并查集
并查集是一种树型数据结构,主要用于处理不相交集合之间的合并和判断某一元素所在的集合(并查集中集体是用其最高父结点表示),这种数据结构维护一个数组,father[],用于记录每个元素的父亲,也就其所在的集合;其主要的操作有两种,查找和合并,查找是为了判断出指定元素所有的集合(树),对于查找算法可以用路径压缩进行优化;合并则是将两个不相交集合按某种标准进行合并成一个新的集合(树);除了这两种主要的操作,并查集还有一个初始化的算法,主要是用于把每个元素都初始化单个元素的集合,也就是其father就是它本身;
相关的代码如下:
1 int father[MAX]; 2 3 int rank[MAX]; 4 //initialize every point as a set. And they are disjoin. 5 void Make_Set(int x) { 6 father[x] = x; 7 rank[x] = 0; 8 } 9 10 int Find_Set(int x) { 11 //没有进行路径压缩的查找; 12 /*return x == father[x] ? father[x] : Find_set(father[x]);*/ 13 //进行了路径压缩的查找,对应的当调用该函数时,一般为x = Find_Set(x) 14 if(x != father[x]) { 15 father[x] = Find_set(father[x]); 16 } 17 return father[x]; 18 } 19 //按秩将两个不相交的集合(也就是其根不相同, find_set不同)行合并; 20 int Union_Set(int x, int y) { 21 x = Find_set(x); 22 y = Find_set(y); 23 24 if(x == y) { 25 return; 26 } 27 if(rank[x] > rank[y]) { 28 father[y] = x; 29 } 30 else { 31 if(rank[x] == rank[y]) { 32 ++rank[y]; 33 } 34 father[x] = y; 35 } 36 }
这里解释下什么叫做路径压缩?路径压缩是为了把查找的O(n)的代码降至O(1), 从直观上来看就是希望让树的结构变成高度为2的多叉树;算法思想是要进行查找时,把没有直接连在根的结点用递归的方式连到根部,这样当再次进行查找本树时,其查找的消耗就为O(1)了,如图: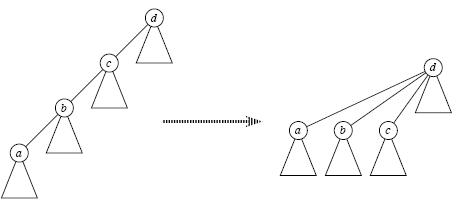
合并时,要记住要有一个的合并规则,根据什么标准进行合并,主要是考虑到哪一个根做为合并后的新根,同时记得要更新新树的标准;
关于并查集可以做下poj里的三个题目:poj_1611, poj_2524, poj_1861;
这里附上poj_1611的代码并说明:
#include<stdio.h> int father[30003], num[30003]; void make_set(int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) father[i] = i; } int find_set(int x) { /*return x == father[x] ? father[x] : find_set(father[x]);*/ //路径压缩优化 if(x != father[x]) { father[x] = find_set(father[x]); } return father[x]; } void union_set(int x, int y) { x = find_set(x); y = find_set(y); //care the union_rule if(x != y) { father[y] = x; //这个是与外部相关的,main中的主要是用每个组的第一个集合的根做为合并后新树的根。 num[x] += num[y]; } } int main() { int n, m, t, i, x, y; while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &t), n+t) { make_set(n); for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) num[i] = 1; while(t--) { scanf("%d", &m); --m; scanf("%d", &x); while(m--) { scanf("%d", &y); union_set(x, y); } } printf("%d\n", num[find_set(0)]); } }
并查集还且个极好的用法就是用来完成最小生成树的Kruskal算法,可以很方便的用于判断是否成环,如果两个点已经在同一个集合中了,则表明加入这两个点后将成环:另外合并的规则主要是看谁的集合中元素个数多;代码如下:
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #define MAX 100 using std::endl; using std::cout; using std::cin; int parent[MAX]; int child[MAX]; struct Edge { int start, end; int weight; }; bool comp(Edge a, Edge b) { return a.weight < b.weight; } int find(int child) { //return child == parent[child] ? child : find(parent[child]); //path_tar(outside child = find(child)) if(child != father[child] { father[child] = find(father[x]); } return father[x]; } bool join(int first, int second) { int root1, root2; root1 = find(first); root2 = find(second); if(root1 == root2) return false; else { if(child[root1] >= child[root2]){ parent[root2] = root1; child[root1] += child[root2]; } else { parent[root1] = root2; child[root2] += child[root1]; } } return true; } int main() { int vertex_num, edge_num, i, sum, total; cin >> vertex_num >> edge_num; Edge edge[edge_num + 1]; // edge[0] is not used //init for(i = 0; i < vertex_num; ++i) { parent[i] = i; child[i] = 1; } for(i = 1; i <= edge_num; ++i) { cin >> edge[i].start >> edge[i].end >> edge[i].weight;} std::sort(edge + 1, edge + 1 + edge_num, comp); for(sum = 0, total = 0, i = 1; i <= edge_num; ++i) { if(join(edge[i].start, edge[i].end)) { sum += edge[i].weight; ++total; cout << "Add the edge: " << edge[i].start << " -> " << edge[i].end << " : "<< edge[i].weight << endl; } if(total == vertex_num - 1) break; } cout << "The sum of the mst is " << sum << endl; }
相关参与网站:http://blog.csdn.net/freezhanacmore/article/details/8629871
http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B9%B6%E6%9F%A5%E9%9B%86


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号