Java 基础 (IO流原理及流的分类)
Java IO 原理
- I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于如读/写文件,网络通讯等。 处理设备之间的数据传输。
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(stream)”的方式进行。
- java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
● 输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
● 输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中。
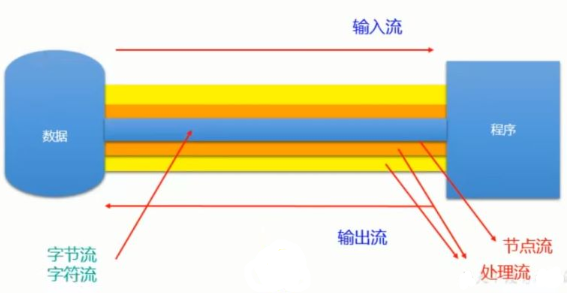
流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流

字符流例子
FileReaderWriterTest.java
package com.klvchen.java;
/*
# 流的体系结构
抽象基类 节点流(或文件流) 缓冲流(处理流的一种)
InputStream FileiInputstream BufferedInputStream
Outputstream FiLeoutputstream BufferedoutputStream
Reader FileReader Bufferedreader
writer Filewriter Bufferedwriter
*/
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("hello.txt"); //相较于当前工程
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
File file1 = new File("day09\\hello.txt"); //相较于当前工程
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());
}
/*
将day09下的hello.txt文件内容读入程序中,并输出到控制台
说明点:
1. read()的理解:返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
2.异常的处理:为了保证流资源一定可以执行关闭操作。需要使用try-catch-finally处理
3.读入的文件一定要存在,否则就会报FiLeNotFoundException。|
*/
@Test
public void testFileReader() {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1. 实例化 File 类的对象,指明要操作的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt"); //相较于当前 Module
//2. 提供具体的流
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.数据的读入
//read():返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
//方式一:
//int data = fr.read();
//while (data != -1) {
// System.out.println((char) data);
// data = fr.read();
//}
//方式二:
int data;
while ((data = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.流的关闭
//try {
// if ( fr != null)
// fr.close();
//} catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
//}
//或
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//对read()操作升级:使用read的重载方法
@Test
public void testFileReader1(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.File类的实例化
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.FileReader流的实例化
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.读入的操作
//read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
//方式一:
//错误的写法
//for (int i = 0; i < cbuf.length; i++) {
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
//}
//正确的写法
//for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
//}
//方式二:
//错误的写法,对应着方式一的错误的写法
//String str = new String(cbuf);
//System.out.print(str);
//正确的写法
String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源的关闭
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/*
从内存中写出数据到硬盘的文件里。
说明:
1.输出操作,对应的 File可以不存在的。并不会报异常
2.
File对应的硬盘中的文件如果不存在,在输出的过程中,会自动创建此文件。
File对应的硬盘中的文件如果存在:
如果流使用的构造器是: FileWriter(file,false)/FileWriter(file):对原有文件的覆盖
如果流使用的构造器是: FileWriter(file,true):不会对原有文件覆盖,而是在原有文件基础上追加内容。
*/
@Test
public void testFileWrite() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件
File file = new File("hello1.txt");
//2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出
fw = new FileWriter(file);
//3.写出操作
fw.write("I have a dream!\n");
fw.write("you need to have a dream!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流资源的关闭
try {
if (fw != null)
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void testFileReaderFileWrite() {
FileWriter fw = null;
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件
File srcFile = new File("hello.txt");
File destFile = new File("hello2.txt");
//不能使用字符流来处理图片等字节数据
//File srcFile = new File("1.png");
//File destFile = new File("2.png");
//2.创建输入和输出的对像
fr = new FileReader(srcFile);
fw = new FileWriter(destFile);
//3.数据的读入和写入操作
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len; //记录每次读入到 cbuf 数组中的字符的个数
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
//每次写出len个字符
fw.write(cbuf, 0 , len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.关闭流资源
try {
if (fw != null)
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fr != null)
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
字节流例子
FileInputOutputStreamTest.java
package com.klvchen.java;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/*
对于文本文件(.txt, .java, .c, .cpp),使用字符流处理
对于非文本文件(.jpg, .mp3 , .mp4, .avi, .doc, .ppt,...),使用字节流处理
*/
public class FileInputOutputStreamTest {
//使用字节流 FileInputStream 处理文本文件,可能出现乱码。
@Test
public void testFileInputStream() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.造流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.读数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len; //记录每次读取的字节的个数
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buffer, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.关闭流
try {
if (fis != null)
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*
实现对图片的复制操作
*/
@Test
public void testFileInputOutputStream() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//
File srcFile = new File("1.png");
File destFile = new File("3.png");
//
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0 ,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null)
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//指定路径下文件的复制
public void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
//
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0 ,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null)
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void testCopyFile() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//String srcPath = "H:\\download\\1.mp4";
//String destPaht = "H:\\download\\2.mp4";
String srcPath = "hello.txt";
String destPaht = "hello3.txt";
copyFile(srcPath, destPaht);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为: " + (end - start)); //7006
}
}



