图像边缘检测的方法与实现
1、图像边缘
OpenCV图像平滑中的“平滑”,从信号处理的角度看,是一种"低通滤波",图像边缘是 像素值变化剧烈 的区域 (“高频”),可视为一种 "高通滤波",对应的场景如下:
1) 深度的不连续 (物体处在不同的物平面上)
2) 表面方向的不连续 (如,正方体不同的两个面)
3) 物体材料不同 (光的反射系数也不同)
4) 场景中光照不同 (如,有树荫的路面)
目前边缘检测的算法,多是求图像的微分,例如:Sobel 图像一阶导, Laplace 图像二阶导
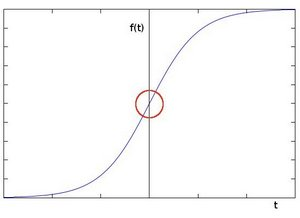
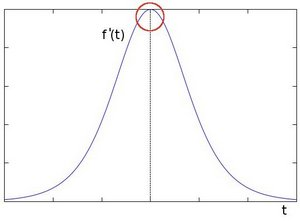
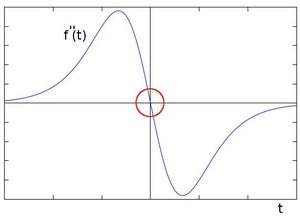
2、索贝尔算子
2.1计算过程
假定输入图像矩阵为 I,卷积核大小为 3x3,则水平一阶导 GxGx 和垂直一阶导 GyGy 分别为:
Gx=⎡⎣⎢−1−2−1000121⎤⎦⎥∗IGy=⎡⎣⎢−101−202−101⎤⎦⎥∗IGx=[−101−202−101]∗IGy=[−1−2−1000121]∗I
输出图像矩阵 GG 为:
G=G2x+G2y−−−−−−−√或简化为G=|Gx|+|Gy|G=Gx2+Gy2或简化为G=|Gx|+|Gy|
对无特征的图像 (flat)、带边缘的图像 (edge)、带角点的图像 (corner),分别求一阶导 dx 和 dy 如下:



2.2 Sobel 卷积核
2.2.1 核大小
分析 Sobel 核的特点,可以看出,Sobel 算子结合了高斯平滑和微分运算,对噪声具有一定的抑制作用
1) 当核大小为 1×11×1 时,取 xorder=1, yorder=0,此时,Sobel 核只有微分运算,不再有高斯平滑:
Kx=[−101]Kx=[−101]
2) 当核大小为 3×33×3 时,取 xorder=1, yorder=0,则 Sobel 核为:
Kx=⎡⎣⎢−1−2−1000121⎤⎦⎥Kx=[−101−202−101]
此时,Sobel 核作为微分运算的近似,不够精确,通常的用 Scharr 核来代替:
Kx=⎡⎣⎢−3−10−30003103⎤⎦⎥Kx=[−303−10010−303]
3) 当核大小为 5×55×5 时,取 xorder=1, yorder=0,按照 Intel IPP 库中的定义,Sobel 核为:
Kx=⎡⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢−1−4−6−4−1−2−8−12−8−20000028682141241⎤⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥Kx=[−1−2021−4−8084−6−120612−4−8084−1−2021]
2.2.2 可分离性
Sobel 卷积核具有可分离性,能被分解为两个一维的卷积核,如下:

根据这个性质,再结合 OpenCV 中的 getDerivKernels() 函数,可求出各种大小的 Sobel 核
// kernel size, when ksie ≤ 0, get Scharr kernel int ksize = 5; Mat kx, ky; getDerivKernels(kx, ky, 1, 0, ksize, false, CV_32F); Mat kernel = ky * kx.t();
2.3 OpenCV 函数
2.3.1 Sobel() 函数
OpenCV 中的 Sobel() 函数如下:dx 和 dy 表示阶数,一般取 0 或 1,不超过 2
void Sobel (
InputArray src, // 输入图像 OutputArray dst, // 输出图像 int ddepth, // 输出图像的深度,-1 表示同 src.depth() int dx, // 水平方向的阶数 int dy, // 垂直方向的阶数 int ksize = 3, // 卷积核大小,常取 1, 3, 5, 7 等奇数 double scale = 1, // 缩放因子,应用于计算结果 double delta = 0, // 增量数值,应用于计算结果 int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT // 边界处理模式 )
2.3.2 Scharr() 函数
Scharr() 函数,本质上就是令 ksize = 3 且使用 Scharr 卷积核的 Sobel() 函数
void Scharr ( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT
)
对于 Scharr 函数,要求 dx 和 dy 都 >= 0 且 dx + dy == 1,假如 dx 和 dy 都设为 1,则会抛出异常。
因此,对于 Sobel 和 Scharr 函数,通常各自求其 x 和 y 方向的导数,然后通过加权来进行边缘检测。
// Gradient X Scharr( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x ); // Gradient Y Scharr( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y ); // Total Gradient (approximate) addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, grad );
3 拉普拉斯算子 (Laplace)
索贝尔算子 (Sobel) 和拉普拉斯算子 (Laplace) 都是对图像进行边缘检测,Sobel 是求一阶导,Laplace 是求二阶导。
Laplace(f)=∂2f∂x2+∂2f∂y2=f(x+1,y)+f(x−1,y)+f(x,y+1)+f(x,y−1)−4f(x,y)Laplace(f)=∂2f∂x2+∂2f∂y2=f(x+1,y)+f(x−1,y)+f(x,y+1)+f(x,y−1)−4f(x,y)
OpenCV 中对应的函数为 Laplacian
void Laplacian ( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int ksize = 1, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT )
4 Canny 算子
Canny 算子,在一阶微分的基础上,增加了非最大值抑制和双阈值检测,是边缘检测算子中最常用的一种,常被其它算子作为标准算子来进行优劣比较。
4.1 算法步骤
1) 用高斯滤波器对输入图像做平滑处理 (大小为 5x5 的高斯核)
K=1159⎡⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢245424912945121512549129424542⎤⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥K=1159[245424912945121512549129424542]
2) 计算图像的梯度强度和角度方向 ( x 和 y 方向上的卷积核)
Kx=⎡⎣⎢−1−2−1000121⎤⎦⎥Ky=⎡⎣⎢−101−202−101⎤⎦⎥Kx=[−101−202−101]Ky=[−1−2−1000121]
G=G2x+G2y−−−−−−−√θ=arctan(GyGx)G=Gx2+Gy2θ=arctan(GyGx)
角度方向近似为四个可能值,即 0, 45, 90, 135
3) 对图像的梯度强度进行非极大抑制
可看做边缘细化:只有候选边缘点被保留,其余的点被移除
4) 利用双阈值检测和连接边缘
若候选边缘点大于上阈值,则被保留;小于下阈值,则被舍弃;处于二者之间,须视其所连接的像素点,大于上阈值则被保留,反之舍弃
4.2 Canny 函数
OpenCV 中的 Canny 函数如下:
void cv::Canny ( InputArray image, // 输入图像 (8位) OutputArray edges, // 输出图像 (单通道,8位) double threshold1, // 下阈值 double threshold2, // 上阈值 int apertureSize = 3, bool L2gradient = false )
一般 上阈值 / 下阈值 = 2 ~ 3
L2gradient 默认 flase,表示图像梯度强度的计算采用近似形式;若为 true,则表示采用更精确的形式。
5 代码示例
5.1 OpenCV 示例
Sobel 或 Scharr 示例中,使用 addWeighted 函数,来加权合成 x 和 y 方向上各自的一阶导数
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> using namespace cv; int main( int, char** argv ) { Mat src, src_gray; Mat grad; const char* window_name = "Sobel Demo - Simple Edge Detector"; int scale = 1; int delta = 0; int ddepth = CV_16S; /// Load an image src = imread( argv[1] ); if( src.empty() ) { return -1; } GaussianBlur( src, src, Size(3,3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT ); /// Convert it to gray cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY ); /// Create window namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); /// Generate grad_x and grad_y Mat grad_x, grad_y; Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; /// Gradient X //Scharr( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); Sobel( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x ); /// Gradient Y //Scharr( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); Sobel( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y ); /// Total Gradient (approximate) addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, grad ); imshow( window_name, grad ); waitKey(0); return 0; }
Laplacian 示例中,利用了高斯滤波函数来降低噪声
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" using namespace cv; int main( int, char** argv ) { Mat src, src_gray, dst; int kernel_size = 3; int scale = 1; int delta = 0; int ddepth = CV_16S; const char* window_name = "Laplace Demo"; // 读图 src = imread("camera1.bmp"); if( src.empty()) return -1; // 高斯滤波 GaussianBlur( src, src, Size(3,3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT ); // 灰度图 cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY ); // 窗体 namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); // Laplace 函数 Mat abs_dst; Laplacian( src_gray, dst, ddepth, kernel_size, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( dst, abs_dst ); // 显示 imshow( window_name, abs_dst ); waitKey(0); }
在 Canny 函数之前,也需要 blur 函数,来进行降噪处理
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> using namespace cv; /// Global variables Mat src, src_gray; Mat dst, detected_edges; int edgeThresh = 1; int lowThreshold; int const max_lowThreshold = 100; int ratio = 3; int kernel_size = 3; const char* window_name = "Edge Map"; /** * @function CannyThreshold * @brief Trackbar callback - Canny thresholds input with a ratio 1:3 */ static void CannyThreshold(int, void*) { /// Reduce noise with a kernel 3x3 blur( src_gray, detected_edges, Size(3,3) ); /// Canny detector Canny( detected_edges, detected_edges, lowThreshold, lowThreshold*ratio, kernel_size ); /// Using Canny's output as a mask, we display our result dst = Scalar::all(0); src.copyTo( dst, detected_edges); imshow( window_name, dst ); } int main( int, char** argv ) { /// Load an image src = imread( argv[1] ); if( src.empty() ) { return -1; } /// Create a matrix of the same type and size as src (for dst) dst.create( src.size(), src.type() ); /// Convert the image to grayscale cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY ); /// Create a window namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); /// Create a Trackbar for user to enter threshold createTrackbar( "Min Threshold:", window_name, &lowThreshold, max_lowThreshold, CannyThreshold ); /// Show the image CannyThreshold(0, 0); /// Wait until user exit program by pressing a key waitKey(0); return 0; }
5.2 简单对比
在进行 Sobel,Laplacian 和 Canny 边缘检测之前,统一调用 GaussianBlur 来降低图像噪声
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" using namespace std; using namespace cv;
int main() { Mat src, src_gray, dst; src = imread("bird.jpg"); if(src.empty()) return -1; imshow("Original", src); Mat grad_x, grad_y, abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; GaussianBlur(src, src, Size(3,3),0); cvtColor(src,src_gray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); Sobel(src_gray, grad_x,CV_16S,0,1); // use CV_16S to avoid overflow convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x ); Sobel(src_gray, grad_y,CV_16S,1,0); // use CV_16S to avoid overflow convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y ); addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, dst ); imshow("Sobel", dst); Laplacian(src_gray,dst,-1,3); imshow("Laplace", dst); Canny(src_gray,dst,100,300); imshow("Canny",dst); waitKey(0);}
三种边缘检测的效果图如下:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号