【转】Spring线程及线程池的使用
spring @Async 线程池使用
最近公司项目正逐渐从dubbo向springCloud转型,在本次新开发的需求中,全部使用springcloud进行,在使用时线程池,考虑使用spring封装的线程池,现将本次使用心得及内容记录下来
一、线程池常规使用方式
之前使用线程池的方式,都是自己定义线程池,然后写多线程类,用线程池去调用,如下:
package cn.leadeon.message.client; import cn.leadeon.comm.log.Log; import cn.leadeon.message.req.MessageProducerReq; import lombok.Data; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * 流量消息发送类,线程池调用 * * @author LiJunJun * @since 2018/9/30 */ @Data public class MessageClientSendMsg { /** * 日志记录器 */ private static final Log LOGGER = new Log(MessageClientSendMsg.class); /** * 线程池 */ private static ExecutorService threadPool; /** * trace */ private String trace; /** * 手机号 */ private String cellNum; /** * 消息实体 */ private MessageProducerReq messageProducerReq; static { threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); } /** * 构造函数 * * @param trace 请求流水 * @param cellNum 电话号码 * @param messageProducerReq 消息实体 */ public MessageClientSendMsg(String trace, String cellNum, MessageProducerReq messageProducerReq) { this.trace = trace; this.cellNum = cellNum; this.messageProducerReq = messageProducerReq; } /** * 消息发送 */ public void sendMsg() { SendMsgRunable sendMsgRunable = new SendMsgRunable(); threadPool.execute(sendMsgRunable); } /** * 发送消息内部类并处理异常,不能影响主线程的业务 */ class SendMsgRunable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { try { MessageClientProducer msgClintProducer = new MessageClientProducer(); msgClintProducer.sendAsyncWithPartition(trace, cellNum, messageProducerReq); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("消息发送失败!,trace:" + trace); } } } }
二、使用spring的线程池
- 线程池的启用
有两种方式,配置文件或者注解
注解:使用@EnableAsync标注启用spring线程池,@Async将方法标注为异步方法,spring扫描到后,执行该方法时,会另起新线程去执行,非常简单
package cn.leadeon.message.test; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author LiJunJun * @since 2018/10/11 */ @Component @EnableAsync public class AsyncTest { @Async public void test1() { System.out.println("异步执行test1!!!"); System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } @Async public void test2() { System.out.println("异步执行test2!!!"); System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } @Async public void test3() { System.out.println("异步执行test3!!!"); System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
配置文件:新增spring的配置文件spring-threadpool.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task.xsd" default-autowire="byName"> <description>流量消息spring线程池配置</description> <!-- 缺省的异步任务线程池 --> <task:annotation-driven executor="messageExecutor"/> <task:executor id="asyncExecutor" pool-size="100-10000" queue-capacity="10"/> <!-- 处理message的线程池 --> <task:executor id="messageExecutor" pool-size="15-50" queue-capacity="100" keep-alive="60" rejection-policy="CALLER_RUNS"/> </beans>
使用注解引入配置文件或者在自己的spring配置文件中import即可
package cn.leadeon.message.test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author LiJunJun
* @since 2018/10/11
*/
@Component
@ImportResource("classpath:/config/spring-threadpool.xml")
public class AsyncTest {
@Async
public void test1() {
System.out.println("异步执行test1!!!");
System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Async
public void test2() {
System.out.println("异步执行test2!!!");
System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Async
public void test3() {
System.out.println("异步执行test3!!!");
System.out.println("线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
配置文件可以自己配置线程池的相关参数,自己可以配置多个线程池,使用时,用@Async(value="beanId")区分即可
注意点:
@EnableAsync注解与<task:annotation-driven executor="messageExecutor"/>等价,两者只能使用其一,不然启动会报错
- java编程方式配置自定义线程池,如下:
package cn.leadeon.message.base.threadpool;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* 流量消息线程池配置
*
* @author LiJunJun
* @since 2018/10/10
*/
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfiguration {
/**
* 核心线程数:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
*/
@Value("${executor.core.pool.size}")
private int corePoolSize;
/**
* 最大线程数:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
*/
@Value("${executor.max.pool.size}")
private int maxPoolSize;
/**
* 缓冲队列200:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
*/
@Value("${executor.queue.capacity}")
private int queueCapacity;
/**
* 允许线程的空闲时间(单位:秒):当超过了核心线程出之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
*/
@Value("${executor.keepalive.Seconds}")
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便我们定位处理任务所在的线程池
*/
@Value("${executor.thread.name.prefix}")
private String threadNamePrefix;
@Bean
public Executor MessageExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix);
// 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略,当线程池没有处理能力的时候,该策略会直接在 execute 方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务;如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
- 测试
package cn.leadeon.message.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
/**
* spring线程池单元测试
*
* @author LiJunJun
* @since 2018/10/11
*/
public class TestSpringThreadPool extends JunitTestBase {
@Autowired
private AsyncTest asyncTest;
/**
* spring线程池单元测试
*/
@Test
public void testThreadPool() {
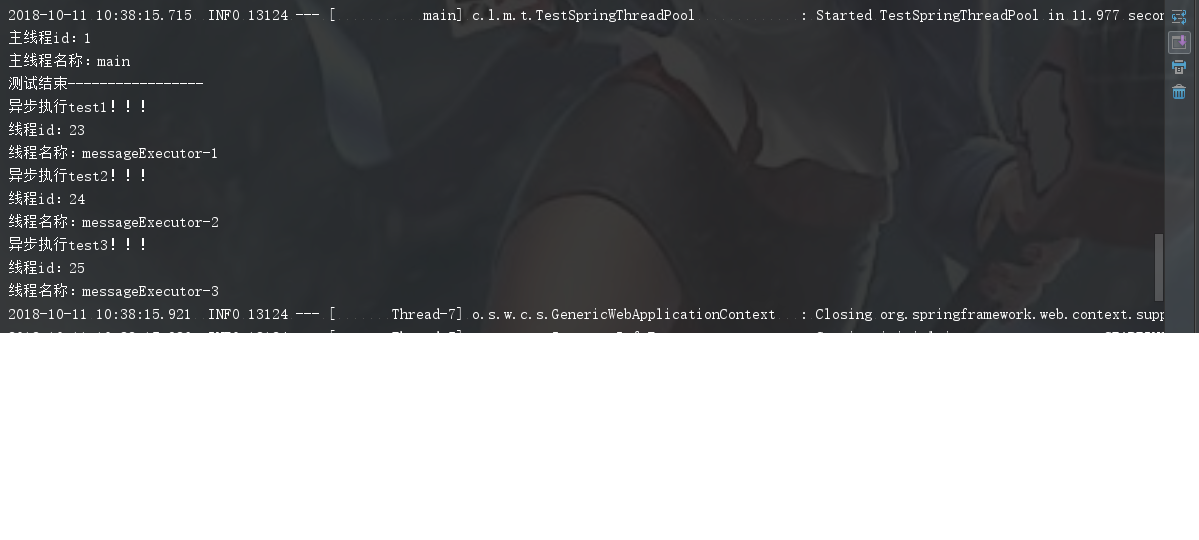
System.out.println("主线程id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("主线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
asyncTest.test1();
asyncTest.test2();
asyncTest.test3();
}
}
测试结果:主线程和异步方法分别使用了不同的线程去调用,测试完成
******************************
xml配置线程池的另一种方式
<!-- 线程池配置 --> <bean id="executor" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor"> <!-- 核心线程数,默认为1 --> <property name="corePoolSize" value="10" /> <!--最大线程数,默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE --> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="50" /> <!--队列最大长度,一般需要设置值>=notifyScheduledMainExecutor.maxNum;默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE --> <property name="queueCapacity" value="10000" /> <!--线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间,默认为60s --> <property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="300" /> <!--线程池对拒绝任务(无线程可用)的处理策略,目前只支持AbortPolicy、CallerRunsPolicy;默认为后者 1. CallerRunsPolicy :这个策略重试添加当前的任务,他会自动重复调用 execute() 方法,直到成功。 2. AbortPolicy :超过队列最大数量后对拒绝的任务抛弃处理,并且抛出异常。 --> <property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"> <bean class="java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy" /> </property> </bean>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号