OpenCV图像分割的方法与实现
一、基于阈值
灰度阈值化,是最简单,速度最快的图像分割方法,广泛用于实时图像处理领域 ,尤其是嵌入式系统中
设输入图像 f,输出图像 g,则阈值化公式为 g(i,j)={10当 f(i, j) ≥ T 时当 f(i, j) < T 时g(i,j)={1当 f(i, j) ≥ T 时0当 f(i, j) < T 时
即,遍历图像中所有像素,当像素值 f(i,j)≥Tf(i,j)≥T 时,分割后的图像元素 g(i,j)g(i,j) 是物体像素,否则为背景像素
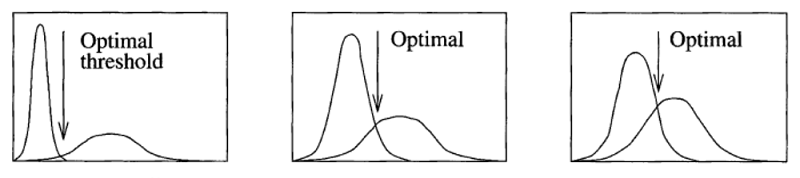
当各物体不接触,且 物体和背景的灰度值差别比较明显 时,灰度阈值化是非常合适的分割方法。
1)固定阈值
固定阈值化函数为 threshold(),如下:
double cv::threshold ( InputArray src, // 输入图像 (单通道,8位或32位浮点型) OutputArray dst, // 输出图像 (大小和类型,都同输入) double thresh, // 阈值 double maxval, // 最大灰度值(使用 THRESH_BINARY 和 THRESH_BINARY_INV类型时) int type // 阈值化类型(THRESH_BINARY, THRESH_BINARY_INV; THRESH_TRUNC; THRESH_TOZERO, THRESH_TOZERO_INV) )
1) THRESH_BINARY
dst(x,y)={maxval0if src(x, y) > threshotherwisedst(x,y)={maxvalif src(x, y) > thresh0otherwise
2) THRESH_TRUNC
dst(x,y)={thresholdsrc(x,y)if src(x, y) > threshotherwisedst(x,y)={thresholdif src(x, y) > threshsrc(x,y)otherwise
3) THRESH_TOZERO
dst(x,y)={src(x,y)0if src(x, y) > threshotherwise
2)自适应阈值
整幅图像使用同一个阈值做二值化,对于一些情况并不适用,尤其是当图像中的不同区域,照明条件各不相同时。这种情况下,就需要自适应阈值算法,该算法可根据像素所在的区域,来确定一个适合的阈值。因此,对于一幅图中光照不同的区域,可取各自不同的阈值做二值化。
OpenCV 中,自适应阈值化函数为 adaptiveThreshold(),如下:
void cv::adaptiveThreshold ( InputArray src, // OutputArray dst, // double maxValue, // int adaptiveMethod, // 自适应阈值算法,目前有 ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C 和 ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C 两种 int thresholdType, // 阈值化类型,同 threshold() 中的 type int blockSize, // 邻域大小 double C // )
3)示例
阈值化类型和阈值可选的代码示例:
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" using namespace cv; int threshold_value = 0; int threshold_type = 3; int const max_value = 255; int const max_type = 4; int const max_BINARY_value = 255; Mat src, src_gray, dst; const char* window_name = "Threshold Demo"; const char* trackbar_type = "Type: \n 0: Binary \n 1: Binary Inverted \n 2: Truncate \n 3: To Zero \n 4: To Zero Inverted"; const char* trackbar_value = "Value"; void Threshold_Demo(int, void*); int main( int, char** argv ) { // 读图 src = imread("Musikhaus.jpg",IMREAD_COLOR); if( src.empty() ) return -1; // 转化为灰度图 cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY ); // 显示窗口 namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); // 滑动条 - 阈值化类型 createTrackbar( trackbar_type, window_name, &threshold_type,max_type,Threshold_Demo); // 滑动条 - 阈值 createTrackbar( trackbar_value,window_name, &threshold_value,max_value,Threshold_Demo); Threshold_Demo(0, 0); waitKey(0); } void Threshold_Demo(int, void*) { /* 0: Binary 1: Binary Inverted 2: Threshold Truncated 3: Threshold to Zero 4: Threshold to Zero Inverted */ threshold(src_gray, dst, threshold_value, max_BINARY_value, threshold_type); imshow(window_name, dst); }
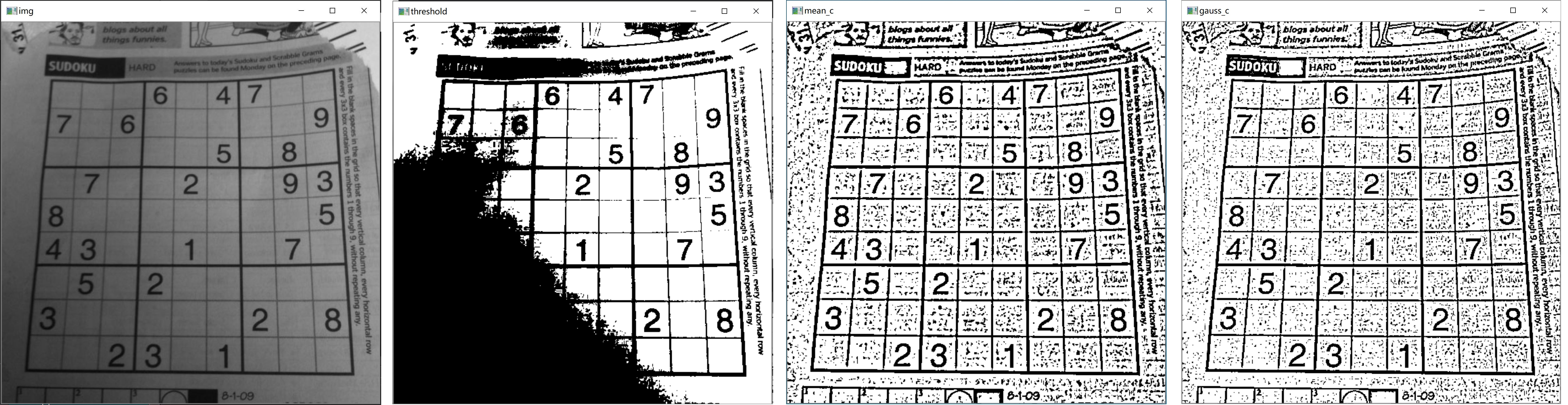
全局阈值和自适应阈值的比较:
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui.hpp> using namespace cv; int main() { // read an image Mat img = imread("sudoku.png"); cvtColor(img,img,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); // adaptive Mat dst1, dst2, dst3; threshold(img, dst1, 100, 255, THRESH_BINARY); adaptiveThreshold(img, dst2, 255,ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C ,THRESH_BINARY,11,2); adaptiveThreshold(img, dst3, 255,ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C ,THRESH_BINARY,11,2); // show images imshow("img", img); imshow("threshold", dst1); imshow("mean_c", dst2); imshow("gauss_c", dst3); waitKey(); }
对比显示的结果为:
二、基于边缘
1)轮廓函数
OpenCV 中,可在图像的边缘检测之后,使用 findContours() 寻找到轮廓,该函数参数如下:
image 一般为二值化图像,可由 compare, inRange, threshold , adaptiveThreshold, Canny 等函数获得
void findContours ( InputOutputArray image, // 输入图像 OutputArrayOfArrays contours, // 检测到的轮廓 OutputArray hierarchy, // 可选的输出向量 int mode, // 轮廓获取模式 (RETR_EXTERNAL, RETR_LIST, RETR_CCOMP,RETR_TREE, RETR_FLOODFILL) int method, // 轮廓近似算法 (CHAIN_APPROX_NONE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1, CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS) Point offset = Point() // 轮廓偏移量 )
hierarchy 为可选的参数,如果不选择该参数,则可得到 findContours 函数的第二种形式
void findContours ( InputOutputArray image, OutputArrayOfArrays contours, int mode, int method, Point offset = Point() )
drawContours() 函数如下:
void drawContours ( InputOutputArray image, // 目标图像 InputArrayOfArrays contours, // 所有的输入轮廓 int contourIdx, // const Scalar & color, // 轮廓颜色 int thickness = 1, // 轮廓线厚度 int lineType = LINE_8, // InputArray hierarchy = noArray(), // int maxLevel = INT_MAX, // Point offset = Point() // )
2)例程
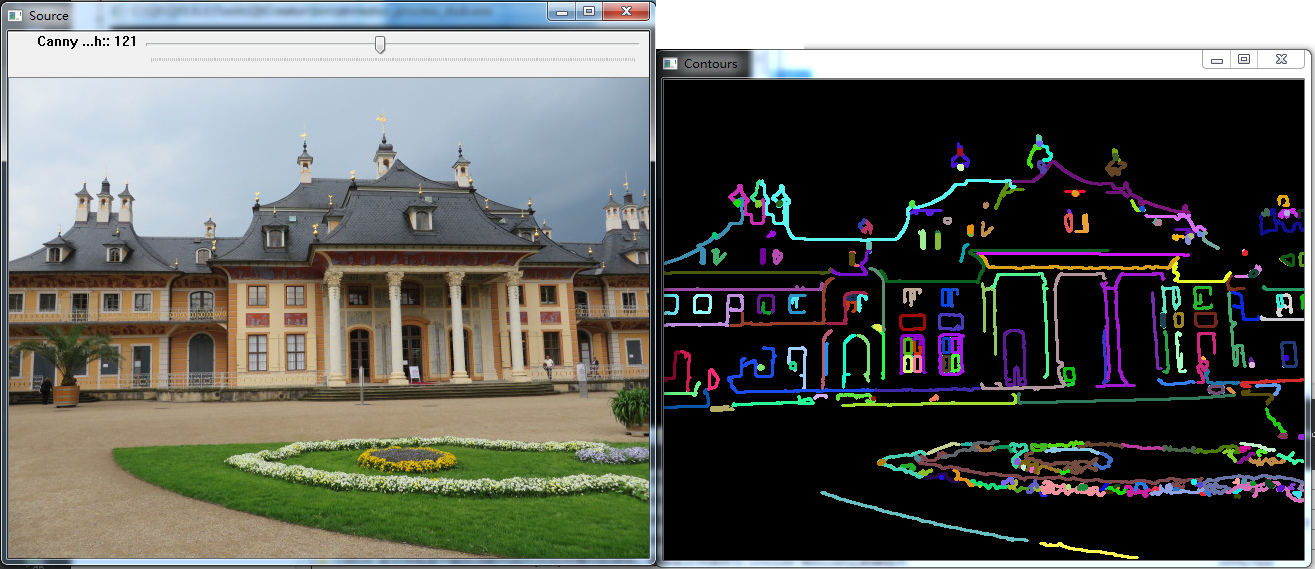
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" using namespace cv; using namespace std; Mat src,src_gray; int thresh = 100; int max_thresh = 255; RNG rng(12345); void thresh_callback(int, void* ); int main( int, char** argv ) { // 读图 src = imread("Pillnitz.jpg", IMREAD_COLOR); if (src.empty()) return -1; // 转化为灰度图 cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY ); blur(src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) ); // 显示 namedWindow("Source", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); imshow( "Source", src ); // 滑动条 createTrackbar("Canny thresh:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback ); // 回调函数 thresh_callback( 0, 0 ); waitKey(0); } // 回调函数 void thresh_callback(int, void* ) { Mat canny_output; vector<vector<Point> > contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarchy; // canny 边缘检测 Canny(src_gray, canny_output, thresh, thresh*2, 3); // 寻找轮廓 findContours( canny_output, contours, hierarchy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) ); Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( canny_output.size(), CV_8UC3); // 画出轮廓 for( size_t i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ ) { Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) ); drawContours( drawing, contours, (int)i, color, 2, 8, hierarchy, 0, Point() ); } namedWindow( "Contours", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); imshow( "Contours", drawing ); }
以 Dresden 的 Schloss Pillnitz 为源图,输出如下: