CentOS 7
此次测试的CentOS 信息如下
CentOS Linux 7(Core) Kernel 3.10.0-1062.e17.x86_64 on an x86_64
1、查看ip
CentOS 7没有ifconfig命令,CentOS7的IP查询命令如下:
ip addr
此命令打印2条信息

centos的ip地址是ens33条目中的inet值,但是ens33 没有 inet 这个属性,那么就说明该系统当前没有分配到IP地址,无法完成通讯。
2、设置CentOS 7获取IP地址
2.1、动态获取ip(前提是你的路由器已经开启了DHCP)
修改网卡配置文件 vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32 (最后一个为网卡名称)
动态获取IP地址需要修改两处地方即可
(1)bootproto=dhcp
(2)onboot=yes

修改后:wq保存后重启网络服务
[root@mini ~]# systemctl restart network
[root@mini ~]#
此时,配置动态IP地址完成,这个时候再查看一下ip addr 就可以看到已经获取了IP地址,可以通过Ping命令进行测试。
2.2、配置静态IP地址
设置静态IP地址与动态iIP差不多,也是要修改网卡配置文件 vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32 (最后一个为网卡名称)
(1)bootproto=static
(2)onboot=yes
(3)在最后加上几行,IP地址、子网掩码、网关、dns服务器
IPADDR=192.168.1.160
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
DNS1=119.29.29.29
DNS2=8.8.8.8
(4)重启网络服务
[root@mini ~]# systemctl restart network
[root@mini ~]#
DNS服务器可以只配一个,我用的是两个免费的dns服务器,查看IP地址,测试联网

命令如下
[root@mini ~]# ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: ens32: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:d2:42:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.160/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global noprefixroute ens32 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::f86e:939e:ff9b:9aec/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever [root@mini ~]# ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (163.177.151.109) 56(84) bytes of data. bytes from 163.177.151.109 (163.177.151.109): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=27.5 ms bytes from 163.177.151.109 (163.177.151.109): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=35.2 ms ^C --- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics --- packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1008ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 27.570/31.425/35.281/3.859 ms
2.3 问题修复
本来好好的虚拟机突然不能上网了。执行命令重启network服务
systemctl network restart
结果
Restarting network (via systemctl): Job for network.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status network.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.Failed
使用命令
systemctl status network.service
结果为
network.service - LSB: Bring up/down networking
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/network)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since 三 2019-12-18 11:34:36 CST; 54s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 3847 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/network start (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
我的ifcfg-ens33文件内容正常,也不存在多余的ifcfg-ens33.old文件,通过搜索帖子说和系统自带的NetworkManager这个管理套件有关系,关掉就可以解决。执行命令如下:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop NetworkManager
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable NetworkManager
重启服务器
reboot
通过ip addr命令查看到网络已恢复正常。
2.4、添加ping命令
有时我们安装的centos 缺少ping命令,可以通过如下方式安装
yum install iputils
3、Linux 关机与重启命令
1、reboot 普通重启
2、shutdown -r now 立刻重启(root用户使用)
3、shutdown -r 10 过10分钟自动重启(root用户使用)
4、shutdown -r 20:35 在时间为20:35时候重启(root用户使用)
如果是通过shutdown命令设置重启的话,可以用shutdown -c命令取消重启
Linux centos关机命令:
1、halt 立刻关机
2、poweroff 立刻关机
3、shutdown -h now 立刻关机(root用户使用)
4、shutdown -h 10 10分钟后自动关机
1.shutdown
shutdown命令安全地将系统关机。 有些用户会使用直接断掉电源的方式来关闭linux,
这是十分危险的。因为linux与windows不同,其后台运行着许多进程,所以强制关机可能
会导致进程的数据丢失﹐使系统处于不稳定的状态﹐甚至在有的系统中会损坏硬件设备。
而在系统关机前使用shutdown命令﹐系统管理员会通知所有登录的用户系统将要关闭。
并且login指令会被冻结﹐即新的用户不能再登录。直接关机或者延迟一定的时间才关机
都是可能的﹐还可能重启。这是由所有进程〔process〕都会收到系统所送达的信号〔signal〕
决定的。这让像vi之类的程序有时间储存目前正在编辑的文档﹐而像处理邮件〔mail〕和
新闻〔news〕的程序则可以正常地离开等等。
shutdown执行它的工作是送信号〔signal〕给init程序﹐要求它改变runlevel。
Runlevel 0被用来停机〔halt〕﹐runlevel 6是用来重新激活〔reboot〕系统﹐
而runlevel 1则是被用来让系统进入管理工作可以进行的状态﹔这是预设的﹐假定没有-h也
没有-r参数给shutdown。要想了解在停机〔halt〕或者重新开机〔reboot〕过程中做了哪些
动作﹐你可以在这个文件/etc/inittab里看到这些runlevels相关的资料。
shutdown 参数说明:
[-t] 在改变到其它runlevel之前﹐告诉init多久以后关机。
[-r] 重启计算器。
[-k] 并不真正关机﹐只是送警告信号给每位登录者〔login〕。
[-h] 关机后关闭电源〔halt〕。
[-n] 不用init﹐而是自己来关机。不鼓励使用这个选项﹐而且该选项所产生的后果往
往不总是你所预期得到的。
[-c] cancel current process取消目前正在执行的关机程序。所以这个选项当然没有
时间参数﹐但是可以输入一个用来解释的讯息﹐而这信息将会送到每位使用者。
[-f] 在重启计算器〔reboot〕时忽略fsck。
[-F] 在重启计算器〔reboot〕时强迫fsck。
[-time] 设定关机〔shutdown〕前的时间。
2.halt
最简单的关机命令
其实halt就是调用shutdown -h。halt执行时﹐杀死应用进程﹐执行sync系统调用﹐
文件系统写操作完成后就会停止内核。
参数说明:
[-n] 防止sync系统调用﹐它用在用fsck修补根分区之后﹐以阻止内核用老版本的超
级块〔superblock〕覆盖修补过的超级块。
[-w] 并不是真正的重启或关机﹐只是写wtmp〔/var/log/wtmp〕纪录。
[-d] 不写wtmp纪录〔已包含在选项[-n]中〕。
[-f] 没有调用shutdown而强制关机或重启。
[-i] 关机〔或重启〕前﹐关掉所有的网络接口。
[-p] 该选项为缺省选项。就是关机时调用poweroff。
3.reboot
reboot的工作过程差不多跟halt一样﹐不过它是引发主机重启﹐而halt是关机。它
的参数与halt相差不多。
4.init
init是所有进程的祖先﹐它的进程号始终为1﹐所以发送TERM信号给init会终止所有的
用户进程﹑守护进程等。shutdown 就是使用这种机制。init定义了8个运行级别(runlevel),
init 0为关机﹐init 1为重启。关于init可以长篇大论﹐这里就不再叙述。另外还有
telinit命令可以改变init的运行级别﹐比如﹐telinit -iS可使系统进入单用户模式﹐
并且得不到使用shutdown时的信息和等待时间。
linux如何修改root管理员密码
以root 身份登录(SSH操作)
输入 passwd 命令 就可以看到提示输入新密码了
输入密码的时候是看不到字符的。
4、CentOS安装wget
yum -y install wget
5、CentOS 7安装gitLab
5.1 执行命令
vm /etc/yum.repos.d/tsinghua.repo
创建文件tsinghua.repo。粘贴内容
[gitlab-ce] name=Gitlab CE Repository baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/gitlab-ce/yum/el$releasever/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
到文本,按ESC按键然后执行
:wq!
命令保存。
5.2 缓存相关包
yum makecache
5.3 安装相关依赖
yum install curl policycoreutils-python openssh-server
5.4 安装gitlab-ce
yum install gitlab-ce
中间会出现如下内容

输入 y ,然后耐心等待下载完成,下载文件660M左右,视网速决定所需时间。
当出现如下画面说明gitLab已经搭建完毕!
Running transaction Installing : gitlab-ce-12.3.5-ce.0.el7.x86_64 1/1 It looks like GitLab has not been configured yet; skipping the upgrade script. *. *. *** *** ***** ***** .****** ******* ******** ******** ,,,,,,,,,***********,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,,,*********,,,,,,,,,,, .,,,,,,,,,,,*******,,,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,*****,,,,,,,,,. ,,,,,,,****,,,,,, .,,,***,,,, ,*,. _______ __ __ __ / ____(_) /_/ / ____ _/ /_ / / __/ / __/ / / __ `/ __ \ / /_/ / / /_/ /___/ /_/ / /_/ / \____/_/\__/_____/\__,_/_.___/ Thank you for installing GitLab! GitLab was unable to detect a valid hostname for your instance. Please configure a URL for your GitLab instance by setting `external_url` configuration in /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb file. Then, you can start your GitLab instance by running the following command: sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure For a comprehensive list of configuration options please see the Omnibus GitLab readme https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/blob/master/README.md Verifying : gitlab-ce-12.3.5-ce.0.el7.x86_64 1/1 Installed: gitlab-ce.x86_64 0:12.3.5-ce.0.el7 Complete!
5.5 配置
上方安装完毕之后还需要进行配置,配置文件所在位置/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
执行命令
vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
显示如下内容
## GitLab configuration settings ##! This file is generated during initial installation and **is not** modified ##! during upgrades. ##! Check out the latest version of this file to know about the different ##! settings that can be configured by this file, which may be found at: ##! https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/raw/master/files/gitlab-config-template/gitlab.rb.template ## GitLab URL ##! URL on which GitLab will be reachable. ##! For more details on configuring external_url see: ##! https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#configuring-the-external-url-for-gitlab external_url 'http://gitlab.example.com' ## Roles for multi-instance GitLab ##! The default is to have no roles enabled, which results in GitLab running as an all-in-one instance. ##! Options: ##! redis_sentinel_role redis_master_role redis_slave_role geo_primary_role geo_secondary_role ##! For more details on each role, see: ##! https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/roles/README.html#roles ##! # roles ['redis_sentinel_role', 'redis_master_role'] ## Legend ##! The following notations at the beginning of each line may be used to ##! differentiate between components of this file and to easily select them using ##! a regex. ##! ## Titles, subtitles etc ##! ##! More information - Description, Docs, Links, Issues etc. ##! Configuration settings have a single # followed by a single space at the ##! beginning; Remove them to enable the setting. ##! **Configuration settings below are optional.** ##! **The values currently assigned are only examples and ARE NOT the default ##! values.** ################################################################################ ################################################################################ ## Configuration Settings for GitLab CE and EE ## ################################################################################ Type :quit<Enter> to exit Vim
我们主要关心配置如下
external_url 'http://gitlab.xxxxxx.com' #改域名,修改成你自己的域名,如果你用的https,改成https://gitlab.xxxxxx.com unicorn['worker_processes'] = 2 #CPU使用核数,默认好像是24核,用不了那么多,改成2 gitlab_rails['time_zone'] = 'Asia/Shanghai' # 时间区域 # #禁止gitlab内部nginx,这里我通过外部nginx(即系统原来已装好的nginx),如果你系统没有装nginx,这里不用改。 添加外部的nginx, nginx['enable'] = false web_server['external_users'] = ['www'] #www为我的nginx运行用户,这里修改为你自己的nginx的运行用户
Gitlab配置的时候可以不绑定域名吗?
可以的。
1.在gitlab的配置gitlab.yml中,host为你本机的ip
2.在gitlab-shell的配置config.yml中,gitlab_url:“http://yourip”
3.建议绑定一个,不然不清楚有没有配置成功。不绑定的话也可以修改host为ip地址,可以是你的本地ip。
改完执行
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
重新加载配置信息。
5.6 配置nginx
新建 /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitlab.conf文件
vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitlab.conf
配置如下
upstream gitlab-workhorse { server unix:/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse/socket; } server{ listen 80; server_name gitlab.xxxxx.com; ## 修改成自己的域名; rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host$request_uri; } ## Normal HTTP host server { listen 443 ssl; ssl_certificate /data/ssl/new/xxxxx.com/cert.pem; ssl_certificate_key /data/ssl/new/xxxxx.com/key.pem; server_name gitlab.xxxxxx.com; ## 修改成自己的域名; root /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public; ## See app/controllers/application_controller.rb for headers set ## Individual nginx logs for this GitLab vhost access_log /var/logs/nginx/gitlab_access.log; # 根据实际情况修改 error_log /var/logs/nginx/gitlab_error.log; # 根据实际情况修改 location ~ ^/(assets)/ { gzip_static on; # to serve pre-gzipped version expires max; add_header Cache-Control public; } location / { client_max_body_size 0; gzip off; ## https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlabhq/issues/694 ## Some requests take more than 30 seconds. proxy_read_timeout 300; proxy_connect_timeout 300; proxy_redirect off; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_pass http://gitlab-workhorse; } }
这里配置了https,你可根据实际情况修改。改好后执行如下命令重新加载nginx配置
systemctl reload nginx
5.7 gitlab后台界面
访问 gitlab.xxxxxx.com,第一次进入后台,会提示修改root密码,修改后重新登录。
------可能用到的操作
如果你的gitlab安装在docker,需要修改gitlab和nginx相关配置。
修改/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
gitlab_workhorse['listen_network'] = "tcp" gitlab_workhorse['listen_addr'] = "172.18.1.17:8080" #docker的ip和端口,根据实际情况修改
修改 /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitlab.conf,将
upstream gitlab-workhorse { server unix:/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse/socket; }
修改为
upstream gitlab-workhorse { server localhost:8080; #根据实际情况修改 }
5.8 补充资料
gitlab 相关操作命令
start 启动所有服务 这个重启也会继续开启 相当systemctl enable
stop 关闭所有服务
restart 重启所有服务
status 查看所有服务状态
tail 查看日志信息
service-list 列举所有启动服务
graceful-kill 平稳停止一个服务
help 帮助
reconfigure 修改配置文件之后,需要重新加载下
show-config 查看所有服务配置文件信息
uninstall 卸载这个软件
cleanse 删除gitlab数据,重新白手起家
gitlab 包含的服务
Restarting previously running GitLab services ok: run: alertmanager: (pid 6798) 0s ok: run: gitaly: (pid 13241) 147348s ok: run: gitlab-monitor: (pid 6813) 1s ok: run: gitlab-workhorse: (pid 6816) 0s ok: run: logrotate: (pid 6825) 1s ok: run: nginx: (pid 6831) 0s ok: run: node-exporter: (pid 6833) 0s ok: run: postgres-exporter: (pid 6839) 1s ok: run: postgresql: (pid 12349) 147445s ok: run: prometheus: (pid 6849) 0s ok: run: redis: (pid 12289) 147452s ok: run: redis-exporter: (pid 6866) 1s ok: run: sidekiq: (pid 6874) 0s ok: run: unicorn: (pid 6882) 1s
6、CentOS 7 找不到ifconfig和netstat命令
通过如下命令安装net-tools工具即可
yum install net-tools
7、CentOS 7 安装vim
第一步执行
rpm -qa | grep vim
第二步执行
yum install -y vim*
6、Linux下安装与卸载docker
一、Docker简介
Docker的三大核心概念:镜像、容器、仓库
镜像:类似虚拟机的镜像、用俗话说就是安装文件。
容器:类似一个轻量级的沙箱,容器是从镜像创建应用运行实例,可以将其启动、开始、停止、删除、而这些容器都是相互隔离、互不可见的。
仓库:类似代码仓库,是Docker集中存放镜像文件的场所。
二、环境要求与安装
1、内核版本必须大于3.10
uname -r
检查内核版本是否符合要求,本人如下
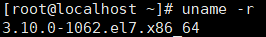
满足条件者可继续了。
2、执行命令从源下载文件
yum -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/e/epel-release-7-12.noarch.rpm
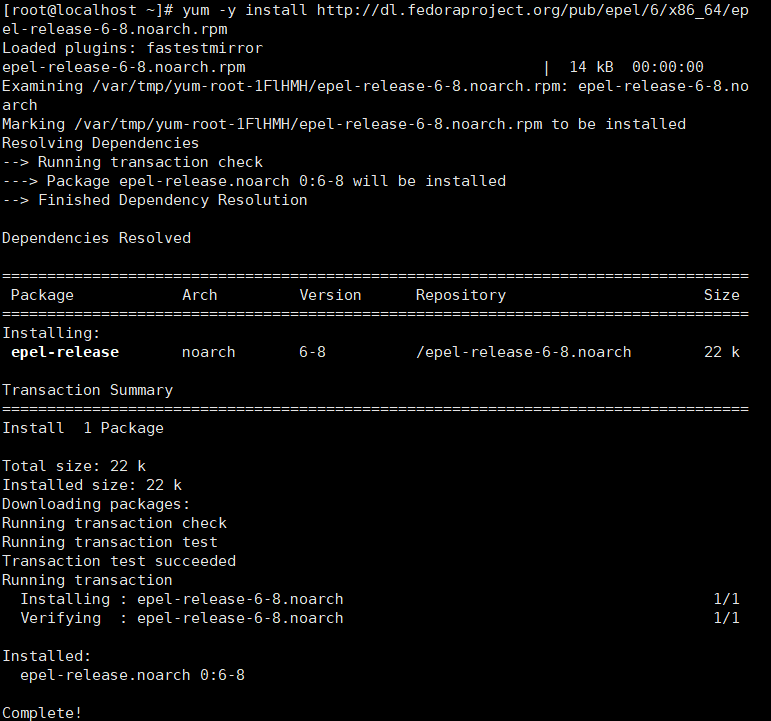
3、下载完毕后,执行下方命令安装docker
yum install docker-io
注意:中途会有询问是否下载的交互,输入y即可
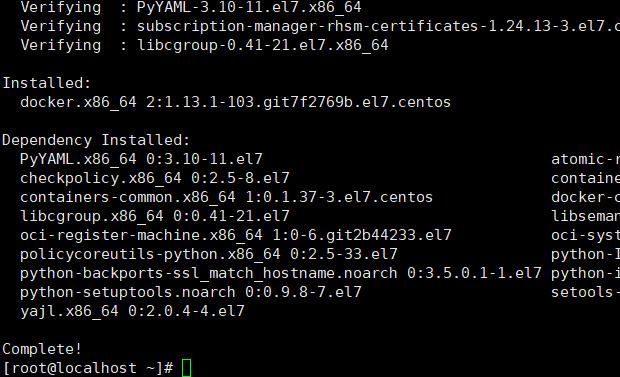
4、执行命令启动docker服务
5、查看docker版本
docker version
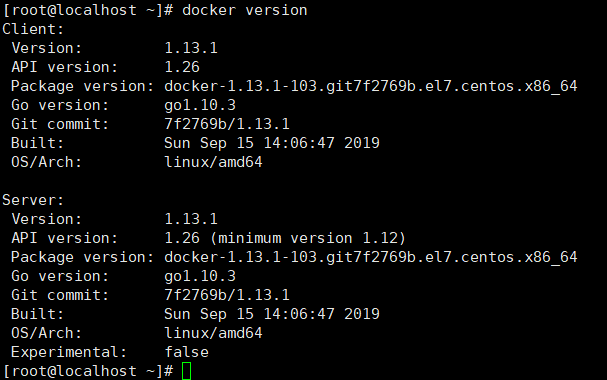
6、修改Docker镜像源为国内镜像以提高镜像下载速度
修改或新增文件
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
文件内容为
{ "registry-mirrors": [ "https://kfwkfulq.mirror.aliyuncs.com", "https://2lqq34jg.mirror.aliyuncs.com", "https://pee6w651.mirror.aliyuncs.com", "https://registry.docker-cn.com", "http://hub-mirror.c.163.com" ], "dns": ["8.8.8.8","8.8.4.4"] }
重启docker
systemctl restart docker
三、Docker的卸载
1、查询docker安装过的包:
yum list installed | grep docker
2、删除安装包:
yum remove 查询出来的和docker匹配的第一个被安装的名字 第二个名字 如果还有就一直往后写 中间用空格隔开 -y
3、删除镜像/容器等
rm -rf /var/lib/docker
卸载完毕


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号