LeetCode买卖股票问题汇总
本文对LeetCode中的买卖股票问题做了一个汇总。
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
如果你最多只允许完成一笔交易(即买入和卖出一支股票一次),设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
注意:你不能在买入股票前卖出股票。
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出: 5
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
方法1
假设当前在第 i 天,令 minPrice 表示前 i-1 天的最低价格;令 maxProfit 表示前 i-1 天的最大收益。那么考虑第 i 天的收益时,存在两种情况:
- 在第 i 天卖出。很显然,想要获得最大收益,应该在前 i-1 天中价格最低的时候买入,即此时的收益为:prices[i] - minPrice。(可能会出现负数,但是没关系)
- 不在第 i 天卖出。那么第 i 天的最大收益就等于前 i -1 天中的最大收益
状态转移方程为
第 i 天最大收益 = max( 在第 i 天卖出的所得收益 , 前 i-1 天的最大收益)
代码实现如下:
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices == null || prices.length == 0) return 0;
int maxProfit = 0, minPrice = prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, prices[i]-minPrice);
minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, prices[i]);
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
方法2:kadane算法
这个解法是从原文作者的链接中找到的解法,该解法使用了kadane's algorithm ,该算法用于解决最大连续子序列问题,可以了解一下。
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int maxCur = 0, maxSoFar = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
maxCur = Math.max(0, maxCur += prices[i] - prices[i-1]);
maxSoFar = Math.max(maxCur, maxSoFar);
}
return maxSoFar;
}
}
根据这一解法,我们其实也可以发现,第121题还可以理解为Maximum Subarray问题。
假设给出的股票价格数组prices = {7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4},我们先计算出第 i 天和第 i-1 天的差值,即 diff = {-6, 4, -2, 3, -2} ,那么计算prices数组完成一笔交易的最大值就等价于在计算diff数组的具有最大和的连续子数组。在这里,就是 4+(-2)+3 = 5, 即prices[4] - prices[1] = 5。
prices = {prices[0], prices[1], prices[2], prices[3], prices[4]}
diff = {prices[1]-prices[0], prices[2]-prices[1], prices[3]-prices[2], prices[4]-prices[3]}
假设在prices中,最大差值:
maxProfit = prices[3] - prices[0]
那么在diff数组中,对应的值:
maxProfit = (prices[1]-prices[0]) + (prices[2]-prices[1]) + (prices[3]-prices[2])
= prices[3] - prices[0]
因此,本题可以转化为求最大连续子序列的和的问题。
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出: 7
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 3 天(股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。
随后,在第 4 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-3 = 3 。
方法1:有限状态机的思想
(注:本题的解法是在做了309题之后,开始尝试用状态机的思想重新思考本题,完全自己解出来了。终于不需要借助题解,独立完成了,说明自己是真的懂的了开心)
考虑到对于任意一天,要么持有股票(定义该状态为 hold),要么不持有股票(定义该状态为 sold)。
-
假设第 i 天为 hold 状态:
- case 1:可能前一天是 hold 状态,即在第 i-1 天持有股票,在第 i 天时继续持有,啥也不干(我们定义“啥也不干”这一动作为 rest);
- case 2:可能前一天是 sold 状态,即在第 i-1天本来是不持有股票的,但是在第 i 天买入了一支新股,因此第 i 天变成了 hold 状态。
-
假设第 i 天为 sold 状态:
- case 1:可能前一天是 hold 状态,即在第 i-1 天持有股票,但是在第 i 天时抛售了,于是变成了 sold 状态;
- case 2:可能前一天是 sold 状态,即在第 i-1天不持有股票的,在第 i 天继续啥也不干。
基于上面的分析,可以画出如下状态机转换示意图(原创图,ppt画的):

上面是理论分析,落实到代码层面,我们定义变量hold和sold表示第 i 天结束后所拥有的收益。很显然,最后的结果保存在sold中,即卖完手中的股票总比还持有股票要多套现一点钱的。根据状态机,我们可以写出如下状态状态转移方程:
假设当前是第 i 天
hold = max(prev_hold, prev_sold - prices[i]);
sold = max(prev_sold, prev_hold + prices[i]);
代码实现如下:
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length == 0) return 0;
int sold = 0, hold = -prices[0]; // 初始化
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int prev_sold = sold;
int prev_hold = hold;
hold = Math.max(prev_hold, prev_sold - prices[i]);
sold = Math.max(prev_sold, prev_hold + prices[i]);
}
return sold;
}
}
方法2:峰谷法
非原创,参考这里 。
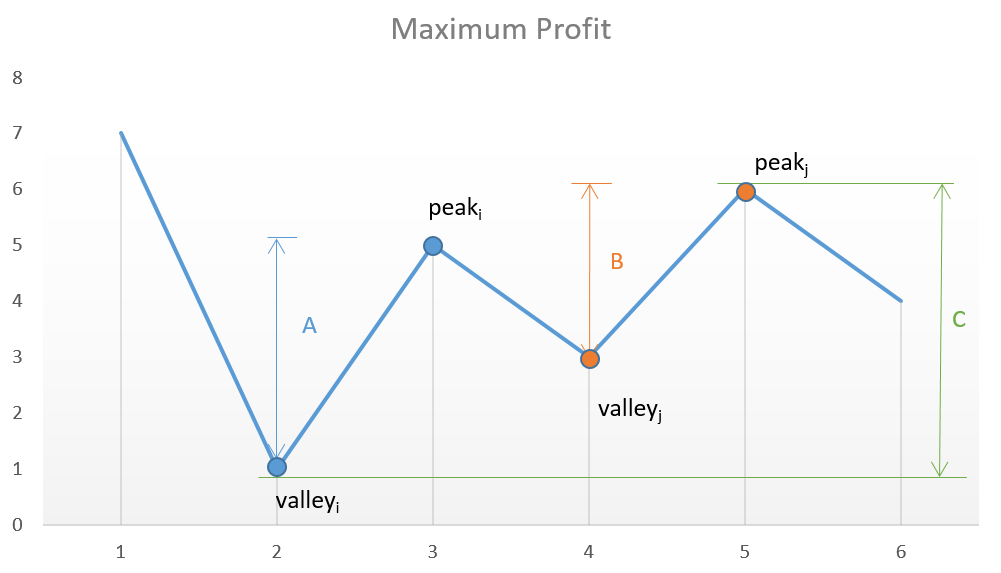
代码实现:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int i = 0;
int valley = prices[0];
int peak = prices[0];
int maxprofit = 0;
while (i < prices.length - 1) {
while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] >= prices[i + 1])
i++;
valley = prices[i];
while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] <= prices[i + 1])
i++;
peak = prices[i];
maxprofit += peak - valley;
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
方法3:在方法2的基础上进一步简化
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1])
maxprofit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 两笔 交易。
注意: 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
输入: [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4]
输出: 6
解释: 在第 4 天(股票价格 = 0)的时候买入,在第 6 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3 。
随后,在第 7 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 8 天 (股票价格 = 4)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 4-1 = 3 。
方法1:基于188题的做法
// 时间复杂度:O(k*n)
// 空间复杂度:O(k*n)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
return maxProfitWithK(2, prices);
}
public int maxProfitWithK(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if(n == 0) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[k+1][n];
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
int maxDiff = dp[i-1][0] - prices[0];
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], prices[j] + maxDiff);
maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, dp[i-1][j]-prices[j]);
}
}
return dp[k][n-1];
}
}
方法2:状态机的思想
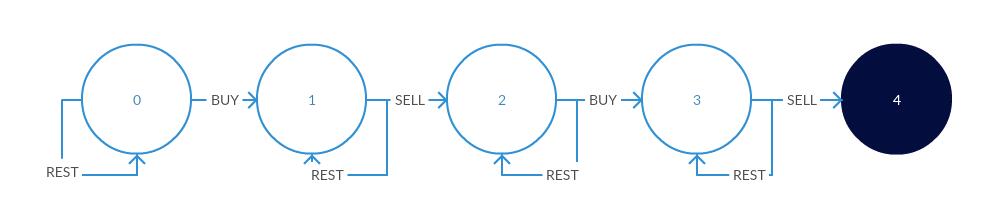
代码实现如下:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length == 0) return 0;
int hold_1 = -prices[0], sold_1 = 0;
int hold_2 = -prices[0], sold_2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
hold_1 = Math.max(hold_1, -prices[i]);
sold_1 = Math.max(sold_1, hold_1 + prices[i]);
hold_2 = Math.max(hold_2, sold_1 - prices[i]);
sold_2 = Math.max(sold_2, hold_2 + prices[i]);
}
return sold_2;
}
}
188. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 k 笔交易。
注意: 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
输入: [3,2,6,5,0,3], k = 2
输出: 7
解释: 在第 2 天 (股票价格 = 2) 的时候买入,在第 3 天 (股票价格 = 6) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-2 = 4 。
随后,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 0) 的时候买入,在第 6 天 (股票价格 = 3) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3 。
本题参考https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDhu5uGq_ic,非常感谢这位印度小哥,你帮我给讲懂了!
方法1:O(k*n^2)
// 时间复杂度:O(k*n^2)
// 空间复杂度:O(k*n)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if(n == 0) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[k+1][n];
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
int maxVal = 0;
for(int m = 0; m < j; m++) {
maxVal = Math.max(maxVal, prices[j]-prices[m]+dp[i-1][m]);
}
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], maxVal);
}
}
return dp[k][n-1];
}
}
方法2:O(k*n)
// 时间复杂度:O(k*n)
// 空间复杂度:O(k*n)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if(n == 0) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[k+1][n];
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
int maxDiff = dp[i-1][0] - prices[0];
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], prices[j] + maxDiff);
maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, dp[i-1][j]-prices[j]);
}
}
return dp[k][n-1];
}
}
方法3:解决内存超限的问题
优化点,当k >= prices.length/2 时,表示可以把所有可能的交易都执行一遍,此时的情况就退回成了股票系列的第122题了。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(k >= n/2) return maxProfitWithGreedy(prices);
int[][] dp = new int[k+1][n];
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
int maxDiff = dp[i-1][0] - prices[0];
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], prices[j] + maxDiff);
maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, dp[i-1][j]-prices[j]);
}
}
return dp[k][n-1];
}
private int maxProfitWithGreedy(int[] prices) {
int maxProfit = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if(prices[i] - prices[i-1] > 0) {
maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i-1];
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
309. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
给定一个整数数组,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 。
设计一个算法计算出最大利润。在满足以下约束条件下,你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票):
你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
卖出股票后,你无法在第二天买入股票 (即冷冻期为 1 天)。
输入: [1,2,3,0,2]
输出: 3
解释: 对应的交易状态为: [买入, 卖出, 冷冻期, 买入, 卖出]
方法1:有限状态机的思想
参考https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oL6mRyTn56M

代码实现如下:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int hold = Integer.MIN_VALUE, sold = 0, rest = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
int prev_rest = rest;
int prev_hold = hold;
rest = Math.max(rest, sold);
hold = Math.max(hold, prev_rest - prices[i]);
sold = prev_hold + prices[i];
}
return Math.max(sold, rest);
}
}
714. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee
给定一个整数数组 prices,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 ;非负整数 fee 代表了交易股票的手续费用。
你可以无限次地完成交易,但是你每笔交易都需要付手续费。如果你已经购买了一个股票,在卖出它之前你就不能再继续购买股票了。
返回获得利润的最大值。
注意:这里的一笔交易指买入持有并卖出股票的整个过程,每笔交易你只需要为支付一次手续费。
0 < prices.length <= 50000.0 < prices[i] < 50000.0 <= fee < 50000.
输入: prices = [1, 3, 2, 8, 4, 9], fee = 2
输出: 8
解释: 能够达到的最大利润:
在此处买入 prices[0] = 1
在此处卖出 prices[3] = 8
在此处买入 prices[4] = 4
在此处卖出 prices[5] = 9
总利润: ((8 - 1) - 2) + ((9 - 4) - 2) = 8.
方法1:有限状态机的思想(几乎等同于第122题)
注意初始化和状态转移时要考虑收付费,其他的思路完全一样。不再赘述。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
if(prices.length == 0) return 0;
int sold = 0, hold = -prices[0]-fee; // 初始化
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int prev_sold = sold;
int prev_hold = hold;
hold = Math.max(prev_hold, prev_sold - prices[i] - fee);
sold = Math.max(prev_sold, prev_hold + prices[i]);
}
return sold;
}
}
方法2:DP思想
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][2];
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
/*
1.在第 i 天结束时,不持有股票
- 在第 i-1 天时就不持有股票
- 在第 i-1 天时持有股票,而在第 i 天卖出
*/
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i-1]);
/*
2.在第 i 天结束时,持有股票
- 在第 i-1 天时就持有股票
- 在第 i-1 天时不持有股票,在第 i 天买入股票(在买入股票时还需扣除手续费)
*/
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] - prices[i-1] - fee);
}
return dp[n][0];
}
}



