Mybatis - 源码解析
入口
public static void statementTest() {
// 1.0 配置解析入口
// mybatis-config.xml - Configuration
// mapper.xml - <Type,MapperProxyFactory>
// mapper.xml#<select|insert|update|delete> - MappedStatement
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is,null,null);
// 2.0 sqlSession获取(DefaultSqlSession 组合了一个 executor对象,具体的语句执行由executor对象完成)
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3.0 获取代理对象
KiqiMapper kiqiMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(KiqiMapper.class);
// 4.0 通过代理对象实现sql语句的执行(代理对象方法 -> 触发管理类MapperProxy<T> -> mapperMethod.invoke()中根据statementId和sql类型调用sqlSession方法)
Kiqi kiqi = kiqiMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
// 4.6 入口,4.0-4.5通过代理对象获取到相应的statementId和type类型,然后调用sqlSession方法
Kiqi kiqi1 = sqlSession.selectOne(null,null);
System.out.println(kiqi);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
配置读取 - SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build();
① 读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件,构建configuration对象
② 读取Mapper.xml配置文件,创建Type-MapperProxyFactory<T>映射,MapperProxyFactory用于生成Mapper代理对象
③ 读取Mapper.xml - insert|update|delete|select标签,构建MappedStatement对象,用于语句执行
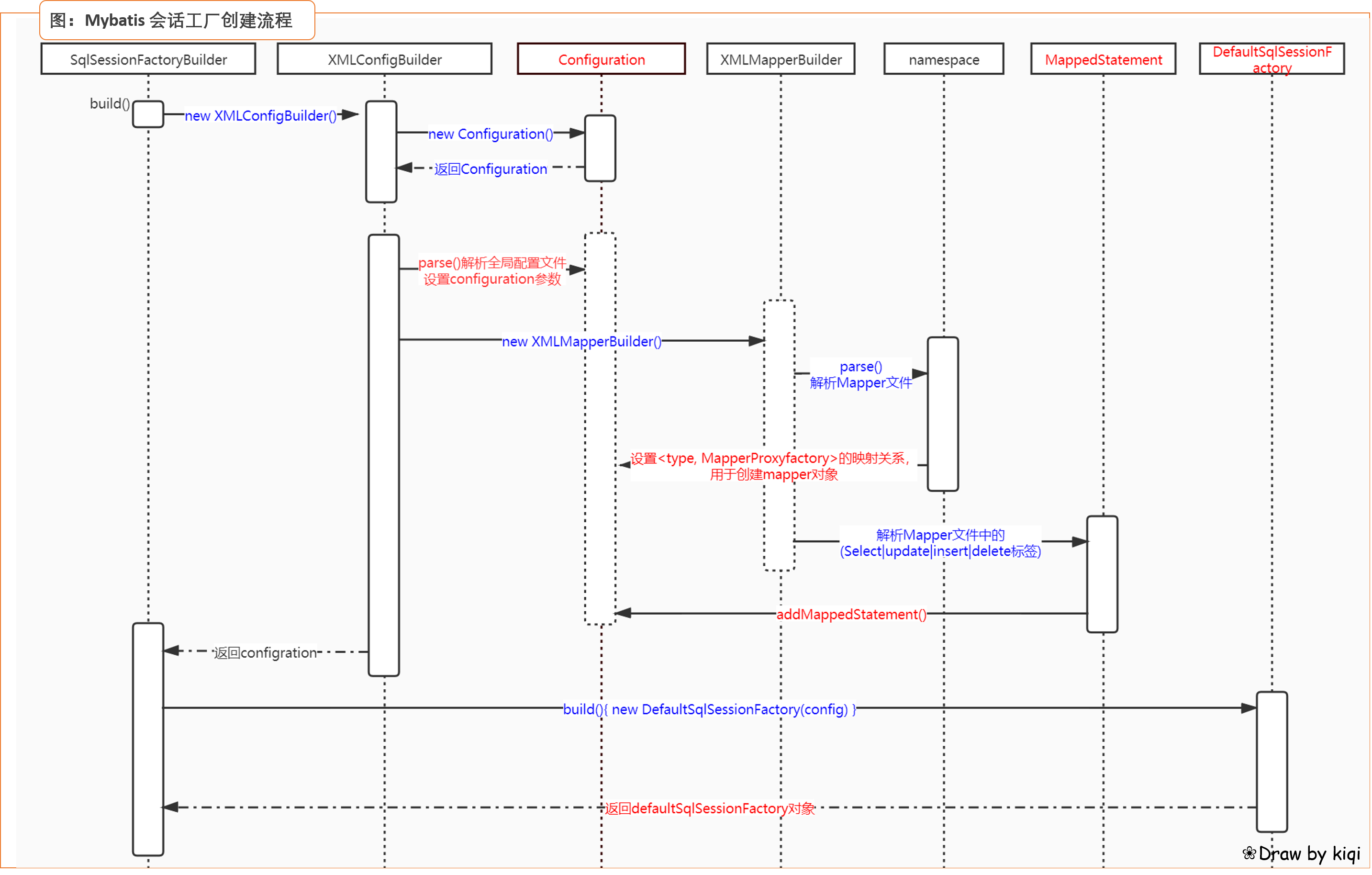
创建会话 - sqlSessionFactory.openSqlSession();
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
// 2.1 获取SqlSession
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 1. 获取事务工厂(事务工厂在config配置文件的environment标签中,通过配置文件设置 --- <transactionManager type="JDBC"/>)
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 2. 创建事务对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 3. 根据事务工厂和执行器配置,创建执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 4. 创建DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
获取mapper代理对象 - session.getMapper();
① 使用Type从configuration中获取到对应的MapperProxyFactory
② MapperProxyFactory
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 3.2 在对mapper.xml文件解析时,构建了classType(namespace)与mapperProxyFactory的映射
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 3.3 创建代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// ...
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 1:类加载器、2:被代理类实现的接口、3:实现了 InvocationHandler 的触发管理类
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 3.4 构建实现了 InvocationHandler接口的 触发管理类(特殊点:未封装被代理对象)
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
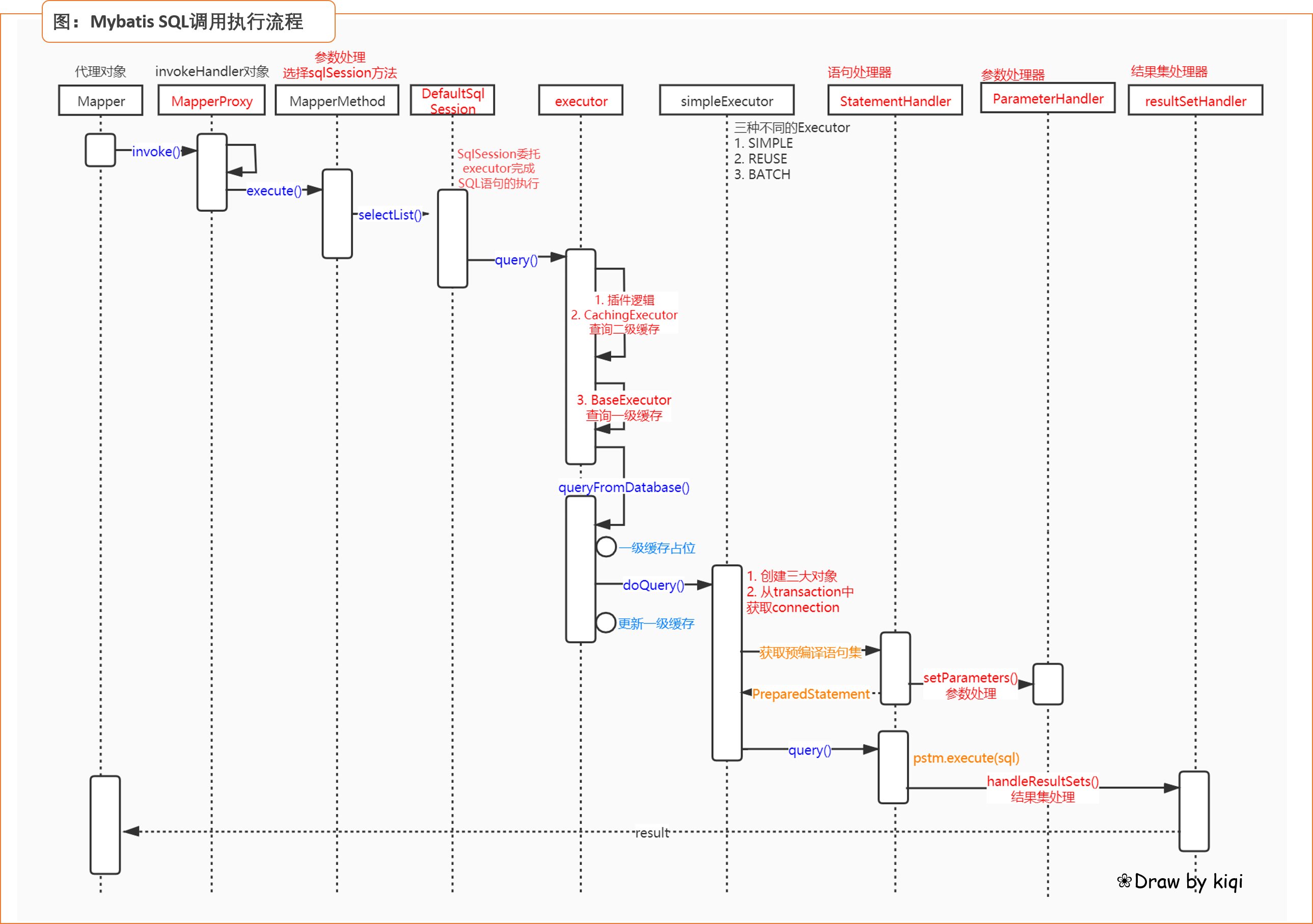
执行mapper代理方法 - mapper.selectAll()
① 根据被调用的代理对象,调用对应的sqlSession方法 - eg: sqlSession.selectList(commandName,param);
调用代理对象方法 -> MapperProxy<T>.invoke()方法 -> MapperMethodInvoker.invoke()方法 -> mapperMethod.execute()方法 -> sqlSession方法
② sqlSession委托executor对象执行sql语句,先完成代理逻辑,再判断缓存是否存在,不存在则进入数据库查询逻辑
sqlSession.selectList() -> Executor.query() -> **intercept代理对象.intercept()** -> CachingExecutor代理对象查询二级缓存 -> baseExecutor查询一级缓存 -> 数据库查询
③ 数据库查询:BaseExecutor.queryFromDatabase() - 实质为对jdbc的封装
- 构建三大对象(StatementHandler,ParameterHandler 和 resultSetHandler)
- 从transaction对象中获取数据库链接connection
- 获取PrepareStatement对象
- 调用ParameterHandler.setParameters()方法,为pstm设置参数
- JDBC:pstm.execute(sql);
- resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(pstm),完成结果集处理
欢迎疑问、期待评论、感谢指点 -- kiqi,愿同您为友
-- 星河有灿灿,愿与之辉


