基于python的数学建模---分支定界算法
- zip函数
a = [1,2,3,4]
b = [5,6,7,8]
i = sum(x * y for x, y in zip(a, b))
print(i)
70
- floor and ceil 函数
import math
a = 34.3
print(math.floor(a))
print(math.ceil(a))
34
35
- all 函数
print(all([1,2,3,4,5]))
print(all([1,2,3,0,5]))
True
False
- enumerate 函数
seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
print(list(enumerate(seasons)))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
- len 函数
A = [[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6]]
print(len(A))
2
- 分支代码
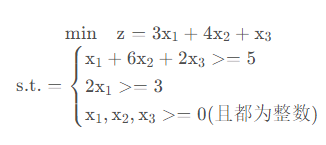
import math from scipy.optimize import linprog import sys def integerPro(c, A, b, Aeq, beq, t=1.0E-8): res = linprog(c, A_ub=A, b_ub=b, A_eq=Aeq, b_eq=beq) bestVal = sys.maxsize # 很大一个数 bestX = res.x if not (type(res.x) is float or res.status != 0): bestVal = sum([x * y for x, y in zip(c, bestX)]) if all(((x - math.floor(x)) <= t or (math.ceil(x) - x) <= t) for x in bestX): return bestVal, bestX else: ind = [i for i, x in enumerate(bestX) if (x - math.floor(x)) > t and (math.ceil(x) - x) > t][0] newCon1 = [0] * len(A[0]) newCon2 = [0] * len(A[0]) newCon1[ind] = -1 newCon2[ind] = 1 newA1 = A.copy() newA2 = A.copy() newA1.append(newCon1) newA2.append(newCon2) newB1 = b.copy() newB2 = b.copy() newB1.append(-math.ceil(bestX[ind])) newB2.append(math.floor(bestX[ind])) r1 = integerPro(c, newA1, newB1, Aeq, beq) r2 = integerPro(c, newA2, newB2, Aeq, beq) if r1[0] < r2[0]: return r1 else: return r2 if __name__ == '__main__': c = [3, 4, 1] A = [[-1, -6, -2], [-2, 0, 0]] b = [-5, -3] Aeq = [[0, 0, 0]] beq = [0] print(integerPro(c, A, b, Aeq, beq))
(8.000000000001586, array([2.00000000e+00, 1.83247535e-13, 2.00000000e+00]))
8是目标函数值,array是变量值x1、x2、x3





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律