对于继承的理解
继承 - 原型继承
什么是原型链???
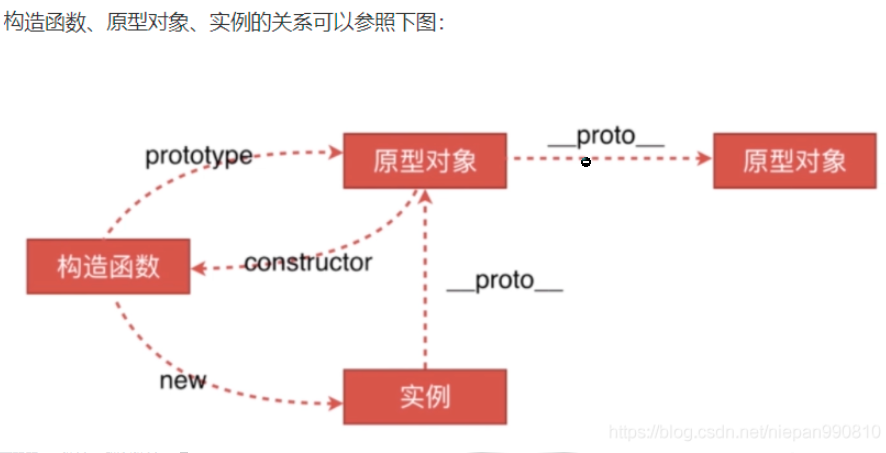
function child(){
this.xx = 'xx'; //子类自己的定义
}
child.prototype = new parent();
//这里new parent()父类对象并没有constructor属性,需要后面加上
child.prototype.constructor = child
例:
// 1. 定义Person构造函数
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log('人类会说话')
}
// 2. 定义Student构造函数
function Student (name, age, className) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
this.className = className
}
// 3. 原型继承: 利用原型链, 继承于父级构造函数, 继承原型上的方法
// 语法: 子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数()
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.study = function() {
console.log('学生在学习')
}
let stu = new Student('张三', 18, '80期')
stu.say()
console.log(stu)
如何让student继承people的方法和属性???
语法:让子类的原型等于父类的实例
子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数()
缺点:
1.不能实现多继承,所有子类的实例的原型都共享一个父类实例属性和方法
2.不能传参
继承 - 组合继承
组合继承有时候也叫伪经典继承,指的是将原型链 和 借用构造函数 call 技术组合到一块
从而发挥二者之长的一种继承模式,其背后的思路: 是使用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承 (主要是方法),而通过借用构造函数来实现对实例属性构造的继承。
// 创建子类、添加子类属性。
function arrange(name){
Person.call(this,name) // 执行父构造,将This指向本身,拉取父私有属性;
}
例:
// 1. 定义Person构造函数
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log('人类会说话')
}
// 2. 定义Student构造函数
function Student (name, age, className) {
//通过改变this指向,将父类的this改成子类的this,这样调用people(),父类的构造函数this.name变成student.name()
//people里的this原先指向people,people.call将people里的this变成指向student
Person.call(this, name, age) // 实现构造属性的继承
this.className = className
}
// 3. 原型继承: 利用原型链, 继承于父级构造函数, 继承原型上的方法
// 语法: 子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数()
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.study = function() {
console.log('学生在学习')
}
let stu = new Student('张三', 18, '80期')
stu.say()
console.log(stu)
// 方法通过 原型继承
// 属性通过 父构造函数的.call(this, name, age)
继承 - 寄生组合继承
// 1. 定义Person构造函数
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log('人类会说话')
}
// 2. 定义Student构造函数
function Student (name, age, className) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.className = className
}
// 3. 原型继承: 利用原型链, 继承于父级构造函数, 继承原型上的方法
// 语法: 子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数()
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype)
Student.prototype.study = function() {
console.log('学生在学习')
}
let stu = new Student('张三', 18, '80期')
stu.say()
console.log(stu)
// 总结:
// Object.create() 以参数的对象, 作为新建对象的__proto__属性的值, 返回新建的对象
es6 - class 实现继承 extends
// 继承关键字 => extends
class Person {
constructor (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
jump () {
console.log('会跳')
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
constructor (name, age, lesson) {
super(name, age) // extends 中, 必须调用 super(), 会触发执行父类的构造函数
this.lesson = lesson
console.log('构造函数执行了')
}
sayHello () {
console.log('会打招呼')
}
}
let teacher1 = new Teacher('zs', 18, '体育')
console.log(teacher1)
本文来自博客园,作者:Kira的学习笔记,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/kira2022/p/16114090.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现