功能。
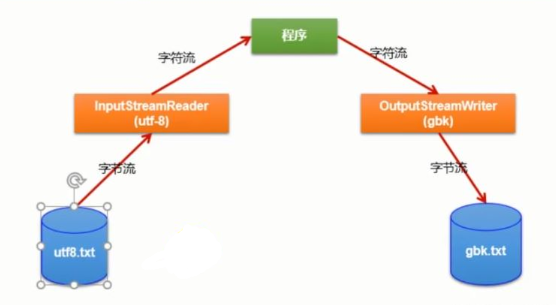
1. 转换流: 属于字符流
InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流OutputStreamWriter:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
2. 作用: 提供字节流与字符流之间的转换
3. 解码: 字节、字节数组 ---> 字符数组、字符串
编码: 字符数组、字符串 ---> 字节、字节数组
4. 字符集
1) ASCII: 美国标准信息交换码。
用一个字节的7位可以表示。
2) ISO8859-1: 拉丁码表。欧洲码表
用一个字节的8位表示。
3) GB2312: 中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码所有字符
4) GBK: 中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。最多两个字节编码
5) Unicode: 国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每个字符分配唯一的字符码。所有的文字都用两个字节来表示。
6) UTF-8: 变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符。
面向传输的众多 UTF (UCS Transfer Format)标准出现了,顾名思义,UTF-8就是每次8个位传输数据,而 UTF-16就是每次16个位。这是为传输而设计的编码,并使编码无国界,这样就可以显示全世界上所有文化的字符了。
Unicode 只是定义了一个庞大的、全球通用的字符集,并为每个字符规定了唯一确定的编号,具体存储成什么样的字节流,取决于字符编码方案。推荐的 Unicode 编码是 UTF-8 和 UTF-16。
InputStreamReaderTest.java
package com.klvchen.java;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt");
//InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); //使用系统默认的字符集
//参数2指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件dbcp.txt保存时使用的字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
isr.close();
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
//1.造文件,造流
File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt");
File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//2.读写过程
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
osw.write(cbuf, 0 ,len);
}
//3.关闭资源
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}


